Basic Cellular Review Powerpoint
... • Normally many on each cell • One tenth to one twentieth size of cilia • Do not move ...
... • Normally many on each cell • One tenth to one twentieth size of cilia • Do not move ...
Homeostasis Keystone Questions of the Day Key
... 6. When dry environmental conditions exist, guard cells close the openings in leaves to reduce the loss of water from the plant. This process is an example of a feedback mechanism that plants use in order to A. maintain homeostasis. B. expend their resources. C. produce more chlorophyll. D. absorb ...
... 6. When dry environmental conditions exist, guard cells close the openings in leaves to reduce the loss of water from the plant. This process is an example of a feedback mechanism that plants use in order to A. maintain homeostasis. B. expend their resources. C. produce more chlorophyll. D. absorb ...
Suggested time: 45 minutes Summary of Key Learning
... Why do the cells need to get bigger before dividing? (Answer = because otherwise the cells would get smaller and smaller with each division) Why does the DNA need to copy itself during S phase? (Answer = because each daughter cell must contain the same genetic information as the parent cell) What is ...
... Why do the cells need to get bigger before dividing? (Answer = because otherwise the cells would get smaller and smaller with each division) Why does the DNA need to copy itself during S phase? (Answer = because each daughter cell must contain the same genetic information as the parent cell) What is ...
Plant Cells
... ● The reaction gets its energy from past reactions stored in the cell. 8. What would happen to the plant without. ● The plant would die from infection and bad bacteria without cell guards. ...
... ● The reaction gets its energy from past reactions stored in the cell. 8. What would happen to the plant without. ● The plant would die from infection and bad bacteria without cell guards. ...
Section 3.5 Introduction
... can then be used to drive other pumps to transport molecules such as sucrose. Some molecules are too large to be transported through proteins. These molecules can be moved in vesicles, so they never actually have to cross the membrane. The movement of these vesicles also requires energy from a cell. ...
... can then be used to drive other pumps to transport molecules such as sucrose. Some molecules are too large to be transported through proteins. These molecules can be moved in vesicles, so they never actually have to cross the membrane. The movement of these vesicles also requires energy from a cell. ...
Passive transport Movement w/o input of energy. Active transport
... Binding sites for Na+ and ATP on its intracellular surface Binding sites for K+ on its extracellular surface ...
... Binding sites for Na+ and ATP on its intracellular surface Binding sites for K+ on its extracellular surface ...
The Cell
... Rough ER: has ribosomes on its surface; proteins are made directly into ER where they can then be modified. Smooth ER: Lipids are produced (steroids, phospholipids) ...
... Rough ER: has ribosomes on its surface; proteins are made directly into ER where they can then be modified. Smooth ER: Lipids are produced (steroids, phospholipids) ...
Final Review Questions
... • What are the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Sample Question: Which of the following statements is not part of the cell theory? A. All living things are composed of cells. B. Cells are the smallest units that retain the properties of life. C. All cells have an outermost ...
... • What are the major differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Sample Question: Which of the following statements is not part of the cell theory? A. All living things are composed of cells. B. Cells are the smallest units that retain the properties of life. C. All cells have an outermost ...
Functions
... e.g. cilia of parameucium and flagellum of bacteria 2 To move materials within an organism, e.g. cilia within the respiratory tract, oviduct ...
... e.g. cilia of parameucium and flagellum of bacteria 2 To move materials within an organism, e.g. cilia within the respiratory tract, oviduct ...
Cell powerpoint
... The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. The Nucleus is the control center of the cell The DNA regulates the function of the cell ...
... The nucleus is the most obvious organelle in any eukaryotic cell. The Nucleus is the control center of the cell The DNA regulates the function of the cell ...
Welcome to Mrs. Thompson`s 5th Grade Class
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. They are only found in plant cells. Chloroplasts are GREEN. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. ...
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. They are only found in plant cells. Chloroplasts are GREEN. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. ...
Cell Theory Lab-honors-bio
... Honors Biology INTRODUCTION: Cells are the basic unit of life because they are the simplest structure that displays all the characteristics of life. Five different scientists’ work led to a very important Cell Theory. You will examine various samples of cells that were important to the contribution ...
... Honors Biology INTRODUCTION: Cells are the basic unit of life because they are the simplest structure that displays all the characteristics of life. Five different scientists’ work led to a very important Cell Theory. You will examine various samples of cells that were important to the contribution ...
Slide ()
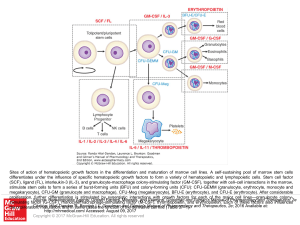
... (SCF), ligand (FL), interleukin-3 (IL-3), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), together with cell–cell interactions in the marrow, stimulate stem cells to form a series of burst-forming units (BFU) and colony-forming units (CFU): CFU-GEMM (granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte ...
... (SCF), ligand (FL), interleukin-3 (IL-3), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), together with cell–cell interactions in the marrow, stimulate stem cells to form a series of burst-forming units (BFU) and colony-forming units (CFU): CFU-GEMM (granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte ...
A Cell is like a Factory
... • The factory floor. The floor of the factory has all the workers, machines, equipment on it • Cytoplasm holds all of the organelles (cell parts) in the plant and animal cells ...
... • The factory floor. The floor of the factory has all the workers, machines, equipment on it • Cytoplasm holds all of the organelles (cell parts) in the plant and animal cells ...
Comparing Plants and animal cells
... It also helps to control water movement inside and between cells. Leaf cells also contain small, round, green organelles called chloroplasts. These contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs energy from the Sun and helps the plant make glucose. ...
... It also helps to control water movement inside and between cells. Leaf cells also contain small, round, green organelles called chloroplasts. These contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs energy from the Sun and helps the plant make glucose. ...
Beats rhythmically to move fluids across cell surface
... Cells are the building blocks of all plants and animals Cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells Cells are the smallest units that perform all vital physiological functions Each cell maintains homeostasis at the cellular level ...
... Cells are the building blocks of all plants and animals Cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells Cells are the smallest units that perform all vital physiological functions Each cell maintains homeostasis at the cellular level ...
R 3.3
... The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the inside of a cell from the outside environment. It plays an active role by controlling the passage of materials into and out of a cell and by responding to signals. The membrane is made of molecules called phospholipids, which consist of three par ...
... The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the inside of a cell from the outside environment. It plays an active role by controlling the passage of materials into and out of a cell and by responding to signals. The membrane is made of molecules called phospholipids, which consist of three par ...
Name
... 8. If a cell has 48 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after mitosis occurs? _____________________________ 9. If a cell has 48 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each cell have after meiosis? _____________________________ 10. The phase of mitosis that is characterized ...
... 8. If a cell has 48 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each daughter cell have after mitosis occurs? _____________________________ 9. If a cell has 48 chromosomes, how many chromosomes will each cell have after meiosis? _____________________________ 10. The phase of mitosis that is characterized ...
The eucaryotic cell
... any other way. One important landmark along this evolutionary road occurred about 1.5 billion years ago, when there was a transition from small cells with relatively simple internal structures - the so-called procaryotic cells, which include the various types of bacteria - to a flourishing of larger ...
... any other way. One important landmark along this evolutionary road occurred about 1.5 billion years ago, when there was a transition from small cells with relatively simple internal structures - the so-called procaryotic cells, which include the various types of bacteria - to a flourishing of larger ...
CHAPTER 7 HOMEOSTASIS AND TRANSPORT Worksheet 1. A
... 33. When water enters the cell, it creates pressure. This pressure is called _____________________________ _______________________________________________. 34. A cell does not expend __________________________ when diffusion takes place. 35. __________________________ is the most common solvent in c ...
... 33. When water enters the cell, it creates pressure. This pressure is called _____________________________ _______________________________________________. 34. A cell does not expend __________________________ when diffusion takes place. 35. __________________________ is the most common solvent in c ...
Cell Division
... checks if chromosomes are lined up in middle of cell. Mutated p53 is most frequent cause of ...
... checks if chromosomes are lined up in middle of cell. Mutated p53 is most frequent cause of ...
Lazar Life Lab- Roles in the Garden Name After working in the
... necessary for cells to operate successfully? A cell is the smallest unit of _life_. Your body is made up of trillions of cells with each one working hard to produce _proteins_. These proteins are used as building blocks for many different things. For example, your ___hair___ and ____skin____ a ...
... necessary for cells to operate successfully? A cell is the smallest unit of _life_. Your body is made up of trillions of cells with each one working hard to produce _proteins_. These proteins are used as building blocks for many different things. For example, your ___hair___ and ____skin____ a ...
The Cell Cycle Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis
... • Growth Phase 2 (G2): During this phase, the cell makes final preparations to divide. For example, it makes additional proteins and organelles. ...
... • Growth Phase 2 (G2): During this phase, the cell makes final preparations to divide. For example, it makes additional proteins and organelles. ...
PPT
... Everything inside the cell except the nucleus Includes all the intracellular structures or organelles that do the work of the cell. Highly compartmentalized by a membranous structure called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ribosomes on the ER synthesize proteins from genetic information ...
... Everything inside the cell except the nucleus Includes all the intracellular structures or organelles that do the work of the cell. Highly compartmentalized by a membranous structure called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ribosomes on the ER synthesize proteins from genetic information ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.