Equations Of State of Hydrogen-Helium and Carbon
... The usual approach to the problem of the Equations Of State (EOS) for White Dwarfs and super giant Planets, under the conditions of high densities and low temperatures, faces two problems. The first has to do with Pressure Ionization : the energy levels of the electrons in the case of extreme pressu ...
... The usual approach to the problem of the Equations Of State (EOS) for White Dwarfs and super giant Planets, under the conditions of high densities and low temperatures, faces two problems. The first has to do with Pressure Ionization : the energy levels of the electrons in the case of extreme pressu ...
The Vampire Stars - d_smith.lhseducators.com
... Large stars begin like any other star • Stars that eventually become Type II supernovae begin with 3 to >100 times the mass of the sun. • A nebula collapses to become a protostar; nuclear fusion ignites becomes a main sequence star (where it lives most of its life); begins to use up its fuel. ...
... Large stars begin like any other star • Stars that eventually become Type II supernovae begin with 3 to >100 times the mass of the sun. • A nebula collapses to become a protostar; nuclear fusion ignites becomes a main sequence star (where it lives most of its life); begins to use up its fuel. ...
14 Things You Didn`t Know About How the Sun Will Die
... 6. The dying star isn't completely dead yet, however. Gravity pushes shells of hydrogen and helium to densities where nuclear fusion can begin, and they are ignited, albeit for a short time. When this happens with the Sun, it will briefly be 2,100 times brighter than we see it now. 7. Some 7 or 8 bi ...
... 6. The dying star isn't completely dead yet, however. Gravity pushes shells of hydrogen and helium to densities where nuclear fusion can begin, and they are ignited, albeit for a short time. When this happens with the Sun, it will briefly be 2,100 times brighter than we see it now. 7. Some 7 or 8 bi ...
The magnitude scale, parallax, the parsec, and Cepheid distances
... • To do this we need a property that does not vary with distance which is correlated with the absolute magnitude, e.g: – Cepheid variables (discovered by HenrieMa LeaviM (1912) • The Period-‐Luminosity r ...
... • To do this we need a property that does not vary with distance which is correlated with the absolute magnitude, e.g: – Cepheid variables (discovered by HenrieMa LeaviM (1912) • The Period-‐Luminosity r ...
BIL3: YILDIZ
... Binarity is one of the essential tools for determination of structure and evolution of stars. Binaries in clusters are peerless. Differentially rotating models is in better agreement with the observations than the NR models or models rotating like a solid body. ...
... Binarity is one of the essential tools for determination of structure and evolution of stars. Binaries in clusters are peerless. Differentially rotating models is in better agreement with the observations than the NR models or models rotating like a solid body. ...
Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar
... Traveling by ship in 1930 to begin his Ph.D. at Cambridge University, he had calculated a number. In his honor this number is now called The Chandrasekhar Limit: its value is 1.4. This number determines the fate of stars. Chandrasekhar published his result in 1931 in the Astrophysical Journal. In se ...
... Traveling by ship in 1930 to begin his Ph.D. at Cambridge University, he had calculated a number. In his honor this number is now called The Chandrasekhar Limit: its value is 1.4. This number determines the fate of stars. Chandrasekhar published his result in 1931 in the Astrophysical Journal. In se ...
the chromospheres of classical cepheids. 111. a search for transition
... short ( < 1 hr). While emission was seen in most of the stars, in the shortest period star, 6 Cep, little significant emission was found. The upper limits we were able to place on the fluxes were, however, larger than the expected values based on the other Cepheids and on nonvariables. In order to d ...
... short ( < 1 hr). While emission was seen in most of the stars, in the shortest period star, 6 Cep, little significant emission was found. The upper limits we were able to place on the fluxes were, however, larger than the expected values based on the other Cepheids and on nonvariables. In order to d ...
From Simulation to Visualization: Astrophysics Goes
... nature on a computer Mathematical abstraction of a physical process (equations) Time sequence ...
... nature on a computer Mathematical abstraction of a physical process (equations) Time sequence ...
Nebular theory
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
milano2006_popov - X-Ray
... of components prior to a neutron star formation, or due to a system disruption after a supernova explosion. • The fraction of such neutron stars in survived binaries is about 1% or lower, i.e. magnetars are expected to be isolated objects. Their most numerous companions are black holes. MNRAS vol. 3 ...
... of components prior to a neutron star formation, or due to a system disruption after a supernova explosion. • The fraction of such neutron stars in survived binaries is about 1% or lower, i.e. magnetars are expected to be isolated objects. Their most numerous companions are black holes. MNRAS vol. 3 ...
Sun: Nuclear Powerhouse - Wayne State University Physics and
... isotope of argon when hit by a neutrino A gallium isotope changes to a radioactive isotope of germanium Neutrinos can interact with protons and neutrons and produce an electron The electron can be detected 26 July 2005 ...
... isotope of argon when hit by a neutrino A gallium isotope changes to a radioactive isotope of germanium Neutrinos can interact with protons and neutrons and produce an electron The electron can be detected 26 July 2005 ...
The Milky Way
... solar masses Additional mass in an extended halo: Total: Approx. 1 trillion solar masses Most of the mass is not emitting any radiation: ...
... solar masses Additional mass in an extended halo: Total: Approx. 1 trillion solar masses Most of the mass is not emitting any radiation: ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... As the planets orbit around the pulsar, they cause it to wobble around, resulting in slight changes of the observed pulsar period. ...
... As the planets orbit around the pulsar, they cause it to wobble around, resulting in slight changes of the observed pulsar period. ...
Continuous Spectrum—Kirchoff`s First Law
... the mass ratio between the most and least massive stars? Also, which stars in the universe are most common, those of high mass or those of low mass? The distribution of the initial masses of stars is an important statistical problem (IMF - Initial Mass Function) ...
... the mass ratio between the most and least massive stars? Also, which stars in the universe are most common, those of high mass or those of low mass? The distribution of the initial masses of stars is an important statistical problem (IMF - Initial Mass Function) ...
Please Highlight this Area and Add your Main Title
... All four variable stars were analyzed using the aforementioned methodology and the photometric light curves seen above were created. The important piece of data that can be extracted from the photometric light curve is the periodicity of the variable star. The periodicity of any variable star descri ...
... All four variable stars were analyzed using the aforementioned methodology and the photometric light curves seen above were created. The important piece of data that can be extracted from the photometric light curve is the periodicity of the variable star. The periodicity of any variable star descri ...
Black Hole Sun: A Total Eclipse Free Public Lecture about Eclipses
... We are interpreting E. C. Pickering’s (A. J. Cannon’s boss) spectra of Mizar (a star in the Big Dipper) in 1889. How can the spectral line of hydrogen appear at different wavelengths? A. The star is moving. B. Hydrogen emits at different wavelengths at different times. C. There was something wrong w ...
... We are interpreting E. C. Pickering’s (A. J. Cannon’s boss) spectra of Mizar (a star in the Big Dipper) in 1889. How can the spectral line of hydrogen appear at different wavelengths? A. The star is moving. B. Hydrogen emits at different wavelengths at different times. C. There was something wrong w ...
Astronomy Assignment #10 Solutions
... 9. Some stars have temperatures of only 3000 K but have over 100X more luminosity than the Sun. How is this possible? The luminosity of a star depends on two factors; its temperature and its surface area. This is summarized in the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R 2 T 4 . Thus a cool star can have a v ...
... 9. Some stars have temperatures of only 3000 K but have over 100X more luminosity than the Sun. How is this possible? The luminosity of a star depends on two factors; its temperature and its surface area. This is summarized in the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R 2 T 4 . Thus a cool star can have a v ...
Astronomy Glossary Key
... traveler got into a space ship travelling at the speed of light, less time would have elapsed for him or her compared to the people they left at home. ...
... traveler got into a space ship travelling at the speed of light, less time would have elapsed for him or her compared to the people they left at home. ...
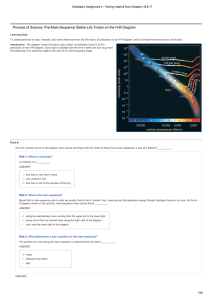
Process of Science: PreMainSequence Stellar Life Tracks on the HR
... luminous— when it is a protostar and therefore does not yet have internal fusion. This fact can be a little surprising, but do not forget that luminosity depends on both surface temperature and size. Protostars are always much larger than the mainsequence stars they will eventually become, which is ...
... luminous— when it is a protostar and therefore does not yet have internal fusion. This fact can be a little surprising, but do not forget that luminosity depends on both surface temperature and size. Protostars are always much larger than the mainsequence stars they will eventually become, which is ...
A black hole: The ultimate space
... The horizon of a black hole When light particles (photons) are emitted from a black hole, they perform work against gravity. This work reduces the energy of the photons. The lower energy implies a red-shift. There is a sphere around a black hole called the horizon, where the photons lose all of the ...
... The horizon of a black hole When light particles (photons) are emitted from a black hole, they perform work against gravity. This work reduces the energy of the photons. The lower energy implies a red-shift. There is a sphere around a black hole called the horizon, where the photons lose all of the ...
Astrology, calendars and the dating of Christian festivals.
... influence the makeup of our species given the millions of years of influence on our supposed development from primitive life forms. If you think objects in rotation cannot have an effect on us well a very simple experiment can be made. Take a rapidly spinning bicycle wheel between both hands and the ...
... influence the makeup of our species given the millions of years of influence on our supposed development from primitive life forms. If you think objects in rotation cannot have an effect on us well a very simple experiment can be made. Take a rapidly spinning bicycle wheel between both hands and the ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.