11/23
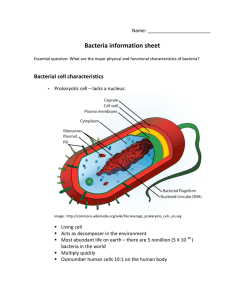
... Gram positive cocci with complex nutritional requirements Parasites of warm-blooded animals Some species are part of the normal microbiota (mouth and vagina) Many species are not thoroughly understood ...
... Gram positive cocci with complex nutritional requirements Parasites of warm-blooded animals Some species are part of the normal microbiota (mouth and vagina) Many species are not thoroughly understood ...
Bacteria
... bacterial DNA as well) 3. Virus breaks out of host cell and invades new bacteria 4. New bacterial host will get old host’s DNA via the ...
... bacterial DNA as well) 3. Virus breaks out of host cell and invades new bacteria 4. New bacterial host will get old host’s DNA via the ...
Micro-organisms and humans - questions
... 1 List the main types of organism included under the heading of 'Micro-organisms' Bacteria 2 Which of the following are not found in bacteria? cytoplasm, cell wall, nuclear membrane, DNA, chromosome, glycogen, cellulose 3 Saprophytic bacteria release ….. A ….. into their surroundings and then absorb ...
... 1 List the main types of organism included under the heading of 'Micro-organisms' Bacteria 2 Which of the following are not found in bacteria? cytoplasm, cell wall, nuclear membrane, DNA, chromosome, glycogen, cellulose 3 Saprophytic bacteria release ….. A ….. into their surroundings and then absorb ...
bacteria - biology3u
... a different cell wall structure than gram – negative bacteria and the stain shows this - Gram positive bacteria are quite common and usually not as pathogenic (cause disease in a host organism) ...
... a different cell wall structure than gram – negative bacteria and the stain shows this - Gram positive bacteria are quite common and usually not as pathogenic (cause disease in a host organism) ...
Unit 4 Review
... Anaerobic bacteria do not require what to grow? ______________________________________. What is meant by normal flora with bacteria? _______________________________________________. Chapter 19 Protists contain what type of cell? _____________________________________________. Protists are classified ...
... Anaerobic bacteria do not require what to grow? ______________________________________. What is meant by normal flora with bacteria? _______________________________________________. Chapter 19 Protists contain what type of cell? _____________________________________________. Protists are classified ...
Abstract Actinobacteria are important members of the soil
... Actinobacteria are important members of the soil ecosystems, where they are involved in organic matter decomposition. It is worth mentioning that their secondary metabolism allows them to produce a variety of different compounds. These compounds include antibiotics, among them aminoglycosides have a ...
... Actinobacteria are important members of the soil ecosystems, where they are involved in organic matter decomposition. It is worth mentioning that their secondary metabolism allows them to produce a variety of different compounds. These compounds include antibiotics, among them aminoglycosides have a ...
Antibiotic resistant bacteria
... microorganisms –chemical warfare to keep foreign microbes out of territory and away from food ...
... microorganisms –chemical warfare to keep foreign microbes out of territory and away from food ...
L6- Problem Solving with Exponential Growth and Decay
... bacteria after t hours. a) What is the doubling time? b) How many bacteria are present after 8 hours? c) How many bacteria are present after 16 hours? ...
... bacteria after t hours. a) What is the doubling time? b) How many bacteria are present after 8 hours? c) How many bacteria are present after 16 hours? ...
Diversity Lab Presentation
... Saprophyte, any organism that derives its nutriment from decaying vegetable or animal matter. Mushrooms, molds, and other types of fungi are the most abundant saprophytes. Certain types of bacteria, some seed plants, and some orchids are also saprophytes. Saprophytes produce enzymes that break down ...
... Saprophyte, any organism that derives its nutriment from decaying vegetable or animal matter. Mushrooms, molds, and other types of fungi are the most abundant saprophytes. Certain types of bacteria, some seed plants, and some orchids are also saprophytes. Saprophytes produce enzymes that break down ...
Where can we find bacteria?
... How can you find bacteria? • You can’t see it, so how do you find it? • Under the right conditions, bacteria grows very fast, exponentially • Some bacteria populations can double every 10 minutes • Bacteria grow in colonies – a colony is a visible mass of bacterial growth on solid medium that devel ...
... How can you find bacteria? • You can’t see it, so how do you find it? • Under the right conditions, bacteria grows very fast, exponentially • Some bacteria populations can double every 10 minutes • Bacteria grow in colonies – a colony is a visible mass of bacterial growth on solid medium that devel ...
Insects and Microbes
... Bacteria are prokaryotes, They have a cell wall. no well-defined nucleus or organelles. Bacterial pathogens are classified according to many factors such as infective dose, site of infection, host range and mode of action. Insect bacterial pathogens includes two main groups Spore formers and non-spo ...
... Bacteria are prokaryotes, They have a cell wall. no well-defined nucleus or organelles. Bacterial pathogens are classified according to many factors such as infective dose, site of infection, host range and mode of action. Insect bacterial pathogens includes two main groups Spore formers and non-spo ...
Bacteria Webquest - Nutley Public Schools
... Please visit the following website: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacterialh.html 12. What are pathogenic bacteria? 13. What do aerobic bacteria require? 14. Where do anaerobic bacteria live and what can they cause? 15. How do facultative anaerobic bacteria differ from the other two? 16. Wha ...
... Please visit the following website: http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacterialh.html 12. What are pathogenic bacteria? 13. What do aerobic bacteria require? 14. Where do anaerobic bacteria live and what can they cause? 15. How do facultative anaerobic bacteria differ from the other two? 16. Wha ...
Nessun titolo diapositiva
... Treatment with highly concentrated mesophilic bacterial aerosol (107UFC/ml) maximun bacterial exposition at the MIPSSZEOMET® = 2107UFC after 20’ aerozolitation at a rate of 0,1 ml/min. resulted in no bacterial leakage/carry over from the filter. This level of exposition far exceeds that normally ...
... Treatment with highly concentrated mesophilic bacterial aerosol (107UFC/ml) maximun bacterial exposition at the MIPSSZEOMET® = 2107UFC after 20’ aerozolitation at a rate of 0,1 ml/min. resulted in no bacterial leakage/carry over from the filter. This level of exposition far exceeds that normally ...
Chapter 28
... 1 µm 1.37 µm Archaea differ greatly from bacteria. Although both are prokaryotes, archaeal cell walls lack peptidoglycan; plasma membranes are made of different kinds of lipids than bacterial plasma membranes; RNA and ribosomal proteins are more like eukaryotes than bacteria. Mostly anaerobic. Examp ...
... 1 µm 1.37 µm Archaea differ greatly from bacteria. Although both are prokaryotes, archaeal cell walls lack peptidoglycan; plasma membranes are made of different kinds of lipids than bacterial plasma membranes; RNA and ribosomal proteins are more like eukaryotes than bacteria. Mostly anaerobic. Examp ...
diplo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate pairing of cells
... diplo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate pairing of cells. strepto - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate filaments. staphylo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate clusters. ...
... diplo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate pairing of cells. strepto - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate filaments. staphylo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate clusters. ...
Ch 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes
... Yogurt, sauerkraut, and buttermilk Digest petroleum and remove human-made waste from water Synthesize drugs and chemicals. ...
... Yogurt, sauerkraut, and buttermilk Digest petroleum and remove human-made waste from water Synthesize drugs and chemicals. ...
Prokaryotes - University of Arizona | Ecology and Evolutionary Biology
... Reconstructing the evolution of living things Systematists study evolutionary relationships • Look for shared derived (=different from ancestor) traits to group organisms • Evidence used: morphology, development, and molecular data (especially DNA sequences) ...
... Reconstructing the evolution of living things Systematists study evolutionary relationships • Look for shared derived (=different from ancestor) traits to group organisms • Evidence used: morphology, development, and molecular data (especially DNA sequences) ...
Screening of some K enyan Medicinal Plants for Antibacterial Activity.
... and Ziziphus abyssinica Hochst for potential antibacterial activity against four medically important bacterial strains, namely: Bacillus cereus ATCC 11778, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Micrococcus lutea ATCC 9341 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. The antibacterial activity of methanol extracts ...
... and Ziziphus abyssinica Hochst for potential antibacterial activity against four medically important bacterial strains, namely: Bacillus cereus ATCC 11778, Escherichia coli ATCC 25922, Micrococcus lutea ATCC 9341 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853. The antibacterial activity of methanol extracts ...