Intro to the Night Sky - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring 2017!
... that all stars do not appear the same. There is a very wide range in brightness. Stars also appear in different colors. Astronomers occasionally use an archaic method of specifying the brightness of an object. This system is called the magnitude system. The brightness of a star as seen in the night ...
... that all stars do not appear the same. There is a very wide range in brightness. Stars also appear in different colors. Astronomers occasionally use an archaic method of specifying the brightness of an object. This system is called the magnitude system. The brightness of a star as seen in the night ...
PDF - Amazing Space, STScI
... Peering into the crowded bulge of our Milky Way galaxy, Hubble looked farther than ever before to nab a group of planet candidates outside our solar system. Astronomers used Hubble to conduct a census of Jupiter-sized extrasolar planets residing in the bulge of our Milky Way galaxy. Looking at a nar ...
... Peering into the crowded bulge of our Milky Way galaxy, Hubble looked farther than ever before to nab a group of planet candidates outside our solar system. Astronomers used Hubble to conduct a census of Jupiter-sized extrasolar planets residing in the bulge of our Milky Way galaxy. Looking at a nar ...
C, N, O abundances and carbon isotope ratios in evolved stars of
... −0.20±0.01, respectively. This means that the ratios of [C/Fe] in investigated stars of these clusters lie below the values obtained for dwarf stars of the Galactic disk, which are solar. Shi et al. (2002) performed an abundance analysis of carbon for a sample of 90 F- and G-type main-sequence disk ...
... −0.20±0.01, respectively. This means that the ratios of [C/Fe] in investigated stars of these clusters lie below the values obtained for dwarf stars of the Galactic disk, which are solar. Shi et al. (2002) performed an abundance analysis of carbon for a sample of 90 F- and G-type main-sequence disk ...
Stellar Distances - Red Hook Central School District
... magnitude to determine distance. • Need to know spectral class (MS, WD, ) of star, & surface temp. & use HR ...
... magnitude to determine distance. • Need to know spectral class (MS, WD, ) of star, & surface temp. & use HR ...
The dramatic change of the fossil magnetic field of HD 190073
... pects of the fossil scenario is the interplay between the dynamo magnetic fields arising in the convective envelope at the beginning of the pre-MS phase, and in the convective core at the end of the pre-MS, and the fossil magnetic field residing inside the radiative layers of the star. HD 190073 is ...
... pects of the fossil scenario is the interplay between the dynamo magnetic fields arising in the convective envelope at the beginning of the pre-MS phase, and in the convective core at the end of the pre-MS, and the fossil magnetic field residing inside the radiative layers of the star. HD 190073 is ...
CPW Science Passage
... CPW Science Passage 9th Grade An astronomy class is given the following facts about stellar evolution. 1. A star’s evolution can be divided in two 3 stages: pre-main sequence (pre-MS), main sequence (MS), and post-main sequence (post-MS). 2. Gravity causes part of a cloud of gas and dust to collapse ...
... CPW Science Passage 9th Grade An astronomy class is given the following facts about stellar evolution. 1. A star’s evolution can be divided in two 3 stages: pre-main sequence (pre-MS), main sequence (MS), and post-main sequence (post-MS). 2. Gravity causes part of a cloud of gas and dust to collapse ...
205 Advances in Natural and Applied Sciences, 4(2): 205-209, 2010 ISSN 1995-0772
... multiple stellar systems. A sub-class of binary systems are X-ray binaries, the systems in which a compact object (a white dwarf, neutron star or a black hole formed after collapse of an ordinary star) and a stellar companion, orbit each other at a distance small enough to enable mass transfer from ...
... multiple stellar systems. A sub-class of binary systems are X-ray binaries, the systems in which a compact object (a white dwarf, neutron star or a black hole formed after collapse of an ordinary star) and a stellar companion, orbit each other at a distance small enough to enable mass transfer from ...
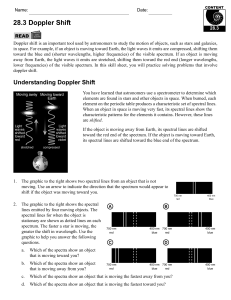
28.3 Doppler Shift
... star moving away from or toward Earth? One of the spectral lines for a star has shifted from 560 nm to 544 nm. What is the speed of the star? Is it moving away from or toward Earth? An astronomer has determined that two galaxies are moving away from Earth. A spectral line for galaxy A is red shifted ...
... star moving away from or toward Earth? One of the spectral lines for a star has shifted from 560 nm to 544 nm. What is the speed of the star? Is it moving away from or toward Earth? An astronomer has determined that two galaxies are moving away from Earth. A spectral line for galaxy A is red shifted ...
personal rights of identity in the sneetches and yertle the turtle
... differentiation. Moreover, even as state courts began to require that same-sex couples be allowed to marry, enactment of the federal Defense of Marriage Act made it possible for the majority to differentiate “real” marriages from, say, “Massachusetts Marriages.” Indeed, some legislators even propose ...
... differentiation. Moreover, even as state courts began to require that same-sex couples be allowed to marry, enactment of the federal Defense of Marriage Act made it possible for the majority to differentiate “real” marriages from, say, “Massachusetts Marriages.” Indeed, some legislators even propose ...
... 3. THE RR LYRAE STARS IN M15 In Clement’s (2002) data base of variables stars, a total of 158 variable stars are known, from which approximately 104 are RR Lyrae type stars. In this work, 33 known RR Lyrae stars, identified in Figs. 1 and 2 and listed in Table 4, have been studied. For all the stars ...
September 2011 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... observed using the finder and a low power eyepiece. Carefully replace the low power eyepiece with a higher magnification (shorter focal length) eyepiece and refocus if necessary. ...
... observed using the finder and a low power eyepiece. Carefully replace the low power eyepiece with a higher magnification (shorter focal length) eyepiece and refocus if necessary. ...
3D GR Hydrodynamic Simulations of Binary Neutron Star
... 1) Capture fluxes on coarse and fine grid AMR boundary 2) Integrate both until coarse and fine grid are aligned in time again 3) Restrict integrated coarse grid flux onto fine grid boundary 4) Difference between integrated coarse grid flux and fine grid flux is correction ...
... 1) Capture fluxes on coarse and fine grid AMR boundary 2) Integrate both until coarse and fine grid are aligned in time again 3) Restrict integrated coarse grid flux onto fine grid boundary 4) Difference between integrated coarse grid flux and fine grid flux is correction ...
IDENTIFICATION OF MAIN-SEQUENCE STARS WITH MID
... SOFIA, MS 211-3, NASA-Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA 94035-1000. ...
... SOFIA, MS 211-3, NASA-Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA 94035-1000. ...
Star formation

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as ""stellar nurseries"" or ""star-forming regions"", collapse to form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.