Ecosystems, Populations, Communities Name: Date - Problem
... Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the graph below and on your knowledge of biology. The graph shows the growth of a population of rabbits in a speci c ecosystem. Rabbit Population in a Speci c Ecosystem ...
... Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the graph below and on your knowledge of biology. The graph shows the growth of a population of rabbits in a speci c ecosystem. Rabbit Population in a Speci c Ecosystem ...
Ecological Pyramids - Learn District 196
... Research by modeling examples Using computer models to simulate plant or animal populations to make predictions Variables can be manipulated in a computer model (meteorologists do this all the time) For example: predicting how climate change and or drought may impact large herbivores (deer & moo ...
... Research by modeling examples Using computer models to simulate plant or animal populations to make predictions Variables can be manipulated in a computer model (meteorologists do this all the time) For example: predicting how climate change and or drought may impact large herbivores (deer & moo ...
What is an Ecosystem? An ecosystem includes all the different
... Each species will respond differently to these abiotic factors. The way that they respond determines where they will live. Different species will do well under different conditions. Every organism has an optimum, a level they thrive at. This is called the optimal zone. i.e. a good amount of water, s ...
... Each species will respond differently to these abiotic factors. The way that they respond determines where they will live. Different species will do well under different conditions. Every organism has an optimum, a level they thrive at. This is called the optimal zone. i.e. a good amount of water, s ...
Document
... Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially. Logistically growth occurs when a population’s growth slows and then stops, following a period of exponential growth. Acting separately or together, limiting factors determine the carrying capacity of an environme ...
... Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially. Logistically growth occurs when a population’s growth slows and then stops, following a period of exponential growth. Acting separately or together, limiting factors determine the carrying capacity of an environme ...
Ecology, biosphere, species, population, community, ecosystem
... through the ecosystem. Explain what abiotic and biotic factors are and how they influence our ecosystem. Explain the difference between competitive and cooperative interaction among species. Explain the difference between habitat and niche, competition, predation and the different types of sym ...
... through the ecosystem. Explain what abiotic and biotic factors are and how they influence our ecosystem. Explain the difference between competitive and cooperative interaction among species. Explain the difference between habitat and niche, competition, predation and the different types of sym ...
SE SW 1
... Describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting these cycles (ex. deforestation, grassland conversion) Compare variations and adaptations of organisms in different ecosystems Physiological, anatomical, and behavioral adaptations Biome ...
... Describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting these cycles (ex. deforestation, grassland conversion) Compare variations and adaptations of organisms in different ecosystems Physiological, anatomical, and behavioral adaptations Biome ...
EAT_working_for_water
... Include things like water purification and regulation as well as carbon sequestration. Genetic diversity and organisation also maintains ecosystems economic worth in terms of recreational value, option value, and existence value. ...
... Include things like water purification and regulation as well as carbon sequestration. Genetic diversity and organisation also maintains ecosystems economic worth in terms of recreational value, option value, and existence value. ...
World Biomes - Appoquinimink High School
... environment, humans, plants, animals • Abiotic Factor- non-living parts of an environment, ex- rock, soil, sun • Habitat- an environment that meets an organism’s needs and functions for survival. Several niches make up a habitat. ...
... environment, humans, plants, animals • Abiotic Factor- non-living parts of an environment, ex- rock, soil, sun • Habitat- an environment that meets an organism’s needs and functions for survival. Several niches make up a habitat. ...
Ecology - Owen
... A large tract of forest may make up one ecosystem, while a puddle of water could be another. ...
... A large tract of forest may make up one ecosystem, while a puddle of water could be another. ...
Unit 2 Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology
... Community interacting populations in a certain area at a certain time ...
... Community interacting populations in a certain area at a certain time ...
Ecosystem-based approach to marine management
... regime, along with its objectives, which will operate in those areas. ● A system of monitoring – this being an essential instrument in order to ensure, firstly, that key management decisions are observed by all parties; and secondly, that evidence is gathered to establish how management regimes are ...
... regime, along with its objectives, which will operate in those areas. ● A system of monitoring – this being an essential instrument in order to ensure, firstly, that key management decisions are observed by all parties; and secondly, that evidence is gathered to establish how management regimes are ...
The Sea Grant programs in the New York Bight are facilitating the
... Climate Change on Management Actions in the Coastal Ecosystems of the New York Bight. The coastal ecosystems of the region are closely coupled through their interaction with the waters of the continental shelf. It is well established that these waters originate and are appreciably freshened by A ...
... Climate Change on Management Actions in the Coastal Ecosystems of the New York Bight. The coastal ecosystems of the region are closely coupled through their interaction with the waters of the continental shelf. It is well established that these waters originate and are appreciably freshened by A ...
Marine Ecosystem Services Program
... Marine Ecosystem Services Supporting Coastal Ecosystems and Communities Ecosystem services are produced by healthy, well-functioning environments and provide great benefit to humans worldwide. Such services include provisioning of food and water resources, as well as regulating and supporting funct ...
... Marine Ecosystem Services Supporting Coastal Ecosystems and Communities Ecosystem services are produced by healthy, well-functioning environments and provide great benefit to humans worldwide. Such services include provisioning of food and water resources, as well as regulating and supporting funct ...
8 Ecology
... Describe the energy flow between species within an ecosystem Producers use energy from the sun to make food and therefore start the chain The arrows represent the direction of energy flow, pointing from the organism being consumed to the organism receiving the energy ...
... Describe the energy flow between species within an ecosystem Producers use energy from the sun to make food and therefore start the chain The arrows represent the direction of energy flow, pointing from the organism being consumed to the organism receiving the energy ...
Comparing Ecosystems
... be classified as natural ecosystems. In a natural ecosystem, the living community is free to interact with the physical and chemical environment. However, this does not mean that the area is untouched by humans: humans are a natural part of many ecosystems. Natural ecosystems haven’t been planned or ...
... be classified as natural ecosystems. In a natural ecosystem, the living community is free to interact with the physical and chemical environment. However, this does not mean that the area is untouched by humans: humans are a natural part of many ecosystems. Natural ecosystems haven’t been planned or ...
10 Science
... collapse an entire food chain. Example p.18 - overhunting sea otters on the west coast threaten populations. Since sea otters feed on sea urchins, sea urchin populations thrived. Sea urchins feed on kelp and so the kelp population decreased. But other fish depend on kelp for food and shelter. Result ...
... collapse an entire food chain. Example p.18 - overhunting sea otters on the west coast threaten populations. Since sea otters feed on sea urchins, sea urchin populations thrived. Sea urchins feed on kelp and so the kelp population decreased. But other fish depend on kelp for food and shelter. Result ...
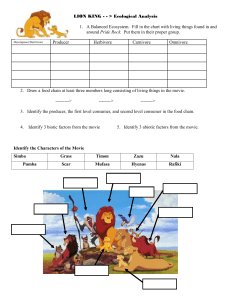
Name
... 16. When Simba falls from exhaustion what animals begin to encircle him? _________ 17. What is the ecological role of the animal in #16. _________________________ 19. When Scar replaces Mufasa the pride's stable ecosystem is replaced by an unstable ecosystem. Describe three ways the movie indicates ...
... 16. When Simba falls from exhaustion what animals begin to encircle him? _________ 17. What is the ecological role of the animal in #16. _________________________ 19. When Scar replaces Mufasa the pride's stable ecosystem is replaced by an unstable ecosystem. Describe three ways the movie indicates ...
6.3.2 populations and sustainability student version
... and reproduction of other organisms. • It is a form of competition because it prevents the plant’s neighbours using the resources in the habitat. • These biochemicals are known as allelochemicals and can have beneficial or detrimental effects on the target organisms and the community. • Allelochemic ...
... and reproduction of other organisms. • It is a form of competition because it prevents the plant’s neighbours using the resources in the habitat. • These biochemicals are known as allelochemicals and can have beneficial or detrimental effects on the target organisms and the community. • Allelochemic ...
Tuning the ecoscope
... in the form of system wide “regime shifts” (Hare & Mantua, 2000). Mesoscale events can trigger huge variability in pelagic fish recruitment success (Roy et al. 2001). In upwelling systems, a small number of pelagic fish species occupy the intermediate trophic level, feeding mostly on phytoplankton a ...
... in the form of system wide “regime shifts” (Hare & Mantua, 2000). Mesoscale events can trigger huge variability in pelagic fish recruitment success (Roy et al. 2001). In upwelling systems, a small number of pelagic fish species occupy the intermediate trophic level, feeding mostly on phytoplankton a ...
Chapters • Lesson 18
... of organisms living on Earth or in an ecosystem. Many human activities can change environmental conditions in ways that alter the biodiversity of an ecosystem. Human actions can greatly affect Earth's biological, physical, and chemical processes. For example, as the human population grows, people us ...
... of organisms living on Earth or in an ecosystem. Many human activities can change environmental conditions in ways that alter the biodiversity of an ecosystem. Human actions can greatly affect Earth's biological, physical, and chemical processes. For example, as the human population grows, people us ...
S R : W
... SIMBIOSYS project addressed impacts of human activity in three key sectors: bioenergy crop cultivation, road landscaping and aquaculture. Impacts of these sectors on genetic, species and landscape biodiversity were assessed. The effect of sectoral activities on the delivery of ecosystem services, in ...
... SIMBIOSYS project addressed impacts of human activity in three key sectors: bioenergy crop cultivation, road landscaping and aquaculture. Impacts of these sectors on genetic, species and landscape biodiversity were assessed. The effect of sectoral activities on the delivery of ecosystem services, in ...
Chapter 4
... new islands or cover the land with lava rock or volcanic ash. – When it begins there is no soil, just ash and rock. – The first species to populate the area are called pioneer species. – The pioneer species on volcanic rock are often lichens. – Lichens are organisms that are formed from the mutualis ...
... new islands or cover the land with lava rock or volcanic ash. – When it begins there is no soil, just ash and rock. – The first species to populate the area are called pioneer species. – The pioneer species on volcanic rock are often lichens. – Lichens are organisms that are formed from the mutualis ...
File ap notes chapter 54
... Availability of water, oxygen, & temperature influence the rate of decomposition & recycling Tropical rain forest recycle rapidly resulting in soil with very little nutrients Soils in temperate deciduous forest may contain 50% of all of the organic materials in the ecosystem Decomposition in tun ...
... Availability of water, oxygen, & temperature influence the rate of decomposition & recycling Tropical rain forest recycle rapidly resulting in soil with very little nutrients Soils in temperate deciduous forest may contain 50% of all of the organic materials in the ecosystem Decomposition in tun ...
Ecosystem Goods and Services
... to a wide range of conditions and processes through which natural ecosystems, and the species that are part of them, help sustain and fulfil human life. These services maintain biodiversity and the production of ecosystem goods, such as seafood, wild game, forage, timber, biomass fuels, natural fibr ...
... to a wide range of conditions and processes through which natural ecosystems, and the species that are part of them, help sustain and fulfil human life. These services maintain biodiversity and the production of ecosystem goods, such as seafood, wild game, forage, timber, biomass fuels, natural fibr ...
Ecosystem services
Humankind benefits in a multitude of ways from ecosystems. Collectively, these benefits are becoming known as ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are regularly involved in the provisioning of clean drinking water and the decomposition of wastes. While scientists and environmentalists have discussed ecosystem services implicitly for decades, the ecosystem services concept itself was popularized by the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) in the early 2000s. This grouped ecosystem services into four broad categories: provisioning, such as the production of food and water; regulating, such as the control of climate and disease; supporting, such as nutrient cycles and crop pollination; and cultural, such as spiritual and recreational benefits. To help inform decision-makers, many ecosystem services are being assigned economic values.