Galaxies
... million years. • Atoms of hydrogen absorb and emit radio waves with a wavelength of 21 cm. – Measure velocity of gas clouds by the doppler shift ...
... million years. • Atoms of hydrogen absorb and emit radio waves with a wavelength of 21 cm. – Measure velocity of gas clouds by the doppler shift ...
Review Sheet and Study Hints - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... Evolution and Formation Describe a theory about the formation of spirals. What evidence do we have for that? In what sense is the formation of ellipticals different from that of spirals? In what sense was Hubble correct/incorrect with this evolutionary proposal? How do galaxies in the pa ...
... Evolution and Formation Describe a theory about the formation of spirals. What evidence do we have for that? In what sense is the formation of ellipticals different from that of spirals? In what sense was Hubble correct/incorrect with this evolutionary proposal? How do galaxies in the pa ...
Our Solar System, Our Galaxy, then the Universe
... Most asteroids are not in Near Earth Orbits. They are in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter which contains roughly 1.7 million asteroids one km or greater across. As each of these has ...
... Most asteroids are not in Near Earth Orbits. They are in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter which contains roughly 1.7 million asteroids one km or greater across. As each of these has ...
proposed research projects for pparc gemini studentships
... systems to establish the links between the properties of their stellar populations (ages and chemical abundances) and their kinematic properties (masses and dynamics). GEMINI spectroscopy will allow us to measure kinematics and line strengths out to large radii. We will combine this information with ...
... systems to establish the links between the properties of their stellar populations (ages and chemical abundances) and their kinematic properties (masses and dynamics). GEMINI spectroscopy will allow us to measure kinematics and line strengths out to large radii. We will combine this information with ...
Introduction - Assets - Cambridge
... with another. This is the subject of textbooks, monographs, and popular books on nuclear and elementary particle physics; and it is not the goal of this book. We experience these nuclei in their lowest energy states, called their “ground states,” nuclei “unheated,” without any extra energy of excita ...
... with another. This is the subject of textbooks, monographs, and popular books on nuclear and elementary particle physics; and it is not the goal of this book. We experience these nuclei in their lowest energy states, called their “ground states,” nuclei “unheated,” without any extra energy of excita ...
Search for Planetary Candidates within the OGLE Stars
... ON EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (WGESP): stars: objects capable of thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen (>0.075 Msun); Brown dwarf: capable of deuterium burning (0.013
... ON EXTRASOLAR PLANETS (WGESP): stars: objects capable of thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen (>0.075 Msun); Brown dwarf: capable of deuterium burning (0.013
The Physical Properties of Normal A Stars
... Si/log Sr, v sin i, and . My “model” was that stars rotating sufficiently fast have normal abundances all over their surfaces. When the rotation decreases below some critical value, the poles begin to show peculiar abundances. These regions with peculiar abundances increase with decreasing rotation ...
... Si/log Sr, v sin i, and . My “model” was that stars rotating sufficiently fast have normal abundances all over their surfaces. When the rotation decreases below some critical value, the poles begin to show peculiar abundances. These regions with peculiar abundances increase with decreasing rotation ...
Stellar Relaxation Times
... center of the Galaxy is not gravitationally affected by other stars. On the other hand, giant molecular clouds have masses that are ~ 108 M. Although the number density of clouds is lower, it’s not 1016 times lower! The masses of these clouds are therefore high enough to scatter stars out of their ...
... center of the Galaxy is not gravitationally affected by other stars. On the other hand, giant molecular clouds have masses that are ~ 108 M. Although the number density of clouds is lower, it’s not 1016 times lower! The masses of these clouds are therefore high enough to scatter stars out of their ...
Here
... the x-axis of the plot, and some measure of the intrinsic luminosity is plotted on the y-axis. ...
... the x-axis of the plot, and some measure of the intrinsic luminosity is plotted on the y-axis. ...
Compa ring between Spectroscopic and Photometric Method for
... within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to the star. Binary systems are classified into tree classes: detached, semidetached and contact systems, as is shown in figure ...
... within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to the star. Binary systems are classified into tree classes: detached, semidetached and contact systems, as is shown in figure ...
PowerPoint Presentation - 18. The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
... – what the ancient Greeks & Romans called a star which suddenly appeared! ...
... – what the ancient Greeks & Romans called a star which suddenly appeared! ...
Stellar Spectra Classification
... Introduction: Classifying stars based on brightness is somewhat problematic. A star’s apparent brightness can be affected by its distance from the observer, its size, or by the presence of interstellar dust. Instead, astronomers classify stars based on the major components of their spectra. Much lik ...
... Introduction: Classifying stars based on brightness is somewhat problematic. A star’s apparent brightness can be affected by its distance from the observer, its size, or by the presence of interstellar dust. Instead, astronomers classify stars based on the major components of their spectra. Much lik ...
Weighing a galaxy / Black holes / Quasars —16 Nov Nov-09
... There is not much light between 7 & 16 kpc. There is little light beyond 7 kpc, but the amount of mass doubles. Where there is mass there is not necessarily light from stars ...
... There is not much light between 7 & 16 kpc. There is little light beyond 7 kpc, but the amount of mass doubles. Where there is mass there is not necessarily light from stars ...
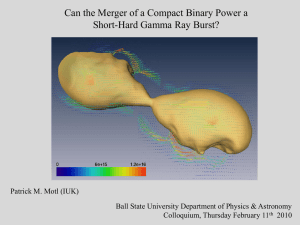
motl_bsu_021210
... Zwicky and Baade hypothesized that stellar explosions (supernovae) may result in a dense star made almost entirely of neutrons. Oppenheimer and collaborators worked out what the structure of such an object would be – they are horrendously small for a star. Pulsars were discovered accidently by Jocel ...
... Zwicky and Baade hypothesized that stellar explosions (supernovae) may result in a dense star made almost entirely of neutrons. Oppenheimer and collaborators worked out what the structure of such an object would be – they are horrendously small for a star. Pulsars were discovered accidently by Jocel ...
HD 140283: A Star in the Solar Neighborhood that Formed Shortly
... parallax would be a nearby extremely metal-deficient star, with a well-determined chemical composition based on high-resolution spectroscopy, which has begun to evolve off the main sequence in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (HRD). The one star that best satisfies these criteria is HD 140283, a brig ...
... parallax would be a nearby extremely metal-deficient star, with a well-determined chemical composition based on high-resolution spectroscopy, which has begun to evolve off the main sequence in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (HRD). The one star that best satisfies these criteria is HD 140283, a brig ...
Radiation vs. Gas Pressure, the Stellar Mass
... the detailed differences are likely to be more complex, e.g. associated with the convective nature of stellar envelopes at lower mass. Nonetheless, it is remarkable how well the overall scalings can be reproduced with just a simple analysis of the two key governing equations for hydrostatic equilibr ...
... the detailed differences are likely to be more complex, e.g. associated with the convective nature of stellar envelopes at lower mass. Nonetheless, it is remarkable how well the overall scalings can be reproduced with just a simple analysis of the two key governing equations for hydrostatic equilibr ...
Stars, Constellations, and Quasars
... observed and studied the nighttime sky, and archaeological evidence such as Stonehenge points to these early studies of astronomy. Ancient cultures also developed elaborate mythologies around stars and constellations and gave them names, some of which are still in use today. ...
... observed and studied the nighttime sky, and archaeological evidence such as Stonehenge points to these early studies of astronomy. Ancient cultures also developed elaborate mythologies around stars and constellations and gave them names, some of which are still in use today. ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.