instructor`s syllabus
... Placement Assessments: ENGL 1301, MATH 0310, College-Level Reading Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students should be able to do the following: 1. Differentiate between rocks and minerals and describe the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, ...
... Placement Assessments: ENGL 1301, MATH 0310, College-Level Reading Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students should be able to do the following: 1. Differentiate between rocks and minerals and describe the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, ...
Quiz Bowl Earth Terms
... Greenhouse effect – Trapping of the Sun’s heat in the atmosphere by gases and particles. Groundwater – Precipitation that soaks into and is stored in the ground, rather than running off into rivers or evaporating. Gyre – A circular water current in an ocean. Habitat – The natural and usual living sp ...
... Greenhouse effect – Trapping of the Sun’s heat in the atmosphere by gases and particles. Groundwater – Precipitation that soaks into and is stored in the ground, rather than running off into rivers or evaporating. Gyre – A circular water current in an ocean. Habitat – The natural and usual living sp ...
Microsoft Word - 2011 KCSE NDTHIWA GEO P1.DOC - KCPE-KCSE
... (ii) Identify three methods you would use to record the data.(3mks) Note making Filling in questionnaire Field sketching Mapping Photographing Videotaping ...
... (ii) Identify three methods you would use to record the data.(3mks) Note making Filling in questionnaire Field sketching Mapping Photographing Videotaping ...
Chapter 3 Plate Tectonics
... • The earth once had a single landmass that broke up into large pieces, which have since drifted apart. • The name of this giant landmass is Pangaea which means all earth. • Wegner’s –Theory of continental drift • One supporting piece of evidence is the fossil Glossopteris( extinct now longer livin ...
... • The earth once had a single landmass that broke up into large pieces, which have since drifted apart. • The name of this giant landmass is Pangaea which means all earth. • Wegner’s –Theory of continental drift • One supporting piece of evidence is the fossil Glossopteris( extinct now longer livin ...
Chapter 14 Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources
... manufacturing processes are helping to decrease our use and waste of such resources. Recent, dramatic increases in the cost of minerals are driving aggressive recycling of many resources and particularly metals (e.g., copper). ...
... manufacturing processes are helping to decrease our use and waste of such resources. Recent, dramatic increases in the cost of minerals are driving aggressive recycling of many resources and particularly metals (e.g., copper). ...
Study Questions for Exam #2
... a. Because the magmas generated are rich in silica (felsic) and thus viscous, i.e. thick b. Because the magmas generated are rich in water and gases, which build up pressure in the ...
... a. Because the magmas generated are rich in silica (felsic) and thus viscous, i.e. thick b. Because the magmas generated are rich in water and gases, which build up pressure in the ...
Earth Systems - Northwest ISD Moodle
... to rise, and colder, denser material to sink which results in the transfer of heat. • Where oceanic and continental plates come together, subduction occurs • Subduction: Plates passing under one another ...
... to rise, and colder, denser material to sink which results in the transfer of heat. • Where oceanic and continental plates come together, subduction occurs • Subduction: Plates passing under one another ...
Metamorphic Rocks ppt
... What happens to rocks that are deeply buried but are not hot enough to melt? They become metamorphosed! Metamorphism refers to changes to rocks that occur in the Earth’s interior. Changes may be new textures, new mineral assemblages, or both. These changes occur w/o the rock melting. ...
... What happens to rocks that are deeply buried but are not hot enough to melt? They become metamorphosed! Metamorphism refers to changes to rocks that occur in the Earth’s interior. Changes may be new textures, new mineral assemblages, or both. These changes occur w/o the rock melting. ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... dominant minerals in carbonate rocks such as limestone are calcite and dolomite (Boggs, ...
... dominant minerals in carbonate rocks such as limestone are calcite and dolomite (Boggs, ...
Global Surveyor finds stripes on Mars
... Mars suggests that plate tectonics once operated there, very early in the planet’s history. There are also discontinuities in the pattern of the stripes, which look like another plate tectonic feature on Earth, transform faults, which reinforces the suggestion. Lines of volcanoes in Tharsis and majo ...
... Mars suggests that plate tectonics once operated there, very early in the planet’s history. There are also discontinuities in the pattern of the stripes, which look like another plate tectonic feature on Earth, transform faults, which reinforces the suggestion. Lines of volcanoes in Tharsis and majo ...
earth interior - Red Hook Central Schools
... Seismic waves tell us that Earth has 3 layers: • Crust (solid rigid outer rock layer) Moho separates crust from mantle • Mantle (beneath the crust, not so solid) 80% of Earth is mantle • Core (outer core = liquid, inner core = solid) made of nickel and iron (magnetic) very dense! Earths interior an ...
... Seismic waves tell us that Earth has 3 layers: • Crust (solid rigid outer rock layer) Moho separates crust from mantle • Mantle (beneath the crust, not so solid) 80% of Earth is mantle • Core (outer core = liquid, inner core = solid) made of nickel and iron (magnetic) very dense! Earths interior an ...
The Earth - Humble ISD
... The Solar System consists of the sun and ________ known planets, as well as other celestial bodies that orbit the sun. The Earth is the ________ planet from the sun. _______________ – layer of gases surrounding the earth. _______________– the solid rock portion of the earth’s surface. Some of the Li ...
... The Solar System consists of the sun and ________ known planets, as well as other celestial bodies that orbit the sun. The Earth is the ________ planet from the sun. _______________ – layer of gases surrounding the earth. _______________– the solid rock portion of the earth’s surface. Some of the Li ...
Name: Number of Questions
... c. damaged coastal areas. d. mass wasting. Section 16-4 Minerals, Rocks, and the Rock Cycle ____ 10. Lava is an example of ____ rock. a. Metamorphic b. Igneous c. Sedimentary d. Plasticized ____ 11. Which of the following is not characteristic of a mineral? a. crystal structure b. organic c. natural ...
... c. damaged coastal areas. d. mass wasting. Section 16-4 Minerals, Rocks, and the Rock Cycle ____ 10. Lava is an example of ____ rock. a. Metamorphic b. Igneous c. Sedimentary d. Plasticized ____ 11. Which of the following is not characteristic of a mineral? a. crystal structure b. organic c. natural ...
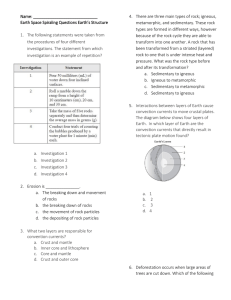
Name: Earth Space Spiraling Questions Earth`s Structure 1. The
... d. Crust and outer core 6. Deforestation occurs when large areas of trees are cut down. Which of the following ...
... d. Crust and outer core 6. Deforestation occurs when large areas of trees are cut down. Which of the following ...
Physics 105 TEST II part II questions
... 4) Why does Jupiter have several distinct cloud layers? 4) _______ A) Clouds form randomly, so on average there are always several layers. B) Different layers represent the various regions where the temperature is cool enough for liquid water to condense. C) Different layers represent clouds made of ...
... 4) Why does Jupiter have several distinct cloud layers? 4) _______ A) Clouds form randomly, so on average there are always several layers. B) Different layers represent the various regions where the temperature is cool enough for liquid water to condense. C) Different layers represent clouds made of ...
Background information - Science Web Australia
... by some of the minerals from the rocks. All that pressure squeezes out the water and cements the sediments together to form rock. Igneous rocks Igneous rocks form when magma from the Earth’s mantle or lower crust cools. Examples of igneous rock include basalt, pumice and obsidian. Igneous rocks such ...
... by some of the minerals from the rocks. All that pressure squeezes out the water and cements the sediments together to form rock. Igneous rocks Igneous rocks form when magma from the Earth’s mantle or lower crust cools. Examples of igneous rock include basalt, pumice and obsidian. Igneous rocks such ...
1. What is rock? 2. The layer of solid rock that surrounds Earth`s
... 11. The mountain range that winds through Earth’s oceans is called the…? 12. As oceanic plates pull apart along the mid-ocean ridge, the process of …?... occurs. 13. When two pieces of continental crust pull apart, a(n) …?... forms. 14. When two plates slide past each other, moving slowly in opposit ...
... 11. The mountain range that winds through Earth’s oceans is called the…? 12. As oceanic plates pull apart along the mid-ocean ridge, the process of …?... occurs. 13. When two pieces of continental crust pull apart, a(n) …?... forms. 14. When two plates slide past each other, moving slowly in opposit ...
Science 7 Unit 5 Planet Earth This book belongs to: Topic 1
... Types of sedimentary rock include: shale (formed from fine clay or mud) sandstone (sand, made of quartz) conglomerate (pebbles and small stones cemented together) limestone (organic sedimentary rock, containing fossils – plant and animal remains) 3. Metamorphic Rock This type of rock has changed its ...
... Types of sedimentary rock include: shale (formed from fine clay or mud) sandstone (sand, made of quartz) conglomerate (pebbles and small stones cemented together) limestone (organic sedimentary rock, containing fossils – plant and animal remains) 3. Metamorphic Rock This type of rock has changed its ...
Igneous Rocks
... Large variety of igneous rocks is produced by large variety of magma compositions Mafic magmas will crystallize into basalt or gabbro if early-formed minerals are not removed from the magma Intermediate magmas will similarly crystallize into diorite or andesite if minerals are not removed Separation ...
... Large variety of igneous rocks is produced by large variety of magma compositions Mafic magmas will crystallize into basalt or gabbro if early-formed minerals are not removed from the magma Intermediate magmas will similarly crystallize into diorite or andesite if minerals are not removed Separation ...
Lecture 13
... Comparison of Planetary Surfaces • Mercury & the Moon • heavily cratered {scars from the heavy bombardment} ...
... Comparison of Planetary Surfaces • Mercury & the Moon • heavily cratered {scars from the heavy bombardment} ...
Unit 5 Defined - www3.telus.net
... carried away by water (3 72) Topic 3 Erosion (read page 373) Erosion - the process of moving soil and rock from one place to another; mechanical weathering caused by the effects of wind and/or water (373) Weathering (mechanical, chemical, and biological weathering) the process in which rocks are bro ...
... carried away by water (3 72) Topic 3 Erosion (read page 373) Erosion - the process of moving soil and rock from one place to another; mechanical weathering caused by the effects of wind and/or water (373) Weathering (mechanical, chemical, and biological weathering) the process in which rocks are bro ...
Geologic History of South Yuba River State Park Bruce Pauly, Univ
... Buttermilk Bend trail, rocks belonging to the Smartville Complex can be examined. Just beyond Signposts 13 and 14, on your left (North side of the trail) is a rock grotto with a bench (Figure 1). This outcrop consists of weathered, metamorphosed (subjected to heat and pressure) granitic rocks. They ...
... Buttermilk Bend trail, rocks belonging to the Smartville Complex can be examined. Just beyond Signposts 13 and 14, on your left (North side of the trail) is a rock grotto with a bench (Figure 1). This outcrop consists of weathered, metamorphosed (subjected to heat and pressure) granitic rocks. They ...
Geological Terms
... and flatten its bottom Glaciations – successive periods during which an area was covered by moving sheets of ice, usually due to cyclical periods of cooling and warming of the earth’s atmosphere Glacier – a huge mass of ice slowly flowing over a land mass, formed from compacted snow in an area where ...
... and flatten its bottom Glaciations – successive periods during which an area was covered by moving sheets of ice, usually due to cyclical periods of cooling and warming of the earth’s atmosphere Glacier – a huge mass of ice slowly flowing over a land mass, formed from compacted snow in an area where ...
3.1 - Weathering Define mechanical and chemical weathering
... Ice in glaciers carries many bits and pieces of rock. Rocks embedded at the bottom of the glacier scrape against the rocks below. ...
... Ice in glaciers carries many bits and pieces of rock. Rocks embedded at the bottom of the glacier scrape against the rocks below. ...
Composition of Mars

The composition of Mars covers the branch of the geology of Mars that describes the make-up of the planet Mars.