Cosmology
... Discuss Olber’s paradox and that although large, the universe cannot be infinite. Problem sheet for homework. Stellar Evolution State the mean solar power received at the Earth’s upper atmosphere as 1400 Wm-2 across all wavelengths. Show that the radiated power of the Sun is therefore 4 x 1026 W. Di ...
... Discuss Olber’s paradox and that although large, the universe cannot be infinite. Problem sheet for homework. Stellar Evolution State the mean solar power received at the Earth’s upper atmosphere as 1400 Wm-2 across all wavelengths. Show that the radiated power of the Sun is therefore 4 x 1026 W. Di ...
Astronomy
... Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself as Apollo and made Callisto his lover. They had a child named Arcas. Of course Zeus knew that both Hera, his wife, and Artemis would be angry with Callisto so to protect ...
... Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself as Apollo and made Callisto his lover. They had a child named Arcas. Of course Zeus knew that both Hera, his wife, and Artemis would be angry with Callisto so to protect ...
October 2013
... constellation of Argo Navis, the great ship of Jason and the Argonauts. Today this constellation, tangled in the Milky Way, has been subdivided into the Keel, the Rear Deck, the Sails and the Compass, with the Flying Fish zooming by the Keel and the Goldfish swimming 'below' (i.e. to the west). Dora ...
... constellation of Argo Navis, the great ship of Jason and the Argonauts. Today this constellation, tangled in the Milky Way, has been subdivided into the Keel, the Rear Deck, the Sails and the Compass, with the Flying Fish zooming by the Keel and the Goldfish swimming 'below' (i.e. to the west). Dora ...
Binary Star Systems - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... http://www.synapses.co.uk/astro/procyon.gif http://www.glyphweb.com/esky/_images/illustrations/procyon.gif ...
... http://www.synapses.co.uk/astro/procyon.gif http://www.glyphweb.com/esky/_images/illustrations/procyon.gif ...
Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers
... Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers 1. (a) The star is nearly a blackbody, the spectrum of a star can be approximated as a blackbody radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position ...
... Exercise 4 (Stars and the universe) Suggested answers 1. (a) The star is nearly a blackbody, the spectrum of a star can be approximated as a blackbody radiation curve. On the curve, there is a peak which shifts to shorter wavelength when the temperature of the blackbody increases. From the position ...
Gizmos: H-R Diagrams
... 5. Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer par ...
... 5. Describe: More than 90 percent of all stars in the universe, including the Sun, are main sequence stars. As main sequence stars age, they move up and to the right on the H-R diagram and become giants or supergiants. Giants and supergiants form when the center of a star collapses and its outer par ...
Astronomy Study Guide
... Know your vocabulary Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing s ...
... Know your vocabulary Apparent brightness—the brightness of a star as seen from Earth Absolute brightness—a star’s brightness as if it were a standard distance from Earth Constellation—an imaginary pattern of stars (example—Orion) Hertzsprung - Russell diagram (H-R diagram)—a graph of stars showing s ...
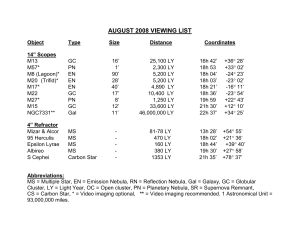
August
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
... M13 At a distance of 25,100 light years, this globular cluster in the constellation Hercules (HER-cueleez) is about 145 light years in diameter. The age of M13 has been estimated at over 10 billion years. It contains over 300,000 stars. At the center, stars are about 500 times more concentrated than ...
Solution Key
... This is just like calculating the distance to the Pleiades, which we did in studio, but in globular clusters, only the low mass stub of the main sequence is visible. You can use any point on that stub to get the distance. For example, at B-V=0.5, the apparent visual magnitude V ≈ 18. The absolute vi ...
... This is just like calculating the distance to the Pleiades, which we did in studio, but in globular clusters, only the low mass stub of the main sequence is visible. You can use any point on that stub to get the distance. For example, at B-V=0.5, the apparent visual magnitude V ≈ 18. The absolute vi ...
Lecture 4 Hydrostatic equilibrium
... the star. Hence changes that involve substantial losses or gains of energy can not take place on timescales shorter than ...
... the star. Hence changes that involve substantial losses or gains of energy can not take place on timescales shorter than ...
The Sun: Our Star (Chapter 14) The source of the Sun`s energy has
... The source of the Sun’s energy has long been a mystery, especially since the great distance between Earth and the Sun was first measured. Geologists argued that Earth’s geology needed 100s of millions of years to form, and physicists argued that no energy source could make the Sun shine for that lon ...
... The source of the Sun’s energy has long been a mystery, especially since the great distance between Earth and the Sun was first measured. Geologists argued that Earth’s geology needed 100s of millions of years to form, and physicists argued that no energy source could make the Sun shine for that lon ...
–1– Lectures 18 and 19 Optical Depth vs. Density Imaging a sphere
... so that τ increases as the cloud collapses and ρ increases. Eventually, collapse and Hoyle fragmentation will produce optically thick fragments. At this point, the cores are no longer isothermal. Since Jeans fragmentation requires an isothermal gas, this will also halt the fragmentation of the colla ...
... so that τ increases as the cloud collapses and ρ increases. Eventually, collapse and Hoyle fragmentation will produce optically thick fragments. At this point, the cores are no longer isothermal. Since Jeans fragmentation requires an isothermal gas, this will also halt the fragmentation of the colla ...
Document
... observed ones MUST be YOUNG!!! -> Would you expect to find Life around planets that orbit these massive stars??? ...
... observed ones MUST be YOUNG!!! -> Would you expect to find Life around planets that orbit these massive stars??? ...
Whiteq
... become cool enough for ionized atoms to recombine, the star's outer layers become unstable. The instability occurs because the temperature for the reaction is borderline, and the recombination releases energy. So, the outer layers contract, and expand, becoming warmer and cooler, and eventually the ...
... become cool enough for ionized atoms to recombine, the star's outer layers become unstable. The instability occurs because the temperature for the reaction is borderline, and the recombination releases energy. So, the outer layers contract, and expand, becoming warmer and cooler, and eventually the ...
ASTR 101 Final Study Guide Use as a guide to the topics as you
... o The mass of a white dwarf is limited by its limiting mass, or Chandrasekhar limit. Past this point, the star would collapse. o If a white dwarf is in a binary system, its gravitational pull may pull in expelled gas from its companion star. This new fuel expands rapidly upon fusing, causing a nova ...
... o The mass of a white dwarf is limited by its limiting mass, or Chandrasekhar limit. Past this point, the star would collapse. o If a white dwarf is in a binary system, its gravitational pull may pull in expelled gas from its companion star. This new fuel expands rapidly upon fusing, causing a nova ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #19 Key
... matter. Perhaps the most compelling is the rather flat rotational curve of the galaxy, i.e., the speeds at which stars and clouds orbit about our galactic center change little with increasing distance from our galactic center all the way out to the most remote objects we can detect. The necessary gr ...
... matter. Perhaps the most compelling is the rather flat rotational curve of the galaxy, i.e., the speeds at which stars and clouds orbit about our galactic center change little with increasing distance from our galactic center all the way out to the most remote objects we can detect. The necessary gr ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.