1 - School of Computing and Information Sciences
... O3. Be familiar with the use of context-free grammars to specify programming language syntax and with recursive descent parsing. O4. Be familiar with natural semantics for imperative and functional programming languages and their use in building interpreters. O5. Be familiar with polymorphic type sy ...
... O3. Be familiar with the use of context-free grammars to specify programming language syntax and with recursive descent parsing. O4. Be familiar with natural semantics for imperative and functional programming languages and their use in building interpreters. O5. Be familiar with polymorphic type sy ...
Chapter 3 - MSU Computer Science
... – Wheeler Jump subroutine call None stored in internal memory ...
... – Wheeler Jump subroutine call None stored in internal memory ...
lecture notes
... with one another? Share information Cooperation Computational speed-up via ...
... with one another? Share information Cooperation Computational speed-up via ...
Prog4IntLecture2Java
... • Methods are actions that objects can perform • They manipulate fields and interact with other objects. ...
... • Methods are actions that objects can perform • They manipulate fields and interact with other objects. ...
Week 06 - Programming Languages
... ! Monday March 3 (next week) there will be a combination help-with-project/pizza session in place of the 12:20 sections " Keep an eye on the website for further information ...
... ! Monday March 3 (next week) there will be a combination help-with-project/pizza session in place of the 12:20 sections " Keep an eye on the website for further information ...
Compiling Compiling a class Compiling a program Compiled Kotlin
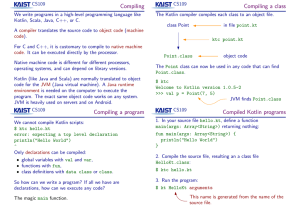
... The Kotlin compiler compiles each class to an object file. in file point.kt ...
... The Kotlin compiler compiles each class to an object file. in file point.kt ...
Steverson
... The Planning Game – Determine the scope of the next release by looking at business priorities and technical estimates Small Releases – Release simple versions of the system often Metaphor – A story of how the system works, the architecture Simple Design – System should be designed as simply as possi ...
... The Planning Game – Determine the scope of the next release by looking at business priorities and technical estimates Small Releases – Release simple versions of the system often Metaphor – A story of how the system works, the architecture Simple Design – System should be designed as simply as possi ...
CS2 (Java) Exam 1 Review - Pennsylvania State University
... solve problem, use methods, methods could get long Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): create objects to model real-world phenomena, send messages to objects, typically shorter methods Event-Driven Programming: create methods that respond to events like mouse clicks, key presses, etc. Others: Functio ...
... solve problem, use methods, methods could get long Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): create objects to model real-world phenomena, send messages to objects, typically shorter methods Event-Driven Programming: create methods that respond to events like mouse clicks, key presses, etc. Others: Functio ...
Chapter 8
... • Capturing the “unambiguous and effectively computable operations” as program instructions ...
... • Capturing the “unambiguous and effectively computable operations” as program instructions ...
PL Intro
... – Changing one thing has no effect on another • As stated by Michael Scott: ▫ Orthogonality means that features can be used in any combination, the combinations all make sense, and the meaning of a given feature is consistent regardless of other features with which it is combined. 261 example: array ...
... – Changing one thing has no effect on another • As stated by Michael Scott: ▫ Orthogonality means that features can be used in any combination, the combinations all make sense, and the meaning of a given feature is consistent regardless of other features with which it is combined. 261 example: array ...
Software Implementation Document - Wilma
... XML: Extensible Markup Language. It is designed to create grammars which describe documents so that they can be used over networks such as the internet. CGI: Common Gateway Interface described the format of data when it is passed from a Web server to a sever-side script. SQL: Structured Query Langua ...
... XML: Extensible Markup Language. It is designed to create grammars which describe documents so that they can be used over networks such as the internet. CGI: Common Gateway Interface described the format of data when it is passed from a Web server to a sever-side script. SQL: Structured Query Langua ...
Syllabus of the Entrance Exam
... Controlling program flow: loops, conditionals, branching, breaking, and continuing. Procedures and functions. Types of parameter passing. Interface and implementation. Concept of the class. Principles of encapsulation and/or information hiding. Concept of the object. Instantiation, copying, destruct ...
... Controlling program flow: loops, conditionals, branching, breaking, and continuing. Procedures and functions. Types of parameter passing. Interface and implementation. Concept of the class. Principles of encapsulation and/or information hiding. Concept of the object. Instantiation, copying, destruct ...
N4Less27.pps
... Repetition (looping) structures use loops, which execute according to the results of conditional statements. ...
... Repetition (looping) structures use loops, which execute according to the results of conditional statements. ...
ppt
... Class examples: Die & SequenceGenerator can define a Die class to model different (numeric) dice properties shared by all dice: number of sides, number of times rolled behaviors/methods shared by all dice: roll it, get # of sides, get # of rolls the roll method generates a random roll and retur ...
... Class examples: Die & SequenceGenerator can define a Die class to model different (numeric) dice properties shared by all dice: number of sides, number of times rolled behaviors/methods shared by all dice: roll it, get # of sides, get # of rolls the roll method generates a random roll and retur ...
CMSC 330: Organization of Programming Languages Course Goal
... Programs are built from objects Objects combine functions and data Often have classes and inheritence ...
... Programs are built from objects Objects combine functions and data Often have classes and inheritence ...
object - Dave Reed
... Class examples: Die & SequenceGenerator can define a Die class to model different (numeric) dice properties shared by all dice: number of sides, number of times rolled behaviors/methods shared by all dice: roll it, get # of sides, get # of rolls the roll method generates a random roll and retur ...
... Class examples: Die & SequenceGenerator can define a Die class to model different (numeric) dice properties shared by all dice: number of sides, number of times rolled behaviors/methods shared by all dice: roll it, get # of sides, get # of rolls the roll method generates a random roll and retur ...
Malegos, Al-Mutairi, Hester - cse.sc.edu
... and XML to make interoperability a reality. • It is not necessary for C# to use this environment but C# was especially design for this environment. ...
... and XML to make interoperability a reality. • It is not necessary for C# to use this environment but C# was especially design for this environment. ...
Employing the LiCAS analysis framework for MONALISA
... the benefits of OO code but: – you have to do all the "heavy lifting" (an OO compiler will do much of that for you) – the users of linear code can get round your design and inadvertently miss the benefits of your design • (C++ "dodgy" OO language for this reason) ...
... the benefits of OO code but: – you have to do all the "heavy lifting" (an OO compiler will do much of that for you) – the users of linear code can get round your design and inadvertently miss the benefits of your design • (C++ "dodgy" OO language for this reason) ...
SelfExploratorium - Department of Computer Science
... This proposal for the future starts by trying to recover the best from the past, particularly the seemingly forgotten ideas of another visionary, Doug Engelbart. ...
... This proposal for the future starts by trying to recover the best from the past, particularly the seemingly forgotten ideas of another visionary, Doug Engelbart. ...
Java Programming 2 – Lecture #16 –
... Storing Objects in Files Java serialization4 is the process of writing Java objects as binary data, e.g. for transmission over a network socket or for saving to a file. Objects that can be serial ...
... Storing Objects in Files Java serialization4 is the process of writing Java objects as binary data, e.g. for transmission over a network socket or for saving to a file. Objects that can be serial ...