CIS101 Introduction to Computing
... The computer can only execute one operation at a time When an expression has more than one operator, they have to be carried out in order determined by rule of mathematics known as “operator precedence” ...
... The computer can only execute one operation at a time When an expression has more than one operator, they have to be carried out in order determined by rule of mathematics known as “operator precedence” ...
Table of contents
... In computer science, polymorphism is the idea of allowing the same code to be used with different types, resulting in more general and abstract implementations. The concept of polymorphism applies to functions as well as types: A function that can evaluate to and be applied to values of different ty ...
... In computer science, polymorphism is the idea of allowing the same code to be used with different types, resulting in more general and abstract implementations. The concept of polymorphism applies to functions as well as types: A function that can evaluate to and be applied to values of different ty ...
Lecture 1, Mon 4 Aug 2008, PDF
... signifying addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. As usual, we can also use in front of an expression to negate its value, as in -(x+y). In addition, the function div and mod signify integer division and remainder, respectively. So div 3 2 is 1, div 7 3 is 2, . . . while mod 10 6 is 4, ...
... signifying addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. As usual, we can also use in front of an expression to negate its value, as in -(x+y). In addition, the function div and mod signify integer division and remainder, respectively. So div 3 2 is 1, div 7 3 is 2, . . . while mod 10 6 is 4, ...
Here are the notes on Chapter 3
... collections, when Java already gives us a set of collections? This set of collections is only a subset of the collections you may want to use. The classes may not be implemented the ...
... collections, when Java already gives us a set of collections? This set of collections is only a subset of the collections you may want to use. The classes may not be implemented the ...
Powerpoint - Princeton University
... • referential transparency: can substitute expression that yield equal results ...
... • referential transparency: can substitute expression that yield equal results ...
Functional programming Primer I COS 320 Compiling Techniques Princeton University
... • referential transparency: can substitute expression that yield equal results ...
... • referential transparency: can substitute expression that yield equal results ...
Simple Program Design
... Modular design Modular design involves grouping tasks together because they all perform the same function. Object-oriented programming ...
... Modular design Modular design involves grouping tasks together because they all perform the same function. Object-oriented programming ...
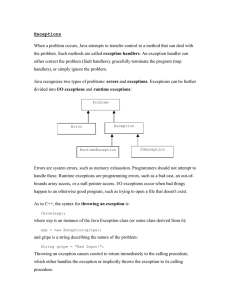
Exceptions
... Errors are system errors, such as memory exhaustion. Programmers should not attempt to handle these. Runtime exceptions are programming errors, such as a bad cast, an out-ofbounds array access, or a null pointer access. I/O exceptions occur when bad things happen to an otherwise good program, such a ...
... Errors are system errors, such as memory exhaustion. Programmers should not attempt to handle these. Runtime exceptions are programming errors, such as a bad cast, an out-ofbounds array access, or a null pointer access. I/O exceptions occur when bad things happen to an otherwise good program, such a ...
Functional Programming
... Peter Selinger Lecture Notes on the Lambda Calculus Chapter 9 – Type Inference Functional Programming ...
... Peter Selinger Lecture Notes on the Lambda Calculus Chapter 9 – Type Inference Functional Programming ...
Slide
... Peter Selinger Lecture Notes on the Lambda Calculus Chapter 9 – Type Inference Functional Programming ...
... Peter Selinger Lecture Notes on the Lambda Calculus Chapter 9 – Type Inference Functional Programming ...
Message Passing, Concurrency, and Parallelism in Erlang
... Presented By: Craig R. Kuehn Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin-Platteville [email protected] ...
... Presented By: Craig R. Kuehn Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering University of Wisconsin-Platteville [email protected] ...
Chapter 1 – Introduction to Computers and C++
... 1.7 History of C • C – Evolved by Ritchie from two previous programming languages, BCPL and B – Used to develop UNIX – Used to write modern operating systems – Hardware independent (portable) – By late 1970's C had evolved to "Traditional C" ...
... 1.7 History of C • C – Evolved by Ritchie from two previous programming languages, BCPL and B – Used to develop UNIX – Used to write modern operating systems – Hardware independent (portable) – By late 1970's C had evolved to "Traditional C" ...
Pattern Intro, Observer
... Pattern Beginnings "Each pattern describes a problem which occurs over and over again in our environment, and then describes the core of the solution to that problem, in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over, without ever doing it the same way twice" "Each pattern is a thre ...
... Pattern Beginnings "Each pattern describes a problem which occurs over and over again in our environment, and then describes the core of the solution to that problem, in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over, without ever doing it the same way twice" "Each pattern is a thre ...
Chapter 11 - Functional Programming, Part II: ML, Delayed
... = unless you really need it: > fun empty L = if L = [] (* wrong! *) then true else false; val empty = fn : ''a list -> bool ...
... = unless you really need it: > fun empty L = if L = [] (* wrong! *) then true else false; val empty = fn : ''a list -> bool ...
Why no one uses functional languages
... the imperative solution may leap immediately to mind or be found in a handy textbook, while a comparable functional solution may require considerable effort to find (even if once found it is more elegant). And though there are a large range of problems that possess efficient solutions in a functiona ...
... the imperative solution may leap immediately to mind or be found in a handy textbook, while a comparable functional solution may require considerable effort to find (even if once found it is more elegant). And though there are a large range of problems that possess efficient solutions in a functiona ...
Computing Science - Thompson Rivers University
... If a large number of variables must be shared among functions, external variables (or also called global variables) are more convenient and efficient than long argument lists. External variables are declared outside of any function, usually with initial values. Automatic variables (local variables a ...
... If a large number of variables must be shared among functions, external variables (or also called global variables) are more convenient and efficient than long argument lists. External variables are declared outside of any function, usually with initial values. Automatic variables (local variables a ...
C Sharp (programming language)
C# (pronounced as see sharp) is a multi-paradigm programming language encompassing strong typing, imperative, declarative, functional, generic, object-oriented (class-based), and component-oriented programming disciplines. It was developed by Microsoft within its .NET initiative and later approved as a standard by Ecma (ECMA-334) and ISO (ISO/IEC 23270:2006). C# is one of the programming languages designed for the Common Language Infrastructure.C# is intended to be a simple, modern, general-purpose, object-oriented programming language. Its development team is led by Anders Hejlsberg. The most recent version is C# 6.0, which was released on July 20, 2015.