12_LectureOutline_LO - AP
... For many cells, the G1 checkpoint, the “restriction point” in mammalian cells, is the most important. If the cell receives a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, it usually completes the cell cycle and divides. If it does not receive a go-ahead signal, the cell exits the cycle and switches to ...
... For many cells, the G1 checkpoint, the “restriction point” in mammalian cells, is the most important. If the cell receives a go-ahead signal at the G1 checkpoint, it usually completes the cell cycle and divides. If it does not receive a go-ahead signal, the cell exits the cycle and switches to ...
Name Plant Cell Riddles Cell Riddles 1. I am a thin protective layer
... piece. I have tiny openings that allow materials to pass in and out of the cell. (Color me orange) _____________________ 2. I am the “Brain” of the cell, and I control all the activities of the cell. (Color me brown) _____________________ 3. I am the jelly-like fluid inside the cell. I provide an ar ...
... piece. I have tiny openings that allow materials to pass in and out of the cell. (Color me orange) _____________________ 2. I am the “Brain” of the cell, and I control all the activities of the cell. (Color me brown) _____________________ 3. I am the jelly-like fluid inside the cell. I provide an ar ...
Homeostatic Control Systems
... – Cells are composed of specific macromolecules that participate is similar chemical reactions or processes • Functional activities of each cell depend on specific structural properties and protein content of the cell • In cells from all living organisms genes are stored in DNA written in the sa ...
... – Cells are composed of specific macromolecules that participate is similar chemical reactions or processes • Functional activities of each cell depend on specific structural properties and protein content of the cell • In cells from all living organisms genes are stored in DNA written in the sa ...
File - MRS. WILSON Science
... pumps to transport molecules such as sucrose. Some molecules are too large to be transported through proteins. These molecules can be moved in vesicles, so they never actually have to cross the membrane. The movement of these vesicles also requires energy from a cell. • Endocytosis is the process of ...
... pumps to transport molecules such as sucrose. Some molecules are too large to be transported through proteins. These molecules can be moved in vesicles, so they never actually have to cross the membrane. The movement of these vesicles also requires energy from a cell. • Endocytosis is the process of ...
Cells
... • Inside these cells are organelles . • What is an organelle?????? • An organelle is are internal structure within the cell that performs certain functions!! • Each organelle has a special function and each organelle is unique in shape. • Where are they found? In the cytoplasm of the cell ...
... • Inside these cells are organelles . • What is an organelle?????? • An organelle is are internal structure within the cell that performs certain functions!! • Each organelle has a special function and each organelle is unique in shape. • Where are they found? In the cytoplasm of the cell ...
File
... Do not have a ____________ Have a ______________ with or without peptidoglycan Lack membrane bound organelles ________________ are prokaryotic cells ...
... Do not have a ____________ Have a ______________ with or without peptidoglycan Lack membrane bound organelles ________________ are prokaryotic cells ...
Mitotic Cell Division - Jocha
... Mitotic cell division represents then the type of cell division that will produce genetically identical copies of cells, which in a human cell means 2 daughter cells having the same 46 chromosomes that were present in the original cell, 23 of which are chromosomes from the father and 23 are chromoso ...
... Mitotic cell division represents then the type of cell division that will produce genetically identical copies of cells, which in a human cell means 2 daughter cells having the same 46 chromosomes that were present in the original cell, 23 of which are chromosomes from the father and 23 are chromoso ...
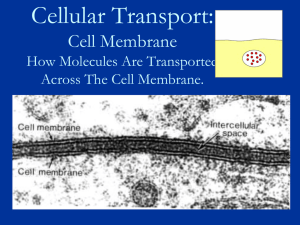
cell membrane
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
... • Lipid bilayer – double layer of phospholipids – polar head of one faces outside and other faces inside of cell – Non-polar tails face towards each other inside bilayer ...
Notes - Endosymbiotic Theory
... The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, prokaryotic cells engulfed other prokaryotic cells by endocytosis. This resulted in the first eukaryotic cells. First ...
... The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, prokaryotic cells engulfed other prokaryotic cells by endocytosis. This resulted in the first eukaryotic cells. First ...
Chapter 12 cell division
... Some external signals are growth factors, proteins released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide For example, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates the division of human fibroblast cells in culture ...
... Some external signals are growth factors, proteins released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide For example, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates the division of human fibroblast cells in culture ...
Lecture slides for 05 Cell Signallling
... into the E.R., the mitochondria and also pumped outside of the cell. • When Ca++ ions flood the cytosol,they can be used as second messenger. ...
... into the E.R., the mitochondria and also pumped outside of the cell. • When Ca++ ions flood the cytosol,they can be used as second messenger. ...
Cell Practice
... 12. Which structures are listed in order from the least complex to the most complex? a. plant cell, leaf, chloroplast, rose bush b. chloroplast, plant cell, leaf, rose bush c. chloroplast, leaf, plant cell, rose bush d. rose bush, leaf, plant cell, chloroplast ...
... 12. Which structures are listed in order from the least complex to the most complex? a. plant cell, leaf, chloroplast, rose bush b. chloroplast, plant cell, leaf, rose bush c. chloroplast, leaf, plant cell, rose bush d. rose bush, leaf, plant cell, chloroplast ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life (Structure & function) 3. All Cells come from pre-existing cells In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? Mitochondria What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesi ...
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life (Structure & function) 3. All Cells come from pre-existing cells In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? Mitochondria What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesi ...
What is an inference
... ...the cell membrane allows some ...extensions of the cytoplasm substances and not others to pass surround and engulf large through particles ...
... ...the cell membrane allows some ...extensions of the cytoplasm substances and not others to pass surround and engulf large through particles ...
Biology Study Guide Review
... of DNA except A. The long strand of nucleotide are twisted into a double helix B. DNA consists of 2 strands of nucleotides joined by hydrogen bonds. C. Every DNA nucleotide contains of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base. D. Short strands of DNA are contained in chromosomes inside the nucleus of ...
... of DNA except A. The long strand of nucleotide are twisted into a double helix B. DNA consists of 2 strands of nucleotides joined by hydrogen bonds. C. Every DNA nucleotide contains of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a base. D. Short strands of DNA are contained in chromosomes inside the nucleus of ...
2 Cells flashcards
... them where they need to go (like a FedEx center!) • Sometimes proteins are modified in the golgi complex. Therefore, this structure receives materials from the rough ER and “packages and ships” them. VESICLES (vacuoles): a sphere of membrane with something in it. Bubble-like containers for various s ...
... them where they need to go (like a FedEx center!) • Sometimes proteins are modified in the golgi complex. Therefore, this structure receives materials from the rough ER and “packages and ships” them. VESICLES (vacuoles): a sphere of membrane with something in it. Bubble-like containers for various s ...
200 300 400 100 200 300 400 100 200 300 400 100 200 300 400
... The nucleus. It controls all the functions of the cell just like our brain controls all the functions of our body. ...
... The nucleus. It controls all the functions of the cell just like our brain controls all the functions of our body. ...
Biology Learning Targets Explained
... fallopian tubes, where sperm from males may be introduced to fertilize the egg, and into the uterus, where a fertilized egg will be developed. 41. The placenta provides nutrients for a developing fetus, as does the umbilical cord later in development. Amniotic fluid and the amniotic sac suspend and ...
... fallopian tubes, where sperm from males may be introduced to fertilize the egg, and into the uterus, where a fertilized egg will be developed. 41. The placenta provides nutrients for a developing fetus, as does the umbilical cord later in development. Amniotic fluid and the amniotic sac suspend and ...
Unit 3 (ch 4)
... chemical activities or cellular metabolism are conducted inside the organelles Plant cells contain some additional organelles and a cell wall ...
... chemical activities or cellular metabolism are conducted inside the organelles Plant cells contain some additional organelles and a cell wall ...
Discovering Cells
... center of the cell and directs all of the cell’s activities. The nucleus is protected by a membrane called the nuclear envelope. ...
... center of the cell and directs all of the cell’s activities. The nucleus is protected by a membrane called the nuclear envelope. ...
Mitosis
Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle in which chromosomes in a cell nucleus are separated into two identical sets of chromosomes, each in its own nucleus. In general, mitosis (division of the nucleus) is often followed by cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. Mitosis and cytokinesis together define the mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other and to their parent cell.The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During mitosis, the chromosomes, which have already duplicated, condense and attach to fibers that pull one copy of each chromosome to opposite sides of the cell. The result is two genetically identical daughter nuclei. The cell may then divide by cytokinesis to produce two daughter cells. Producing three or more daughter cells instead of normal two is a mitotic error called tripolar mitosis or multipolar mitosis (direct cell triplication / multiplication). Other errors during mitosis can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) or cause mutations. Certain types of cancer can arise from such mutations.Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells and the process varies in different organisms. For example, animals undergo an ""open"" mitosis, where the nuclear envelope breaks down before the chromosomes separate, while fungi undergo a ""closed"" mitosis, where chromosomes divide within an intact cell nucleus. Furthermore, most animal cells undergo a shape change, known as mitotic cell rounding, to adopt a near spherical morphology at the start of mitosis. Prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, divide by a different process called binary fission.