Conjugation B. Binary Fission C. Transformation D. Mitotic Cell
... In the Mitotic Cell Cycle, A. Four daughter cells are produced B. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell did. C. only cells in sex organs are involved. D. The mother cells remain. E. Each daughter cell has the same amount of cytoplasm as did the mother cell. ...
... In the Mitotic Cell Cycle, A. Four daughter cells are produced B. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes as the mother cell did. C. only cells in sex organs are involved. D. The mother cells remain. E. Each daughter cell has the same amount of cytoplasm as did the mother cell. ...
eukaryote - UniMAP Portal
... intricate complex of membranous organelles and vesicles that move materials into the cell from outside, from inside to outside, and within the cell ...
... intricate complex of membranous organelles and vesicles that move materials into the cell from outside, from inside to outside, and within the cell ...
Intro to Cells and Cell Parts
... up and you can move your mouse all around to see all the parts and then click on the word below to find out their meanings. Answer all questions below as you explore an animal cell 6) Repeat step 4 but with plant cell. Write it down in your SCIENCE JOURNAL! *You only have to know(memorize) the cell ...
... up and you can move your mouse all around to see all the parts and then click on the word below to find out their meanings. Answer all questions below as you explore an animal cell 6) Repeat step 4 but with plant cell. Write it down in your SCIENCE JOURNAL! *You only have to know(memorize) the cell ...
Cells Alive! Webquest Handout
... up and you can move your mouse all around to see all the parts and then click on the word below to find out their meanings. Answer all questions below as you explore an animal cell 6) Repeat step 4 but with plant cell. Write it down in your SCIENCE JOURNAL! *You only have to know(memorize) the cell ...
... up and you can move your mouse all around to see all the parts and then click on the word below to find out their meanings. Answer all questions below as you explore an animal cell 6) Repeat step 4 but with plant cell. Write it down in your SCIENCE JOURNAL! *You only have to know(memorize) the cell ...
Cell Organelles
... 7. ___________ uses oxygen during aerobic respiration to produce high amounts of ATP 8. ___________ Control center of cell – stores DNA 9. ___________ Captures light energy during photosynthesis 10. ___________ used during cellular respiration to release ATP 11. ___________ only found in plant cell ...
... 7. ___________ uses oxygen during aerobic respiration to produce high amounts of ATP 8. ___________ Control center of cell – stores DNA 9. ___________ Captures light energy during photosynthesis 10. ___________ used during cellular respiration to release ATP 11. ___________ only found in plant cell ...
A plant cell consists of many organelles. Each one of them plays its
... fruits and vegetables are orange or red when they ripen. Vacuole- every plant cell has only one large vacuole. It helps in plant growth. The vacuole also plays a very important structure for the plant. Chloroplasts- the chloroplast allows the important process of photosynthesis to occur. This is whe ...
... fruits and vegetables are orange or red when they ripen. Vacuole- every plant cell has only one large vacuole. It helps in plant growth. The vacuole also plays a very important structure for the plant. Chloroplasts- the chloroplast allows the important process of photosynthesis to occur. This is whe ...
File - mrsolson.com
... The plasma membrane, a feature of all cells, is appropriately called the gatekeeper of the cell because it maintains the identity and integrity of the cells as it “stands guard” over what enters and leaves. The fluid mosaic model combines phospholipids and proteins to form a flexible, asymmetric ...
... The plasma membrane, a feature of all cells, is appropriately called the gatekeeper of the cell because it maintains the identity and integrity of the cells as it “stands guard” over what enters and leaves. The fluid mosaic model combines phospholipids and proteins to form a flexible, asymmetric ...
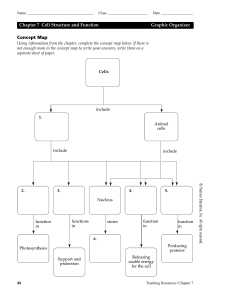
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
The Cell Cycle
... • chromatids – sister chromatids: each chromosome consists of 2 identical sister chromatids. (separated during cell division) • centromere – spot where each pair of chromatids is attached (protein disk) • entering cell division in humans = 46 chromosomes each with sister chromatids. ...
... • chromatids – sister chromatids: each chromosome consists of 2 identical sister chromatids. (separated during cell division) • centromere – spot where each pair of chromatids is attached (protein disk) • entering cell division in humans = 46 chromosomes each with sister chromatids. ...
Cytology 20 Questions - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 10) A bacterial cell's DNA is found in its A) nucleoid region. C) ribosomes. ...
... 10) A bacterial cell's DNA is found in its A) nucleoid region. C) ribosomes. ...
LAB-Plastids - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. Using a toothpick, scrape a few cells off the potato and smear it on the slide, Add 1 drop of water then place the cover slip over the top. 2. Using the high power objective, make a detailed drawing of the cells in the field of view. 3. Add 1 drop of iodine to the edge of the cover slip and draw ...
... 1. Using a toothpick, scrape a few cells off the potato and smear it on the slide, Add 1 drop of water then place the cover slip over the top. 2. Using the high power objective, make a detailed drawing of the cells in the field of view. 3. Add 1 drop of iodine to the edge of the cover slip and draw ...
1. Organelle: A structure within a cell. 2. Chromosome: A threadlike
... 2. Down the concentration gradient 3. The higher the temperature the quicker the molecules move so the faster the rate of diffusion ...
... 2. Down the concentration gradient 3. The higher the temperature the quicker the molecules move so the faster the rate of diffusion ...
The cell wall
... What is photosynthesis? The process by which light energy and CO2 and water produce O2 and energy What is cellular respiration? The process by which O2 and sugar produce CO2, H2O and energy How are the two processes related? Plants use our CO2 and we use their O2 What is diffusion? When something go ...
... What is photosynthesis? The process by which light energy and CO2 and water produce O2 and energy What is cellular respiration? The process by which O2 and sugar produce CO2, H2O and energy How are the two processes related? Plants use our CO2 and we use their O2 What is diffusion? When something go ...
Chapter 5 Section 2
... – In animal cells, the membrane pinches together to separate the cytoplasm. In plant cells, a cell plate forms and divides the cell, along which the cell membrane and cell wall re-form. ...
... – In animal cells, the membrane pinches together to separate the cytoplasm. In plant cells, a cell plate forms and divides the cell, along which the cell membrane and cell wall re-form. ...
Passive Transport
... The movement of small particles into an area where they are more concentrated using membrane proteins ...
... The movement of small particles into an area where they are more concentrated using membrane proteins ...
THROUGH THE CELL MEMBRANE!!!
... The cell membrane is said to be SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE. What does this mean?? - it means that the cell membrane only allows certain substances to pass in or out of the cell. - It “selects” what can enter and leave the cell. ...
... The cell membrane is said to be SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE. What does this mean?? - it means that the cell membrane only allows certain substances to pass in or out of the cell. - It “selects” what can enter and leave the cell. ...
Document
... begins growing. A typical human cell has about 2 meters of DNA. Before the cell can divide, all of this DNA must be copied and then the two copies separated so that each daughter cell ends up with a complete set of DNA. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus; hu ...
... begins growing. A typical human cell has about 2 meters of DNA. Before the cell can divide, all of this DNA must be copied and then the two copies separated so that each daughter cell ends up with a complete set of DNA. Each species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in each cell nucleus; hu ...
Mitochondrion
... Passive Transport-materials do not need energy to move from higher concentration to lower to a lower concentration Active Transport-materials need energy to move from a higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis-water moving from higher concentration to a lower concentration ...
... Passive Transport-materials do not need energy to move from higher concentration to lower to a lower concentration Active Transport-materials need energy to move from a higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis-water moving from higher concentration to a lower concentration ...
Ch. 3: “Cell Structure” Section 3: “Cell Organelles” Describe the role
... • Ribosomes are partially assembled in a region of the nucleus called the nucleolus. Ribosomes and the Endoplasmic Reticulum • Ribosomes are the cellular structures on which proteins are made. • The Endoplasmic Reticulum or ER is an extensive system of internal membranes that move proteins and other ...
... • Ribosomes are partially assembled in a region of the nucleus called the nucleolus. Ribosomes and the Endoplasmic Reticulum • Ribosomes are the cellular structures on which proteins are made. • The Endoplasmic Reticulum or ER is an extensive system of internal membranes that move proteins and other ...
5.2 St.1e Flashcard List
... the third (last) stage of the cell cycle; the cytoplasm and organelles are divided into two new cells along with the two new nuclei; cytokinesis results in two identical new daughter cells identical to the original parent cell. As soon as cytokinesis ends, each new daughter cell goes immediately int ...
... the third (last) stage of the cell cycle; the cytoplasm and organelles are divided into two new cells along with the two new nuclei; cytokinesis results in two identical new daughter cells identical to the original parent cell. As soon as cytokinesis ends, each new daughter cell goes immediately int ...
Life Science
... animal cells. These include the cell wall, a very large vacuole, and chloroplasts. You will notice these structures immediately when you look at plant cells under the microscope. Cell walls help a plant cell maintain its shape. The walls also help the plant keep its structure consistent. If the wind ...
... animal cells. These include the cell wall, a very large vacuole, and chloroplasts. You will notice these structures immediately when you look at plant cells under the microscope. Cell walls help a plant cell maintain its shape. The walls also help the plant keep its structure consistent. If the wind ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.