The Degenerate Remnants of Massive Stars
... may form directly or indirectly as a consequence of the core collapse of a sufficiently massive supergiant star. Could also form when a neutron star stips away enough mass from a companion. Intermediate Mass Black Holes: may exist in a range of 100 to in excess of 1000 M . Ultraluminous X-ray Sourc ...
... may form directly or indirectly as a consequence of the core collapse of a sufficiently massive supergiant star. Could also form when a neutron star stips away enough mass from a companion. Intermediate Mass Black Holes: may exist in a range of 100 to in excess of 1000 M . Ultraluminous X-ray Sourc ...
Thoughts and New Theory`s on Stars and Planets By Barry L
... The 1 point indicates that Neutrinos have the capability to exceed the speed of light ;however, the physical laws of this universe would not permit it to go past it. The theory I would like to state is Neutrinos must have the ability to traverse different dimensions because it has very little mass. ...
... The 1 point indicates that Neutrinos have the capability to exceed the speed of light ;however, the physical laws of this universe would not permit it to go past it. The theory I would like to state is Neutrinos must have the ability to traverse different dimensions because it has very little mass. ...
Carbon Stars - The OzSky Star Safari
... thousand years blows off a nearly spherical shell of gas (this event has lasted for about 150 years based on velocity calculations). ...
... thousand years blows off a nearly spherical shell of gas (this event has lasted for about 150 years based on velocity calculations). ...
Ch 13 Death of Stars(4-5?-13)
... What is a black hole? • A black hole is an object whose gravity is so powerful that not even light can escape it. • A place where gravity has crushed matter into oblivion, creating a true hole in the universe from which nothing can ever escape, not even light. ...
... What is a black hole? • A black hole is an object whose gravity is so powerful that not even light can escape it. • A place where gravity has crushed matter into oblivion, creating a true hole in the universe from which nothing can ever escape, not even light. ...
Ch. 13 Death of Stars(11-16-10)-3
... than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Nothing stops the collapse and produces an object so co ...
... than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Nothing stops the collapse and produces an object so co ...
The Great Nebula in Orion
... temperature and luminosity. From these measurements, we can determine the radius, mass, age, and even the mass accretion rate of each star. This catalog of stellar properties will be the largest uniform survey of young stars ever achieved. The Hubble images reveal dozens of candidates for brown dwar ...
... temperature and luminosity. From these measurements, we can determine the radius, mass, age, and even the mass accretion rate of each star. This catalog of stellar properties will be the largest uniform survey of young stars ever achieved. The Hubble images reveal dozens of candidates for brown dwar ...
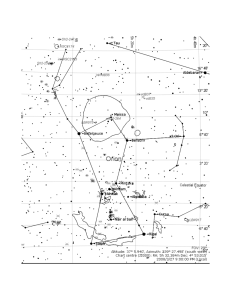
Finding the North Star
... …is known to astronomers as “Polaris” because of its place over the North Pole. …is really useful if you are in the Earth’s northern hemisphere, and you are lost in the wilderness on a clear night. ...
... …is known to astronomers as “Polaris” because of its place over the North Pole. …is really useful if you are in the Earth’s northern hemisphere, and you are lost in the wilderness on a clear night. ...
Finding the North Star
... …is known to astronomers as “Polaris” because of its place over the North Pole. …is really useful if you are in the Earth’s northern hemisphere, and you are lost in the wilderness on a clear night. ...
... …is known to astronomers as “Polaris” because of its place over the North Pole. …is really useful if you are in the Earth’s northern hemisphere, and you are lost in the wilderness on a clear night. ...
Powerpoint
... All these effects are unnoticeable in our daily experience! They are tiny in Earth’s gravity, but large in a black hole’s. ...
... All these effects are unnoticeable in our daily experience! They are tiny in Earth’s gravity, but large in a black hole’s. ...
Interstellar Medium (ISM) Star Formation Formation of Planetary Systems
... Clearing the Protosolar Nebula Four effects cleared the nebula: 1. Radiation pressure-light streaming from the sun pushed against the particles of the solar nebula. 2. The solar wind—flow of ionized H helped push dust and gas out of the nebula. 3. Sweeping of space debris by the planets—the moon ...
... Clearing the Protosolar Nebula Four effects cleared the nebula: 1. Radiation pressure-light streaming from the sun pushed against the particles of the solar nebula. 2. The solar wind—flow of ionized H helped push dust and gas out of the nebula. 3. Sweeping of space debris by the planets—the moon ...
pptx
... at very high temperature the Sun is in fact 73% H, 25% He, 2% everything else (Cecilia Payne, 1924) ...
... at very high temperature the Sun is in fact 73% H, 25% He, 2% everything else (Cecilia Payne, 1924) ...
Measuring Motion, Doppler Effect—28 Oct Outline • Announcements
... Provisional model: Two stars are in orbit. Test against evidence. How can the two stars move so as to show the same wavelength, for example, as on Oct 1? (If possible, you want explanations that do not depend on special accidents.) A. The stars move in the same direction at the same speed o ...
... Provisional model: Two stars are in orbit. Test against evidence. How can the two stars move so as to show the same wavelength, for example, as on Oct 1? (If possible, you want explanations that do not depend on special accidents.) A. The stars move in the same direction at the same speed o ...
May 2010 - Pomona Valley Amateur Astronomers
... Rachel explains that warped stars feed black holes to fatten them up and gives the reason to the fact that the huge amounts of gases are believed to be the formation of a skewed ring of stars, which would facilitate the flow of gas, by sapping its speed so that it spirals in towards the back hole. I ...
... Rachel explains that warped stars feed black holes to fatten them up and gives the reason to the fact that the huge amounts of gases are believed to be the formation of a skewed ring of stars, which would facilitate the flow of gas, by sapping its speed so that it spirals in towards the back hole. I ...
Planetarium Activity 1 Learning to measure brightness and Limiting
... and Orion) fix their position in the sky when the lights are off so that its approximated location can be found as the lights brighten. Use dots to Sketch the constellations on your worksheet and connect the stars with dash line. 2. As the lights are raised the first time, note the relative order in ...
... and Orion) fix their position in the sky when the lights are off so that its approximated location can be found as the lights brighten. Use dots to Sketch the constellations on your worksheet and connect the stars with dash line. 2. As the lights are raised the first time, note the relative order in ...
Activity 1: The Scientific Method
... observations and calculations have produced data on many stars’ distances, temperatures, luminosities (brightness), as well as the radial motion of these stars. The goal of this activity is to use the scientific method to determine if any of this data is correlated and to determine a model of the re ...
... observations and calculations have produced data on many stars’ distances, temperatures, luminosities (brightness), as well as the radial motion of these stars. The goal of this activity is to use the scientific method to determine if any of this data is correlated and to determine a model of the re ...
Where to Look: Habitable Zones
... Fred Hoyle: “The chance that higher life forms might have emerged in this way is comparable to the chance that a tornado sweeping through a junkyard might assemble a Boeing 747 from the materials therein.” ...
... Fred Hoyle: “The chance that higher life forms might have emerged in this way is comparable to the chance that a tornado sweeping through a junkyard might assemble a Boeing 747 from the materials therein.” ...
Deriving the Isoradius Lines (optional, mathematical
... Question 1: The table below summarizes the relationship between spectral type, temperature, and color for stars. Note that the surface temperature of the stars in the table increases. ...
... Question 1: The table below summarizes the relationship between spectral type, temperature, and color for stars. Note that the surface temperature of the stars in the table increases. ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.