Production of Manganese-53 in a Self
... Introduction: The presence of short-lived radioactivities in the early Solar nebula has been inferred from excesses of their daughter isotopes embedded within primitive meteorites found and analyzed via various physical and chemical means over the last 50 years. The challenge is to reconcile the abu ...
... Introduction: The presence of short-lived radioactivities in the early Solar nebula has been inferred from excesses of their daughter isotopes embedded within primitive meteorites found and analyzed via various physical and chemical means over the last 50 years. The challenge is to reconcile the abu ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... Telescopes: Collect and focus different types of electromagnetic radiation including visible light. Observatory: A building that contains one or more telescopes. ...
... Telescopes: Collect and focus different types of electromagnetic radiation including visible light. Observatory: A building that contains one or more telescopes. ...
Part 7
... Figure 13.1: Upper section: a schematic plot of the potential between two charged nucleons as a function of separation. At `large' separations (& 10−15 m), the repulsive Coulomb force is given by eqtn. (13.8); classically, particles cannot come closer than the point r1 at which the relative kinetic ...
... Figure 13.1: Upper section: a schematic plot of the potential between two charged nucleons as a function of separation. At `large' separations (& 10−15 m), the repulsive Coulomb force is given by eqtn. (13.8); classically, particles cannot come closer than the point r1 at which the relative kinetic ...
Conceptual Physics
... story. They would mutually annihilate each other, with most of the matter converting to radiant energy (this is what happened to the anti-atom created in 1995, when it encountered normal matter and rapidly annihilated in a puff of energy). This process, more so than any other known, results in the m ...
... story. They would mutually annihilate each other, with most of the matter converting to radiant energy (this is what happened to the anti-atom created in 1995, when it encountered normal matter and rapidly annihilated in a puff of energy). This process, more so than any other known, results in the m ...
the spectrum of a partially ionized jet sodium ionization in t
... We present the results of a study of the sodium ionization and excitation in the winds of low-luminosity, pre-main-sequence stars. Line profiles for the Nal doublet at 5990,5986 Aare discussed and compared with the observations for those T Tauri stars with P-Cygni profiles. We find that the observed ...
... We present the results of a study of the sodium ionization and excitation in the winds of low-luminosity, pre-main-sequence stars. Line profiles for the Nal doublet at 5990,5986 Aare discussed and compared with the observations for those T Tauri stars with P-Cygni profiles. We find that the observed ...
SUPERNOVAE A. Supernovae.-Several years ago, Baade andI
... E. Breakdown of the Electric Fields Surrounding the Stellar Remnant.The space charges and the electric fields in the ejected gaseous masses will break down when the radiation from the stellar remnant decreases to a point where it is not any more able to support these space charges. At that stage the ...
... E. Breakdown of the Electric Fields Surrounding the Stellar Remnant.The space charges and the electric fields in the ejected gaseous masses will break down when the radiation from the stellar remnant decreases to a point where it is not any more able to support these space charges. At that stage the ...
The Role of Radioactive Isotopes in Astrophysics
... There could hardly be two more different scientists than the two that made the first significant steps toward nucleosynthesis in stars of the elements heavier than carbon. Both were Europeans disrupted in careers by world war II. The originator of nucleosynthesis in stars arose from non-privileged Y ...
... There could hardly be two more different scientists than the two that made the first significant steps toward nucleosynthesis in stars of the elements heavier than carbon. Both were Europeans disrupted in careers by world war II. The originator of nucleosynthesis in stars arose from non-privileged Y ...
ppt - Wladimir Lyra
... The star gets very luminous and swells. The expansion cools the outer layers. The star becomes a red giant. ...
... The star gets very luminous and swells. The expansion cools the outer layers. The star becomes a red giant. ...
PHY-105: Final Stages of Stellar Evolution
... For type II, as we have seen, the mechanism is the catastrophic collapse of an iron core. Photodisintegration → ν burst, which preceeds maximum light and can be used to “trigger” on supernovae. Remnant is either a neutron star or black hole – we’ll look at both of these in more detail next lecture(s ...
... For type II, as we have seen, the mechanism is the catastrophic collapse of an iron core. Photodisintegration → ν burst, which preceeds maximum light and can be used to “trigger” on supernovae. Remnant is either a neutron star or black hole – we’ll look at both of these in more detail next lecture(s ...
Test 2 - Constellations - ppt
... constellations Many of the stars form specific patterns, or ________ How many named constellations are there?? ...
... constellations Many of the stars form specific patterns, or ________ How many named constellations are there?? ...
Review
... time and has been expanding ever since n Universe began as an infinitely hot, dense concentration of energy n Evidences for big bang - Universal expansion - Cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation: microwave radiations fall on Earth from all directions in a form of background signals (contin ...
... time and has been expanding ever since n Universe began as an infinitely hot, dense concentration of energy n Evidences for big bang - Universal expansion - Cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation: microwave radiations fall on Earth from all directions in a form of background signals (contin ...
Introductory Presentation on Cosmic Rays
... electromagnetic energy (gamma ray) traveling through matter. This is one of the principal ways in which high energy gamma rays are absorbed in matter. For the pair production to occur the photon energy must be at least equivalent to the mass of two electrons, i.e. 1.02 MeV because the mass of a sing ...
... electromagnetic energy (gamma ray) traveling through matter. This is one of the principal ways in which high energy gamma rays are absorbed in matter. For the pair production to occur the photon energy must be at least equivalent to the mass of two electrons, i.e. 1.02 MeV because the mass of a sing ...
Nature template
... than 130 M versus the mass of the upper mass cutoff. The simulation uses 60,000 systems, each with test points having a mass distribution that follows a single power law initial mass function truncated at the cutoff. The Geneva stellar evolution models are used to convert intial masses into deredde ...
... than 130 M versus the mass of the upper mass cutoff. The simulation uses 60,000 systems, each with test points having a mass distribution that follows a single power law initial mass function truncated at the cutoff. The Geneva stellar evolution models are used to convert intial masses into deredde ...
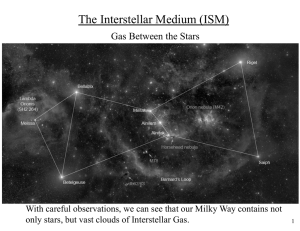
The Interstellar Medium (ISM)
... Why is the gas ionized and why does it trace star-forming regions? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star f ...
... Why is the gas ionized and why does it trace star-forming regions? Remember, takes energetic UV photons to ionize H. Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star f ...
Life as a Low
... clusters show star becomes larger, redder, and more luminous after its time on the main sequence is over. ...
... clusters show star becomes larger, redder, and more luminous after its time on the main sequence is over. ...
The Chemical Composition of an Extrasolar Kuiper-Belt
... Kuiper-Belt-Object analog into the white dwarf’s tidal radius. This finding shows that analogs to objects in our Kuiper Belt exist around other stars and could be responsible for the delivery of volatiles to terrestrial planets beyond the solar system. Key words: Kuiper belt: general – planetary syst ...
... Kuiper-Belt-Object analog into the white dwarf’s tidal radius. This finding shows that analogs to objects in our Kuiper Belt exist around other stars and could be responsible for the delivery of volatiles to terrestrial planets beyond the solar system. Key words: Kuiper belt: general – planetary syst ...
Lesson 01 - Big Bang Theory
... Nothing is beyond the expansion space __________ and if you go the edge you will end up back at the start _________________! ...
... Nothing is beyond the expansion space __________ and if you go the edge you will end up back at the start _________________! ...
Oxygen isotopes in circumstellar Al_2O_3 grains from meteorites
... formed in the solar system. In light of the indications that an 16 0 carrier was present in the early solar system, it is surprising that the first recognized presolar oxide grains are 17 0 rich. The presence of identifiable 16 0-rich carrier grains has not been established. It is possible that the ...
... formed in the solar system. In light of the indications that an 16 0 carrier was present in the early solar system, it is surprising that the first recognized presolar oxide grains are 17 0 rich. The presence of identifiable 16 0-rich carrier grains has not been established. It is possible that the ...
insert - Athens
... see? Stars of course. Thousands of them. In fact on a dark night, you may be able to see about three thousand stars without the aid of binoculars or a telescope. WHAT IS A STAR? Stars are glowing, rotating balls of gas. Even though you may see thousands of stars, you are only seeing a small fraction ...
... see? Stars of course. Thousands of them. In fact on a dark night, you may be able to see about three thousand stars without the aid of binoculars or a telescope. WHAT IS A STAR? Stars are glowing, rotating balls of gas. Even though you may see thousands of stars, you are only seeing a small fraction ...
Here
... • Summary: 4 hydrogen nuclei (which are protons) combine to form 1 helium nucleus (which has two protons and two neutrons). • The details are a bit complex: In the Sun, 6 hydrogen nuclei are involved in a sequence that produces two hydrogen nuclei and one helium nucleus. This is the proton-proton ...
... • Summary: 4 hydrogen nuclei (which are protons) combine to form 1 helium nucleus (which has two protons and two neutrons). • The details are a bit complex: In the Sun, 6 hydrogen nuclei are involved in a sequence that produces two hydrogen nuclei and one helium nucleus. This is the proton-proton ...
The Anthropic Principle 165.00 Kb
... • Right relation to supernovae: – More or closer – exterminate life – Less or further – too few heavy elements ...
... • Right relation to supernovae: – More or closer – exterminate life – Less or further – too few heavy elements ...
Diapositive 1 - University of Surrey
... Nowadays, it is commonly accepted that stellar energy is due to nuclear reactions occurring in the core (Eddington 1920) and that stellar nucleosynthesis can explain all the nuclei with A>=12 and one part with A<12. ...
... Nowadays, it is commonly accepted that stellar energy is due to nuclear reactions occurring in the core (Eddington 1920) and that stellar nucleosynthesis can explain all the nuclei with A>=12 and one part with A<12. ...
Here
... • Summary: 4 hydrogen nuclei (which are protons) combine to form 1 helium nucleus (which has two protons and two neutrons). • The details are a bit complex: In the Sun, 6 hydrogen nuclei are involved in a sequence that produces two hydrogen nuclei and one helium nucleus. This is the proton-proton ...
... • Summary: 4 hydrogen nuclei (which are protons) combine to form 1 helium nucleus (which has two protons and two neutrons). • The details are a bit complex: In the Sun, 6 hydrogen nuclei are involved in a sequence that produces two hydrogen nuclei and one helium nucleus. This is the proton-proton ...
Nucleosynthesis
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons, primarily protons and neutrons. The first nuclei were formed about three minutes after the Big Bang, through the process called Big Bang nucleosynthesis. It was then that hydrogen and helium formed to become the content of the first stars, and this primeval process is responsible for the present hydrogen/helium ratio of the cosmos.With the formation of stars, heavier nuclei were created from hydrogen and helium by stellar nucleosynthesis, a process that continues today. Some of these elements, particularly those lighter than iron, continue to be delivered to the interstellar medium when low mass stars eject their outer envelope before they collapse to form white dwarfs. The remains of their ejected mass form the planetary nebulae observable throughout our galaxy.Supernova nucleosynthesis within exploding stars by fusing carbon and oxygen is responsible for the abundances of elements between magnesium (atomic number 12) and nickel (atomic number 28). Supernova nucleosynthesis is also thought to be responsible for the creation of rarer elements heavier than iron and nickel, in the last few seconds of a type II supernova event. The synthesis of these heavier elements absorbs energy (endothermic) as they are created, from the energy produced during the supernova explosion. Some of those elements are created from the absorption of multiple neutrons (the R process) in the period of a few seconds during the explosion. The elements formed in supernovas include the heaviest elements known, such as the long-lived elements uranium and thorium.Cosmic ray spallation, caused when cosmic rays impact the interstellar medium and fragment larger atomic species, is a significant source of the lighter nuclei, particularly 3He, 9Be and 10,11B, that are not created by stellar nucleosynthesis.In addition to the fusion processes responsible for the growing abundances of elements in the universe, a few minor natural processes continue to produce very small numbers of new nuclides on Earth. These nuclides contribute little to their abundances, but may account for the presence of specific new nuclei. These nuclides are produced via radiogenesis (decay) of long-lived, heavy, primordial radionuclides such as uranium and thorium. Cosmic ray bombardment of elements on Earth also contribute to the presence of rare, short-lived atomic species called cosmogenic nuclides.