The Parent Stars of New Extrasolar Planet System Candidates
... have so much in common with the sun, their chances of possessing earth-like planets may be greater that the other three stars examined. The remaining stars, Gliese 876 and HR 5568 are different because of the old ages calculated by the stellar evolution model. Gliese 876 is known to be poor in metals ...
... have so much in common with the sun, their chances of possessing earth-like planets may be greater that the other three stars examined. The remaining stars, Gliese 876 and HR 5568 are different because of the old ages calculated by the stellar evolution model. Gliese 876 is known to be poor in metals ...
Starlight And Atoms
... In a hot gas, the free electrons also collide with each other, and the other atoms in the gas… These collisions accelerate the electrons (change their speed and direction). ...
... In a hot gas, the free electrons also collide with each other, and the other atoms in the gas… These collisions accelerate the electrons (change their speed and direction). ...
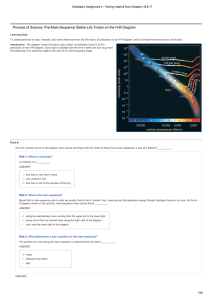
Process of Science: PreMainSequence Stellar Life Tracks on the HR
... Notice that the rotation rate increases as the formation process progresses. This is a consequence of the law of conservation of angular momentum: The cloud inevitably starts with some small net rotation, so as it contracts (reducing the radius of the rotation) the rotation must speed up to keep the ...
... Notice that the rotation rate increases as the formation process progresses. This is a consequence of the law of conservation of angular momentum: The cloud inevitably starts with some small net rotation, so as it contracts (reducing the radius of the rotation) the rotation must speed up to keep the ...
Module 6: “The Message of Starlight Assignment 9: Parallax, stellar
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
... At this point there is no way to avoid the units that astronomers use: we have mentioned magnitude already, which is a brightness scale in which very bright stars are roughly magnitude 0, faint stars are magnitude 5, and really faint stars have larger and larger magnitudes. These are further divide ...
Chapter 10: The Sun-
... Too massive to have formed from solitary star in current universe, but smaller than standard supermassive black holes. ...
... Too massive to have formed from solitary star in current universe, but smaller than standard supermassive black holes. ...
Hipparcos distance estimates of the Ophiuchus and the Lupus cloud
... dark molecular clouds and their dense cores. One of the main motivations for these investigations is the study of the process of star and planet formation in its entirety, and a deeper understanding of the effects of the local environment. A key aspect of the scientific analysis of a dark molecular c ...
... dark molecular clouds and their dense cores. One of the main motivations for these investigations is the study of the process of star and planet formation in its entirety, and a deeper understanding of the effects of the local environment. A key aspect of the scientific analysis of a dark molecular c ...
Searching for Dwarf Galaxies and Population III Star
... sources is the chemically unevolved surroundings of a large galaxy or proto-cluster of galaxies at high redshift. The central sources are likely to have ionized a local “bubble” through which strong Lyman emission can escape from surrounding dwarf galaxies. Thus, near-infrared observations of thes ...
... sources is the chemically unevolved surroundings of a large galaxy or proto-cluster of galaxies at high redshift. The central sources are likely to have ionized a local “bubble” through which strong Lyman emission can escape from surrounding dwarf galaxies. Thus, near-infrared observations of thes ...
Astronomy 401 Lecture 4 Kinematics of the Milky Way 1 The local
... proton and electron changing from a parallel to antiparallel configuration. When this transition occurs, the atom emits a photon with wavelength 21.10611405413 cm, or frequency 1420.40575177 MHz. This transition is highly forbidden with an extremely small probability of 2.9 × 10−15 s−1 , which means ...
... proton and electron changing from a parallel to antiparallel configuration. When this transition occurs, the atom emits a photon with wavelength 21.10611405413 cm, or frequency 1420.40575177 MHz. This transition is highly forbidden with an extremely small probability of 2.9 × 10−15 s−1 , which means ...
Galaxies - Stockton University
... – Material coming into the black-hole is hot and ionized. Photons radiated by the black-hole interact mostly with electrons and exert an outward force on them. The electrons are electrostatically coupled to protons which are gravitationally attracted to the black-hole. ...
... – Material coming into the black-hole is hot and ionized. Photons radiated by the black-hole interact mostly with electrons and exert an outward force on them. The electrons are electrostatically coupled to protons which are gravitationally attracted to the black-hole. ...
Lecture_17ppt
... • Escape velocity, Vesc – Critical velocity object must have to just escape the gravitational field of the Earth – VVesc : object never falls back to Earth
• In fact, escape velocity given in general by
...
... • Escape velocity, Vesc – Critical velocity object must have to just escape the gravitational field of the Earth – V
Publisher: Emily Barrosse Acquisitions Editor: Kelley Tyner
... (Types Ib and Ic are variations of explosions of heavyweight stars, and we won’t discuss them further here.) If too much matter is added to the white dwarf by its companion, causing the white dwarf to reach the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 solar masses, it can no longer support itself. The white dwarf ...
... (Types Ib and Ic are variations of explosions of heavyweight stars, and we won’t discuss them further here.) If too much matter is added to the white dwarf by its companion, causing the white dwarf to reach the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 solar masses, it can no longer support itself. The white dwarf ...
blackbody
... temperature but different sizes. The temperature of both stars is 4000 K. Use Wien's law and the Applet to find the peak wavelength. ...
... temperature but different sizes. The temperature of both stars is 4000 K. Use Wien's law and the Applet to find the peak wavelength. ...
arXiv:astro-ph/0701792v1 29 Jan 2007
... density profile for gas and dark matter in his calculations, involving different central gas density. He found that there is no solution satisfying the equations if the ratio of the central gas density to the central dark matter density is larger than certain threshold value. Above such threshold va ...
... density profile for gas and dark matter in his calculations, involving different central gas density. He found that there is no solution satisfying the equations if the ratio of the central gas density to the central dark matter density is larger than certain threshold value. Above such threshold va ...
Stars: flux, luminosity, color, and temperature
... This is the same way your eye determines color, but the bands are different. ...
... This is the same way your eye determines color, but the bands are different. ...
The Peculiar Physics of Line-Driving
... * Line-force requires nonlocal solution of radiation transfer, in principle in hundreds of spectral lines of varying strength ...
... * Line-force requires nonlocal solution of radiation transfer, in principle in hundreds of spectral lines of varying strength ...
Compa ring between Spectroscopic and Photometric Method for
... physical laboratories for studying the properties of individual stars. If one star expands enough to fill Roche lobe, then the transfer of mass from this star to her companion can begin. Such system is called a semi-detached binary system. In case when both stars fill, or even expand beyond, their R ...
... physical laboratories for studying the properties of individual stars. If one star expands enough to fill Roche lobe, then the transfer of mass from this star to her companion can begin. Such system is called a semi-detached binary system. In case when both stars fill, or even expand beyond, their R ...
Constants and Equations
... a) AM CVn stars are binary systems with an orbital period of less than 65 minutes. b) AM CVn stars may produce a type II supernova after the white dwarf reaches a critical mass. c) AM CVn stars are sources of gravitational waves. d) AM CVn stars are binary systems where a white dwarf accretes mass f ...
... a) AM CVn stars are binary systems with an orbital period of less than 65 minutes. b) AM CVn stars may produce a type II supernova after the white dwarf reaches a critical mass. c) AM CVn stars are sources of gravitational waves. d) AM CVn stars are binary systems where a white dwarf accretes mass f ...
Rethinking the Speed of Sound - University of Tennessee Physics
... solid) determine how fast sound travels. The speed of sound tends to increase with the density or the temperature of the medium it’s travelling through. In water at 20°C, for example, the speed of sound is 1,482 meters per second; it moves through steel at 5,960 meters per second. As Steiner and Bed ...
... solid) determine how fast sound travels. The speed of sound tends to increase with the density or the temperature of the medium it’s travelling through. In water at 20°C, for example, the speed of sound is 1,482 meters per second; it moves through steel at 5,960 meters per second. As Steiner and Bed ...
Nearby Stars - How far away is it
... Lalande 21185 is another dime red star. Recent analysis indicates that it may also be accompanied by at least two orbiting planets, but his has not been confirmed. Planet hunting is a hot topic these days and research is ongoing. Sirius A & B - 8.6 light-years This Hubble Space Telescope image shows ...
... Lalande 21185 is another dime red star. Recent analysis indicates that it may also be accompanied by at least two orbiting planets, but his has not been confirmed. Planet hunting is a hot topic these days and research is ongoing. Sirius A & B - 8.6 light-years This Hubble Space Telescope image shows ...
The Universe
... is part of a galaxy called the Milky Way. All the (individual) stars we can see on Earth all also part of the Milky Way. Previously we stated that our Solar system ends at the Oort cloud. The distance from the Sun to the Oort cloud can be expressed used the next big unit of distance in astronomy: th ...
... is part of a galaxy called the Milky Way. All the (individual) stars we can see on Earth all also part of the Milky Way. Previously we stated that our Solar system ends at the Oort cloud. The distance from the Sun to the Oort cloud can be expressed used the next big unit of distance in astronomy: th ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.