Galaxies - Stockton University
... interstellar extinction is very significant. This has the effect of making the distribution of stars appear more centered upon us than it really is (Kapteyn's model) as well as rather small. At the same time, it makes the globular clusters appear fainter and more distant so makes Shapley's model too ...
... interstellar extinction is very significant. This has the effect of making the distribution of stars appear more centered upon us than it really is (Kapteyn's model) as well as rather small. At the same time, it makes the globular clusters appear fainter and more distant so makes Shapley's model too ...
Astronomy 200 Problem Set No
... 1. List of stars measured including their names, positions, magnitudes, and signal/noise ratios in their spectra. 2. List of assigned spectral types for the stars. 3. A color-magnitude diagram with both spectral types and temperatures indicated (use Table 1). Plot apparent magnitudes on the vertical ...
... 1. List of stars measured including their names, positions, magnitudes, and signal/noise ratios in their spectra. 2. List of assigned spectral types for the stars. 3. A color-magnitude diagram with both spectral types and temperatures indicated (use Table 1). Plot apparent magnitudes on the vertical ...
phys-1600 - Dave Heppenstall
... • 15% of the moon's surface are dark surfaces thousands of miles across which are now understood to be frozen lava flows. • The intense cratering on the moon can be traced back to around 4 million years ago. • The Earth also experienced this large-scale cratering, but unlike the Earth, the moon did ...
... • 15% of the moon's surface are dark surfaces thousands of miles across which are now understood to be frozen lava flows. • The intense cratering on the moon can be traced back to around 4 million years ago. • The Earth also experienced this large-scale cratering, but unlike the Earth, the moon did ...
The Bible and big bang cosmology
... Ph.D. Astronomy Ph.D. Astronomy Ph.D. Astronomy Ph.D. Astrophysics Ph.D. Astrophysics Ph.D. Mathematical Physics Ph.D. Condensed Matter Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Nuclear Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Aeronautics Ph.D. Combustion Theory Ph.D. Nuclear Engineer ...
... Ph.D. Astronomy Ph.D. Astronomy Ph.D. Astronomy Ph.D. Astrophysics Ph.D. Astrophysics Ph.D. Mathematical Physics Ph.D. Condensed Matter Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Nuclear Physics Ph.D. Physics Ph.D. Aeronautics Ph.D. Combustion Theory Ph.D. Nuclear Engineer ...
Gamma Ray Bursts - University of Arizona
... Model • GRB occurs after supernova explosion • Iron produced in supernova can then be lit up by gammaray burst – producing iron lines! • Iron lines observed! ...
... Model • GRB occurs after supernova explosion • Iron produced in supernova can then be lit up by gammaray burst – producing iron lines! • Iron lines observed! ...
Top 10
... early humans were capable of an artistic appreciation of the world around them, but it also tells us what animals were cohabiting with humans at the time. These are dated by not only geological methods, but also by radiocarbon dating of the pigments in the paintings themselves. A foot-tall lion-head ...
... early humans were capable of an artistic appreciation of the world around them, but it also tells us what animals were cohabiting with humans at the time. These are dated by not only geological methods, but also by radiocarbon dating of the pigments in the paintings themselves. A foot-tall lion-head ...
$doc.title
... gradually puffed up (thicker) due to dynamical effects • The thick disk: it could be a thin disk that was dynamically heated by minor mergers with other galaxies • The bulge: the original, self-enriched stellar population that formed at the bottom of the galaxy’s potential well • The bar: formed ...
... gradually puffed up (thicker) due to dynamical effects • The thick disk: it could be a thin disk that was dynamically heated by minor mergers with other galaxies • The bulge: the original, self-enriched stellar population that formed at the bottom of the galaxy’s potential well • The bar: formed ...
Frank Timmes (ASU)
... 1. SN Ia 2011fe (M101) discovered by the Palomar Transient Factory about 11 hours after the explosion. No evidence for circumbinary material and progenitor likely a CO WD. 2. However, PTF 11kx was a SN Ia that exploded in a system with circumbinary material and they suggest that the progenitor was a ...
... 1. SN Ia 2011fe (M101) discovered by the Palomar Transient Factory about 11 hours after the explosion. No evidence for circumbinary material and progenitor likely a CO WD. 2. However, PTF 11kx was a SN Ia that exploded in a system with circumbinary material and they suggest that the progenitor was a ...
The coupling between the core/cusp and missing satellite problems
... We calculate the energy that baryons must inject in cold dark matter (CDM) haloes in order to remove centrally-divergent DM cusps on scales relevant to observations of dwarf spheroidal galaxies (dSphs). We estimate that the CDM haloes often associated with the Milky Way’s dSphs (Mvir /M⊙ ∼ 109−10 ) ...
... We calculate the energy that baryons must inject in cold dark matter (CDM) haloes in order to remove centrally-divergent DM cusps on scales relevant to observations of dwarf spheroidal galaxies (dSphs). We estimate that the CDM haloes often associated with the Milky Way’s dSphs (Mvir /M⊙ ∼ 109−10 ) ...
Helium Production in Big Bang Weighing a Galaxy12 Nov 11/12/2010
... Changing free neutrons & protons in BB • Radiation in the universe can supply energy to change n into p. – More precisely, to supply energy to electrons and positrons to change n into p. ...
... Changing free neutrons & protons in BB • Radiation in the universe can supply energy to change n into p. – More precisely, to supply energy to electrons and positrons to change n into p. ...
Gravity-Bending Find Leads to Kepler Meeting Einstein
... While working for the National Park Service in Arizona, my wife and I were fortunate to live just 70 air miles west of Kitt Peak, and witness the 1966 Leonid meteor shower 1,000 meteors per minute with trains lasting four to five seconds. (Yes, that’s per minute, not per hour!) Months later, a frie ...
... While working for the National Park Service in Arizona, my wife and I were fortunate to live just 70 air miles west of Kitt Peak, and witness the 1966 Leonid meteor shower 1,000 meteors per minute with trains lasting four to five seconds. (Yes, that’s per minute, not per hour!) Months later, a frie ...
Presentation - Relativity Group
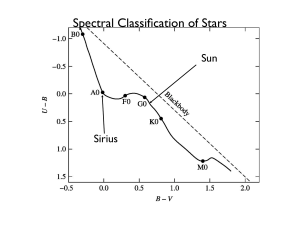
... • How are stars classified into spectral types? • Stars are classified according to their spectra, with different spectral types generally corresponding to different temperatures. In order from hottest to coolest, the major spectral types are O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. These are subdivided into number ...
... • How are stars classified into spectral types? • Stars are classified according to their spectra, with different spectral types generally corresponding to different temperatures. In order from hottest to coolest, the major spectral types are O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. These are subdivided into number ...
click here
... • Hot, massive stars end up in the upper left; cool, low mass stars end up in the lower right. • In addition, there are poorly populated areas. One, in the lower left, is populated by hot, very tiny stars (white dwarfs). Another, in the upper right, is populated by giant stars on the giant branch (p ...
... • Hot, massive stars end up in the upper left; cool, low mass stars end up in the lower right. • In addition, there are poorly populated areas. One, in the lower left, is populated by hot, very tiny stars (white dwarfs). Another, in the upper right, is populated by giant stars on the giant branch (p ...
Part IV: Stars
... formation and stellar evolution. This section also introduces the very important idea of the balance between pressure and gravity within a star. Among astronomers, this kind of equilibrium is known as hydrostatic equilibrium. We have found that the word hydrostatic is so foreign to students that the ...
... formation and stellar evolution. This section also introduces the very important idea of the balance between pressure and gravity within a star. Among astronomers, this kind of equilibrium is known as hydrostatic equilibrium. We have found that the word hydrostatic is so foreign to students that the ...
Homework 1 SOLUTIONS - University of Colorado Boulder
... d). Is this accuracy good enough for the wayfinder to find Hawaii? Explain using your knowledge of the techniques for making “land fall” described in class. Yes, clouds can be seen over the Big Island for > 100 miles away. Specific types of birds fly out from their nests each morning and return each ...
... d). Is this accuracy good enough for the wayfinder to find Hawaii? Explain using your knowledge of the techniques for making “land fall” described in class. Yes, clouds can be seen over the Big Island for > 100 miles away. Specific types of birds fly out from their nests each morning and return each ...
Document
... Origin of the anomalous abundances The Ap phenomenon must be a surface phenomenon since the overabundance of rare earth elements (e.g. Eu is overabundant by a factor of up to 104 ) is so great that a signficant fraction of the supply of such elements in the Universe would be contained in Ap stars i ...
... Origin of the anomalous abundances The Ap phenomenon must be a surface phenomenon since the overabundance of rare earth elements (e.g. Eu is overabundant by a factor of up to 104 ) is so great that a signficant fraction of the supply of such elements in the Universe would be contained in Ap stars i ...
Stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes during its lifetime. Depending on the mass of the star, this lifetime ranges from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are born from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star.Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its life. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing through the subgiant stage until it reaches the red giant phase. Stars with at least half the mass of the Sun can also begin to generate energy through the fusion of helium at their core, whereas more-massive stars can fuse heavier elements along a series of concentric shells. Once a star like the Sun has exhausted its nuclear fuel, its core collapses into a dense white dwarf and the outer layers are expelled as a planetary nebula. Stars with around ten or more times the mass of the Sun can explode in a supernova as their inert iron cores collapse into an extremely dense neutron star or black hole. Although the universe is not old enough for any of the smallest red dwarfs to have reached the end of their lives, stellar models suggest they will slowly become brighter and hotter before running out of hydrogen fuel and becoming low-mass white dwarfs.Stellar evolution is not studied by observing the life of a single star, as most stellar changes occur too slowly to be detected, even over many centuries. Instead, astrophysicists come to understand how stars evolve by observing numerous stars at various points in their lifetime, and by simulating stellar structure using computer models.In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at z = 6.60. Such stars are likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., at high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen that are needed for the later formation of planets and life as we know it.