learning outcomes - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... list organisms that are hosts to viruses state the size range of virions identify the parts of a virion and describe their function distinguish enveloped from noneveloped viruses describe the types of capsid symmetry describe the five steps common to the life cycles of all viruses discuss the roles ...
... list organisms that are hosts to viruses state the size range of virions identify the parts of a virion and describe their function distinguish enveloped from noneveloped viruses describe the types of capsid symmetry describe the five steps common to the life cycles of all viruses discuss the roles ...
the magnitude of the impact - Science Speaks: HIV & TB News
... 1. Life saving benefits of ART in HIV disease are ...
... 1. Life saving benefits of ART in HIV disease are ...
Directions for this Template
... • Positivity rate among tested contacts: 40.8% • Average number of unique contacts per case: 8 (range: 0-80) • HCV co-infection: 167/181 (92%) ...
... • Positivity rate among tested contacts: 40.8% • Average number of unique contacts per case: 8 (range: 0-80) • HCV co-infection: 167/181 (92%) ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... that causes HIV infection and is transmitted from one person to another by blood, semen, vaginal secretions and breast milk. HIV attacks the immune system and cause AIDS. The infected person can be without symptoms or illness for 10-20 years and feel well. However, presence of the infection can be d ...
... that causes HIV infection and is transmitted from one person to another by blood, semen, vaginal secretions and breast milk. HIV attacks the immune system and cause AIDS. The infected person can be without symptoms or illness for 10-20 years and feel well. However, presence of the infection can be d ...
HIV Antibody Testing - San Diego State University
... There are NUMEROUS TREATMENT OPTIONS AVAILABLE for someone who tests positive for HIV, and the sooner someone with HIV is evaluated the better. It's recommended that HIV-infected individuals SEEK EVALUATION PROMPTLY with an HIV infectious disease specialist, get tested for other sexually transmitted ...
... There are NUMEROUS TREATMENT OPTIONS AVAILABLE for someone who tests positive for HIV, and the sooner someone with HIV is evaluated the better. It's recommended that HIV-infected individuals SEEK EVALUATION PROMPTLY with an HIV infectious disease specialist, get tested for other sexually transmitted ...
Document
... Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in HIV population in Zambia is not known Knowledge of the local burden will help in policy and planning purposes Knowledge of the local correlates will alert physicians to identify susceptible individuals who may require further ...
... Prevalence of psychiatric disorders in HIV population in Zambia is not known Knowledge of the local burden will help in policy and planning purposes Knowledge of the local correlates will alert physicians to identify susceptible individuals who may require further ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... • Transmitted by blood, breast feeding, sexually, and other bodily fluids • Can happen to anyone! ...
... • Transmitted by blood, breast feeding, sexually, and other bodily fluids • Can happen to anyone! ...
Created with Sketch. Fighting infection card game
... vial such as a medicine pottle (the protein coat). Viruses are able to enter living cells (pop the ‘virus’ into a plastic bag ‘cell’) and take over the cell machinery to replicate the DNA or RNA and make more protein coats, in order to increase in number. They then either burst out of the infected c ...
... vial such as a medicine pottle (the protein coat). Viruses are able to enter living cells (pop the ‘virus’ into a plastic bag ‘cell’) and take over the cell machinery to replicate the DNA or RNA and make more protein coats, in order to increase in number. They then either burst out of the infected c ...
HIV Infection and AIDS: An Overview
... not reach noticeable levels in the blood for 1 to 3 months after infection. It may take the antibodies as long as 6 months to be produced in quantities large enough to show up in standard blood tests. Hence, to determine whether a person has been recently infected (acute infection), a healthcare pro ...
... not reach noticeable levels in the blood for 1 to 3 months after infection. It may take the antibodies as long as 6 months to be produced in quantities large enough to show up in standard blood tests. Hence, to determine whether a person has been recently infected (acute infection), a healthcare pro ...
Slapped Cheek Syndrome
... In pregnant women, like some other infections, this virus may affect the unborn child. Most women are immune to this virus but it is best to be safe, therefore if you are pregnant try and avoid contact with people who have Slapped Cheek. If you think you may have been in contact with Slapped Cheek p ...
... In pregnant women, like some other infections, this virus may affect the unborn child. Most women are immune to this virus but it is best to be safe, therefore if you are pregnant try and avoid contact with people who have Slapped Cheek. If you think you may have been in contact with Slapped Cheek p ...
WELCOME [www.msasc.org]
... WHAT IS HIV/AIDS? HIV=VIRUS THAT CAUSES AIDS Human ImmunodeficiencyVirus that Destroys T Cells, which are necessary for Healthy Immune System. INCUBATION PERIOD: Conversion to HIV positive within 25 Days to 3 months. Rarely Longer Than 6 months Can be HIV POSITIVE but not have developed AIDS ...
... WHAT IS HIV/AIDS? HIV=VIRUS THAT CAUSES AIDS Human ImmunodeficiencyVirus that Destroys T Cells, which are necessary for Healthy Immune System. INCUBATION PERIOD: Conversion to HIV positive within 25 Days to 3 months. Rarely Longer Than 6 months Can be HIV POSITIVE but not have developed AIDS ...
May Phylogenetic Analysis Support Epidemiological Investigation in
... Viral Molecular Evolution Viruses normally lives in an environment ( host) in continue evolution ...
... Viral Molecular Evolution Viruses normally lives in an environment ( host) in continue evolution ...
Viruses and Bacteria - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... • Transmitted by blood, breast feeding, sexually, and other bodily fluids • Can happen to anyone! ...
... • Transmitted by blood, breast feeding, sexually, and other bodily fluids • Can happen to anyone! ...
research abstract form
... Tufts-New England Medical Center Infectious Disease clinic or from prison medical centers in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts2. The mean plasma RNA was 66,720 copies/mL; mean CD4 cell count was 612 cells/mm3. A 1.4 KB fragment of gag-pol was amplified using RT-PCR (35 cycle) and nested PCR (25 cycl ...
... Tufts-New England Medical Center Infectious Disease clinic or from prison medical centers in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts2. The mean plasma RNA was 66,720 copies/mL; mean CD4 cell count was 612 cells/mm3. A 1.4 KB fragment of gag-pol was amplified using RT-PCR (35 cycle) and nested PCR (25 cycl ...
Biology\Viruses, Bacteria, & Infectious Diseases
... 2) The RNA may be transcribed in reverse using reverse transcriptase to make DNA. The DNA makes new RNA which then directs viral protein synthesis. This type of virus is called a retrovirus. (Ex: AIDS virus) ...
... 2) The RNA may be transcribed in reverse using reverse transcriptase to make DNA. The DNA makes new RNA which then directs viral protein synthesis. This type of virus is called a retrovirus. (Ex: AIDS virus) ...
Teacher Preparation Notes for Some Similarities between the
... Important defenses include barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes, chemicals such as acid in the stomach, inflammation and phagocytic cells. The specific immune system also contributes to defenses against infection, but more slowly, as discussed in 5 below. (Any good biology text will provid ...
... Important defenses include barriers such as the skin and mucous membranes, chemicals such as acid in the stomach, inflammation and phagocytic cells. The specific immune system also contributes to defenses against infection, but more slowly, as discussed in 5 below. (Any good biology text will provid ...
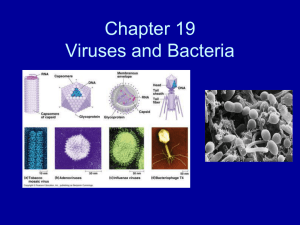
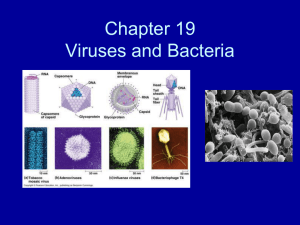
VIRUS
... HN/H/G glycoprotein SPIKES F glycoprotein SPIKES helical nucleocapsid (RNA minus NP protein) ...
... HN/H/G glycoprotein SPIKES F glycoprotein SPIKES helical nucleocapsid (RNA minus NP protein) ...
Key Concepts - Web.UVic.ca
... HIV is spreading at twice the predicted rate Limiting exposure to STIs is complex Many social responses to HIV increase stigma Fear of stigma is problematic because many: ...
... HIV is spreading at twice the predicted rate Limiting exposure to STIs is complex Many social responses to HIV increase stigma Fear of stigma is problematic because many: ...
Communicable diseases - PGGCG
... that 8,500 persons will become infected with HIV each day while an estimated 4,000 persons will die from HIV /AIDS related deaths each day. ...
... that 8,500 persons will become infected with HIV each day while an estimated 4,000 persons will die from HIV /AIDS related deaths each day. ...
CH 18 Viruses and Bacteria Study Guide
... 2. Why is a virus considered a nonliving parasite? 1) Cannot grow, develop or move 2) cannot reproduce on their own. 3. What was the first virus to be discovered? Tobacco Mosaic 4. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus 5. Know the difference between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles. Lytic: ...
... 2. Why is a virus considered a nonliving parasite? 1) Cannot grow, develop or move 2) cannot reproduce on their own. 3. What was the first virus to be discovered? Tobacco Mosaic 4. What does HIV stand for? Human Immunodeficiency Virus 5. Know the difference between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles. Lytic: ...
EXISTING
... virus. Orthomyxoviridae: Swine, Equine, Avian Influenza Viruses. Coronaviridae: Infectious Bronchitis virus, Transmissible gastroenteritis virus; Arterivirdae: Equine viral arteritis virus, Picornaviridae: FMD virus, Duck viral hepatitis virus; Caliciviridae: Feline calici Virus, Togaviridae: Equine ...
... virus. Orthomyxoviridae: Swine, Equine, Avian Influenza Viruses. Coronaviridae: Infectious Bronchitis virus, Transmissible gastroenteritis virus; Arterivirdae: Equine viral arteritis virus, Picornaviridae: FMD virus, Duck viral hepatitis virus; Caliciviridae: Feline calici Virus, Togaviridae: Equine ...
HIV Infection and the Central Nervous System: A Primer
... adherence to cART often achieve reduction of the viral load to undetectable levels, curbing the destruction of CD4+ T lymphocytes (Gulick et al. 1997), but not eradicating the virus which reemerges in nearly all patients when cART is stopped. As these lymphocytes repopulate their numbers, the immune ...
... adherence to cART often achieve reduction of the viral load to undetectable levels, curbing the destruction of CD4+ T lymphocytes (Gulick et al. 1997), but not eradicating the virus which reemerges in nearly all patients when cART is stopped. As these lymphocytes repopulate their numbers, the immune ...
18.1 Studying Viruses and Prokaryotes
... – can infect many organisms – 50 – 200 nm • Viroid: Infectious particle that is made only of single-stranded RNA. – causes disease in plants – passed through seeds or pollen ...
... – can infect many organisms – 50 – 200 nm • Viroid: Infectious particle that is made only of single-stranded RNA. – causes disease in plants – passed through seeds or pollen ...
HIV

The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a lentivirus (a subgroup of retrovirus) that causes HIV infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). AIDS is a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype. Infection with HIV occurs by the transfer of blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate, or breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells.HIV infects vital cells in the human immune system such as helper T cells (specifically CD4+ T cells), macrophages, and dendritic cells. HIV infection leads to low levels of CD4+ T cells through a number of mechanisms, including apoptosis of uninfected bystander cells, direct viral killing of infected cells, and killing of infected CD4+ T cells by CD8 cytotoxic lymphocytes that recognize infected cells. When CD4+ T cell numbers decline below a critical level, cell-mediated immunity is lost, and the body becomes progressively more susceptible to opportunistic infections.










![WELCOME [www.msasc.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008487945_1-9b8077c1ce9315c5f485a9d3d20d15f6-300x300.png)