Molecular mechanisms in cell biology
... malformations during embryonic development. In addition, pathogens like bacteria and viruses affect cell homeostasis often resulting in cell degeneration and cell death. The understanding of molecular mechanisms of the “normal life cycle” of a cell is a prerequisite to understand aberrations, which ...
... malformations during embryonic development. In addition, pathogens like bacteria and viruses affect cell homeostasis often resulting in cell degeneration and cell death. The understanding of molecular mechanisms of the “normal life cycle” of a cell is a prerequisite to understand aberrations, which ...
Arabidopsis Formin AtFH6 Is a Plasma Membrane
... et al., 1997). The FH2 domain of BNI1p was recently shown to nucleate actin filaments and to associate with the barbed end of growing actin filaments (Pruyne et al., 2002; Sagot et al., 2002b). Although FH proteins are required for organization of the actin cytoskeleton, some formins also have been ...
... et al., 1997). The FH2 domain of BNI1p was recently shown to nucleate actin filaments and to associate with the barbed end of growing actin filaments (Pruyne et al., 2002; Sagot et al., 2002b). Although FH proteins are required for organization of the actin cytoskeleton, some formins also have been ...
S3R Shunt Regulation Module
... N cells are continuous off and provide full section current to the bus ...
... N cells are continuous off and provide full section current to the bus ...
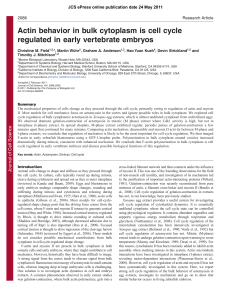
Actin behavior in bulk cytoplasm is cell cycle regulated in early
... seem to grow in thickness (black chevrons). At the last time-points the entire gel undergoes rapid coordinated inward movement (white chevrons). The gel moves very fast once contraction starts and also tended to change in focal plane at this time point, which made it difficult to follow individual b ...
... seem to grow in thickness (black chevrons). At the last time-points the entire gel undergoes rapid coordinated inward movement (white chevrons). The gel moves very fast once contraction starts and also tended to change in focal plane at this time point, which made it difficult to follow individual b ...
FREE Sample Here
... c. anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis ANS: a. The same events occur in both, but only in prophase I of meiosis will homologous chromosomes pair and crossing over occur. b. There is essentially no visible difference; only the number of chromosomes present is different. c. In both cases chr ...
... c. anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis ANS: a. The same events occur in both, but only in prophase I of meiosis will homologous chromosomes pair and crossing over occur. b. There is essentially no visible difference; only the number of chromosomes present is different. c. In both cases chr ...
Chapter 2—Cells and Cell Division - College Test bank
... a. prophase of mitosis and prophase I of meiosis b. interphase preceding meiosis I and interphase preceding meiosis II c. anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis ANS: a. The same events occur in both, but only in prophase I of meiosis will homologous chromosomes pair and crossing over occur. b ...
... a. prophase of mitosis and prophase I of meiosis b. interphase preceding meiosis I and interphase preceding meiosis II c. anaphase of mitosis and anaphase I of meiosis ANS: a. The same events occur in both, but only in prophase I of meiosis will homologous chromosomes pair and crossing over occur. b ...
Six Kingdoms PPT 3-22-17
... Originally the two bacteria were grouped together in one kingdom called Monera. Now they are separated into two kingdoms: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria ...
... Originally the two bacteria were grouped together in one kingdom called Monera. Now they are separated into two kingdoms: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria ...
Prokaryotic
... 5 things you observe about these cells. (Example…tell me how they are similar or how they are different) Cell A Cell B ...
... 5 things you observe about these cells. (Example…tell me how they are similar or how they are different) Cell A Cell B ...
Mikrobiologický ústav LF MU a FN u sv. Anny v Brně
... replicated chromosomes and separates them cell wall grows into the cell at a particular spot and forms a septum that ultimately divides the maternal cell into two daughter cells ...
... replicated chromosomes and separates them cell wall grows into the cell at a particular spot and forms a septum that ultimately divides the maternal cell into two daughter cells ...
03_Bacterial_Growth_2014 - IS MU
... replicated chromosomes and separates them cell wall grows into the cell at a particular spot and forms a septum that ultimately divides the maternal cell into two daughter cells ...
... replicated chromosomes and separates them cell wall grows into the cell at a particular spot and forms a septum that ultimately divides the maternal cell into two daughter cells ...
Sci 14_Unit C_
... 1. Describe, in general terms, the exchange of matter by the digestive and circulatory systems, the functional relationship between the two systems and the need for a healthy diet and lifestyle • assess the nutrient components of prepared foods by reading labels, and evaluate a variety of popular di ...
... 1. Describe, in general terms, the exchange of matter by the digestive and circulatory systems, the functional relationship between the two systems and the need for a healthy diet and lifestyle • assess the nutrient components of prepared foods by reading labels, and evaluate a variety of popular di ...
Movement of Substances
... gradient in the uptake of water by plants and its effect on plant and animals tissues ...
... gradient in the uptake of water by plants and its effect on plant and animals tissues ...
plant responses to internal and external signals
... Hager and colleagues found that cells treated with addition IAA increased the number of proton pumps by 80% relative to untreated control cells. They also found that the acidity of the cell wall changed from a pH of 5.5 to one of 4.5. Cosgrove found two classes of cell wall proteins that actively in ...
... Hager and colleagues found that cells treated with addition IAA increased the number of proton pumps by 80% relative to untreated control cells. They also found that the acidity of the cell wall changed from a pH of 5.5 to one of 4.5. Cosgrove found two classes of cell wall proteins that actively in ...
human-heredity-9th-edition-michael-cummings-test-bank
... 1. How many autosomes are present in a human egg? ____________________ ANS: 22 2. ____________________ is a disease that occurs when cells escape from controls that are part of the cell cycle. ANS: cancer 3. What is the chromosomal structure that anchors the spindle fiber to the chromosome? ________ ...
... 1. How many autosomes are present in a human egg? ____________________ ANS: 22 2. ____________________ is a disease that occurs when cells escape from controls that are part of the cell cycle. ANS: cancer 3. What is the chromosomal structure that anchors the spindle fiber to the chromosome? ________ ...
Chapter 39 Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals
... Hager and colleagues found that cells treated with addition IAA increased the number of proton pumps by 80% relative to untreated control cells. They also found that the acidity of the cell wall changed from a pH of 5.5 to one of 4.5. Cosgrove found two classes of cell wall proteins that actively in ...
... Hager and colleagues found that cells treated with addition IAA increased the number of proton pumps by 80% relative to untreated control cells. They also found that the acidity of the cell wall changed from a pH of 5.5 to one of 4.5. Cosgrove found two classes of cell wall proteins that actively in ...
18 – 1 What is the nervous system? Key Terms
... nerves branch many times and extend to all parts of your body. Each of the nerves in your body is made up of nerve cells called neurons. Neurons can be either large or small. Some neurons are among the largest cells in your body. In fact, one neuron in your leg can be as long as 1meter. The job of a ...
... nerves branch many times and extend to all parts of your body. Each of the nerves in your body is made up of nerve cells called neurons. Neurons can be either large or small. Some neurons are among the largest cells in your body. In fact, one neuron in your leg can be as long as 1meter. The job of a ...
Cellular Reproduction
... Mitosis and Cytokinesis • During mitosis the mitotic spindle, a footballshaped structure of microtubules, guides the separation of two sets of daughter chromosomes. • Spindle microtubules grow from structures within the cytoplasm called centrosomes. ...
... Mitosis and Cytokinesis • During mitosis the mitotic spindle, a footballshaped structure of microtubules, guides the separation of two sets of daughter chromosomes. • Spindle microtubules grow from structures within the cytoplasm called centrosomes. ...
PDF
... therapeutics (Lens et al., 2010; Goldenson and Crispino, 2015; Malumbres and Pérez de Castro, 2015). Today, the study of the Aurora family of protein kinases continues to be a highly dynamic and interactive field of research, many of whose aspects will be covered in the articles comprising this Rese ...
... therapeutics (Lens et al., 2010; Goldenson and Crispino, 2015; Malumbres and Pérez de Castro, 2015). Today, the study of the Aurora family of protein kinases continues to be a highly dynamic and interactive field of research, many of whose aspects will be covered in the articles comprising this Rese ...
HW_CH11-Biol1406.doc
... 1. When a cell divides, what must it pass on to its offspring? a. a complete set of genetic instructions (that is, one copy of every gene) b. a complete set of messenger RNA molecules, so that the offspring cells can express every gene c. cytoplasmic components needed for survival, such as ribosomes ...
... 1. When a cell divides, what must it pass on to its offspring? a. a complete set of genetic instructions (that is, one copy of every gene) b. a complete set of messenger RNA molecules, so that the offspring cells can express every gene c. cytoplasmic components needed for survival, such as ribosomes ...
Diffusion and Osmosis
... concentration. Eventually, they are evenly spread throughout the solution. This means the molecules have reached a dynamic equilibrium. The concentration of dye molecules is the same throughout the solution (equilibrium), but the molecules continue to move (dynamic). ...
... concentration. Eventually, they are evenly spread throughout the solution. This means the molecules have reached a dynamic equilibrium. The concentration of dye molecules is the same throughout the solution (equilibrium), but the molecules continue to move (dynamic). ...
DianaPlantSciences creates natural, plant
... original plant. Our research also allows us to select the best plant cells to carry forward in our products, similar to breeding dogs or horses with the best physiological characteristics. The first DianaPlantSciences product, Cocovanol™ is based on the cocoa polyphenols with a variety of known heal ...
... original plant. Our research also allows us to select the best plant cells to carry forward in our products, similar to breeding dogs or horses with the best physiological characteristics. The first DianaPlantSciences product, Cocovanol™ is based on the cocoa polyphenols with a variety of known heal ...
Meiosis/Mitosis Webquest
... many times as necessary to answer questions & summarize the first stage of meiosis. 1. At the start of this example how many chromosomes are in the cell? 2. What happens in the “S” phase to the chromosomes? 3. If a chromosome replicates but remains attached does it count as one or two chromosomes? 4 ...
... many times as necessary to answer questions & summarize the first stage of meiosis. 1. At the start of this example how many chromosomes are in the cell? 2. What happens in the “S” phase to the chromosomes? 3. If a chromosome replicates but remains attached does it count as one or two chromosomes? 4 ...
OBJECTIVES • To explore cell structure and morphology in
... • Distinguish among the three morphological types of bacteria. • Identify cellular structures of a typical plant cell. • Identify cellular structures of a typical animal cell. Understanding the nature of cell structure and function is important to an understanding of organisms. All organisms are com ...
... • Distinguish among the three morphological types of bacteria. • Identify cellular structures of a typical plant cell. • Identify cellular structures of a typical animal cell. Understanding the nature of cell structure and function is important to an understanding of organisms. All organisms are com ...
Hematopoiesis: Stem Cells
... transformation. Unlike normal haematopoiesis, where signalling pathways that have been proposed to regulate self-renewal are tightly regulated (top), during transformation of stem cells, the same mechanisms may be dysregulated to allow uncontrolled self-renewal (middle). Furthermore, if the transfor ...
... transformation. Unlike normal haematopoiesis, where signalling pathways that have been proposed to regulate self-renewal are tightly regulated (top), during transformation of stem cells, the same mechanisms may be dysregulated to allow uncontrolled self-renewal (middle). Furthermore, if the transfor ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.