CHAPTER 11 CELL COMMUNICATION
... For example, neurotransmitter molecules released at a synapse between two neurons bind as ligands to ion channels on the receiving cell, causing the channels to open. Ions flow in and trigger an electrical signal that propagates down the length of the receiving cell. ...
... For example, neurotransmitter molecules released at a synapse between two neurons bind as ligands to ion channels on the receiving cell, causing the channels to open. Ions flow in and trigger an electrical signal that propagates down the length of the receiving cell. ...
Studies on the in vivo and in vitro dynamics of the bacterial MinD
... The cell division in Escherichia coli requires the septal machinery to be precisely placed at the middle of a cell. The dynamic pole-to-pole oscillation of the Min system is critical to the division site placement and consequently prevents the inadequate division which results in the production of u ...
... The cell division in Escherichia coli requires the septal machinery to be precisely placed at the middle of a cell. The dynamic pole-to-pole oscillation of the Min system is critical to the division site placement and consequently prevents the inadequate division which results in the production of u ...
7-3 Cell Boundaries
... • Some Carrier proteins do not extend through the membrane. • They bond and drag molecules through the lipid bilayer and release them on the opposite side. ...
... • Some Carrier proteins do not extend through the membrane. • They bond and drag molecules through the lipid bilayer and release them on the opposite side. ...
The Euglena
... Euglena are unicellular organisms classified into the Kingdom Protist, and the Phylum Euglenophyta. All euglena have chloroplasts and can make their own food by photosynthesis. They are not completely autotrophic though, euglena can also absorb food from their environment; euglenas usually live in q ...
... Euglena are unicellular organisms classified into the Kingdom Protist, and the Phylum Euglenophyta. All euglena have chloroplasts and can make their own food by photosynthesis. They are not completely autotrophic though, euglena can also absorb food from their environment; euglenas usually live in q ...
chromosomes
... • Before a cell divides, it duplicates all of its chromosomes, resulting in two copies called sister chromatids containing identical genes. • Two sister chromatids are joined together tightly at a narrow “waist” called the centromere. • When the cell divides, the sister chromatids of a duplicated ch ...
... • Before a cell divides, it duplicates all of its chromosomes, resulting in two copies called sister chromatids containing identical genes. • Two sister chromatids are joined together tightly at a narrow “waist” called the centromere. • When the cell divides, the sister chromatids of a duplicated ch ...
Lab 2 - Exploring Cell Anatomy and Diversity
... All eukaryotic organisms are composed of cells, whether they exist as single cells, colonies of cells, or in multicellular form. Your body is composed of billions of cells, most of which are very small, with specialized structures that allow for a diversity of functions. All eukaryotic cells have th ...
... All eukaryotic organisms are composed of cells, whether they exist as single cells, colonies of cells, or in multicellular form. Your body is composed of billions of cells, most of which are very small, with specialized structures that allow for a diversity of functions. All eukaryotic cells have th ...
unit-4-notes-cell-membranes
... – Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of high concentration to an area of low concentration. – Diffusion often requires a membrane in living things. – For example, oxygen gas moves outside of the cell to the inside of the cell to be used for cellular respiration. – The mitochondria ...
... – Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of high concentration to an area of low concentration. – Diffusion often requires a membrane in living things. – For example, oxygen gas moves outside of the cell to the inside of the cell to be used for cellular respiration. – The mitochondria ...
A1980KG03400001
... amoebae did not seem to be attractive to leukocytes. The fact that the amoebae of the slime mold Polysphondylium pallidum, which secreted cyclic AMP, did not respond to it, showed its specificity. The results became outright discouraging when the supernatant of D. discoideum amoebae did not attract ...
... amoebae did not seem to be attractive to leukocytes. The fact that the amoebae of the slime mold Polysphondylium pallidum, which secreted cyclic AMP, did not respond to it, showed its specificity. The results became outright discouraging when the supernatant of D. discoideum amoebae did not attract ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... Some of my inventions… (pause) maybe you have heard of some… include the telescope, the early microscope, an early prototype of the respirator for breathing under water; and a balance spring found in watches and clocks. I also invented equations for laws of physics and instruments related to studyin ...
... Some of my inventions… (pause) maybe you have heard of some… include the telescope, the early microscope, an early prototype of the respirator for breathing under water; and a balance spring found in watches and clocks. I also invented equations for laws of physics and instruments related to studyin ...
What are the basic functions of microfilaments? Insights from studies
... Studies in animal cells have provided us with a picture of F-actin as the backbone of many structurally and functionally diverse assemblies coexisting within any given cell. Microfilaments are important for cell shape determination, cell motility, and various contractile activities, as well as for p ...
... Studies in animal cells have provided us with a picture of F-actin as the backbone of many structurally and functionally diverse assemblies coexisting within any given cell. Microfilaments are important for cell shape determination, cell motility, and various contractile activities, as well as for p ...
Protocols for next session
... You should have been given a ‘blank’, i.e. a sealed cuvette with sterile media. Absorbance is always measured relative to the blank. Be sure to measure the absorbance of the blank with every culture measurement! 3. Properly dispose of the sample cuvette, and repeat these steps for the next ~3 hours. ...
... You should have been given a ‘blank’, i.e. a sealed cuvette with sterile media. Absorbance is always measured relative to the blank. Be sure to measure the absorbance of the blank with every culture measurement! 3. Properly dispose of the sample cuvette, and repeat these steps for the next ~3 hours. ...
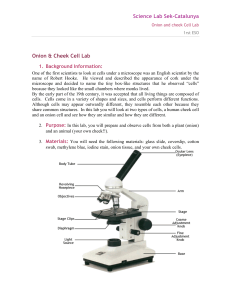
Onion and cheek Cell Lab
... name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living th ...
... name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living th ...
PROTISTS - SharpSchool
... Amoebas are unicellular protists that are able to change their shape constantly because their PSEUDOPODS are constantly changing. Pseudopods also help amoebas to get food by ENGULFING and move towards the light. ...
... Amoebas are unicellular protists that are able to change their shape constantly because their PSEUDOPODS are constantly changing. Pseudopods also help amoebas to get food by ENGULFING and move towards the light. ...
Muscle Contraction and Rigor Mortis KEY
... Normally, in the resting state, these cells build up the electric potential across their membrane by actively pumping out calcium ions. Upon receiving a signal from a neuron, the muscle cells open the calcium channels in their cell membrane, and the calcium ions rush in due to the voltage difference ...
... Normally, in the resting state, these cells build up the electric potential across their membrane by actively pumping out calcium ions. Upon receiving a signal from a neuron, the muscle cells open the calcium channels in their cell membrane, and the calcium ions rush in due to the voltage difference ...
From the Nucleus Toward the Cell Periphery: a Guided
... Cell Biology, Zoological Institute, Technical University of Braunschweig, D-38092 Braunschweig, Germany; and 2Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, New York 10461 ...
... Cell Biology, Zoological Institute, Technical University of Braunschweig, D-38092 Braunschweig, Germany; and 2Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York, New York 10461 ...
Galectin
... Galectin-1 is mitogenic for lymphocytes (Pitts and Yang, 1981), but has a growth-inhibitory activity for some mammalian cells (Wells & Mallucci, 1991) which is apparently independent of their beta-galactoside binding site (Scott & Zhang, 2002). ...
... Galectin-1 is mitogenic for lymphocytes (Pitts and Yang, 1981), but has a growth-inhibitory activity for some mammalian cells (Wells & Mallucci, 1991) which is apparently independent of their beta-galactoside binding site (Scott & Zhang, 2002). ...
Transport Within Cells
... All living things, all plants, animals, and humans, are composed of cells. A cell is the smallest living unit of matter. They are membrane covered structures that contains all of the materials necessary for life. You are composed of cells. Some living organisms are only 1 cell. They are called unice ...
... All living things, all plants, animals, and humans, are composed of cells. A cell is the smallest living unit of matter. They are membrane covered structures that contains all of the materials necessary for life. You are composed of cells. Some living organisms are only 1 cell. They are called unice ...
Chapter 5 Membrane Structure and Function
... movement – A ______ is a substance that can move or change shape in response to external forces – A ____________ is a substance that can be dissolved (dispersed as ions or molecules) in a solvent – A ___________ is a fluid capable of dissolving a solute ...
... movement – A ______ is a substance that can move or change shape in response to external forces – A ____________ is a substance that can be dissolved (dispersed as ions or molecules) in a solvent – A ___________ is a fluid capable of dissolving a solute ...
EMBO Workshop on Cell Size Regulation
... Edda Klipp - Determinants of yeast cell size in individual cells and for a cell population Jan M. Skotheim – On the biosynthetic mechanism coupling cell growth to division at G1/S Naama Barkai - Interplay between protein expression and cell size regulation in budding yeast Short talk – Rafae ...
... Edda Klipp - Determinants of yeast cell size in individual cells and for a cell population Jan M. Skotheim – On the biosynthetic mechanism coupling cell growth to division at G1/S Naama Barkai - Interplay between protein expression and cell size regulation in budding yeast Short talk – Rafae ...
Cells ppt
... Cells contain a network of protein fibers, called the cytoskeleton, which functions in structural support and motility. Scientists believe that motility and cellular regulation result when the cytoskeleton interacts with proteins called motor proteins. ...
... Cells contain a network of protein fibers, called the cytoskeleton, which functions in structural support and motility. Scientists believe that motility and cellular regulation result when the cytoskeleton interacts with proteins called motor proteins. ...
Chapter 4 The Cell
... Cells contain a network of protein fibers, called the cytoskeleton, which functions in structural support and motility. Scientists believe that motility and cellular regulation result when the cytoskeleton interacts with proteins called motor proteins. ...
... Cells contain a network of protein fibers, called the cytoskeleton, which functions in structural support and motility. Scientists believe that motility and cellular regulation result when the cytoskeleton interacts with proteins called motor proteins. ...
slides pdf - Auburn University
... trans face: nearest to the plasma membrane; a fully matured cisterna breaks into many vesicles that are set up to go to the proper destination (such as the plasma membrane or another organelle) taking their contents with them ...
... trans face: nearest to the plasma membrane; a fully matured cisterna breaks into many vesicles that are set up to go to the proper destination (such as the plasma membrane or another organelle) taking their contents with them ...
chapter 3: biological bases of behavior
... Excitatory PSP: a positive voltage shift; increases likelihood that a postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials Inhibitory PSP: neg. voltage shift; decreases likelihood that a postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials ...
... Excitatory PSP: a positive voltage shift; increases likelihood that a postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials Inhibitory PSP: neg. voltage shift; decreases likelihood that a postsynaptic neuron will fire action potentials ...
Cytokinesis

Cytokinesis (cyto- + kinesis) is the process during cell division in which the cytoplasm of a single eukaryotic cell is divided to form two daughter cells. It usually initiates during the early stages of mitosis, and sometimes meiosis, splitting a mitotic cell in two, to ensure that chromosome number is maintained from one generation to the next. After cytokinesis two (daughter) cells will be formed that are exact copies of the (parent) original cell. After cytokinesis, each daughter cell is in the interphase portion of the cell cycle. In animal cells, one notable exception to the normal process of cytokinesis is oogenesis (the creation of an ovum in the ovarian follicle of the ovary), where the ovum takes almost all the cytoplasm and organelles, leaving very little for the resulting polar bodies, which then die. Another form of mitosis without cytokinesis occurs in the liver, yielding multinucleate cells. In plant cells, a dividing structure known as the cell plate forms within the centre of the cytoplasm and a new cell wall forms between the two daughter cells.Cytokinesis is distinguished from the prokaryotic process of binary fission.