Lecture Slides
... • Lysosomes have several types of digestive functions. – Many cells engulf nutrients in tiny cytoplasmic sacs called food vacuoles. ...
... • Lysosomes have several types of digestive functions. – Many cells engulf nutrients in tiny cytoplasmic sacs called food vacuoles. ...
Membrane - Hinsdale South High School
... high concentration of water around cell problem: cell gains water, ...
... high concentration of water around cell problem: cell gains water, ...
Notes: Cell Division & the Cell Cycle (Ch. 12)
... ● Somatic (nonreproductive) cells have two sets of chromosomes (DIPLOID) ● Gametes (reproductive cells: sperm and eggs) have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells ...
... ● Somatic (nonreproductive) cells have two sets of chromosomes (DIPLOID) ● Gametes (reproductive cells: sperm and eggs) have half as many chromosomes as somatic cells ...
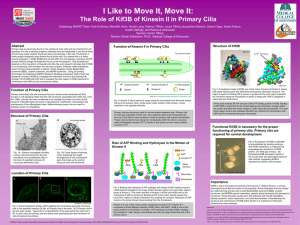
Abstract Importance Structure of Primary Cilia A B Functional Kif3B
... Fig. 3: Kinesin II (blue) carries its cargo along the microtubule from the base toward the tip of the primary cilium, while dynein (red), another motor protein, moves materials in the opposite direction. Primary cilia are structures used for communication between cells. Primary cilia do not have org ...
... Fig. 3: Kinesin II (blue) carries its cargo along the microtubule from the base toward the tip of the primary cilium, while dynein (red), another motor protein, moves materials in the opposite direction. Primary cilia are structures used for communication between cells. Primary cilia do not have org ...
Unusual Prokaryotic Envelope Cyanobacterial Cell Walls
... peptidoglycan of gram-positive bacteria, with a thickness ranging from 20 to 40 nm, usually forms a physical barrier for the dye. In gram-negative bacteria, however, with their relatively thin sacculus of 2 to 6 nm, the stain can easily be washed out. Together with other characteristics, such as the ...
... peptidoglycan of gram-positive bacteria, with a thickness ranging from 20 to 40 nm, usually forms a physical barrier for the dye. In gram-negative bacteria, however, with their relatively thin sacculus of 2 to 6 nm, the stain can easily be washed out. Together with other characteristics, such as the ...
Cellular Structures I
... b. Not function, not what they look like, but GENE EXPRESSION. c. All cells have the same genome, but differ in which genes are expressed. d. The compliment of genes expressed creates a profile of proteins for a given cell. e. Proteins in the cell dictate what the cell will look like and how it func ...
... b. Not function, not what they look like, but GENE EXPRESSION. c. All cells have the same genome, but differ in which genes are expressed. d. The compliment of genes expressed creates a profile of proteins for a given cell. e. Proteins in the cell dictate what the cell will look like and how it func ...
Part 1 - Jobworks Biology
... without any input of energy from the cell. No energy is needed because the substances are moving from an area where they have a higher concentration to an area where they have a lower concentration. Concentration refers to the number of particles of a substance per unit of volume. The more particles ...
... without any input of energy from the cell. No energy is needed because the substances are moving from an area where they have a higher concentration to an area where they have a lower concentration. Concentration refers to the number of particles of a substance per unit of volume. The more particles ...
Cells_and_Tissues__Ch_3__S2015_Part_1
... In between cell divisions, chromosomes exist in long fine threads of chromatin When a cell is about to divide, chromosomes coil and condense ...
... In between cell divisions, chromosomes exist in long fine threads of chromatin When a cell is about to divide, chromosomes coil and condense ...
The Cell Membrane
... Active Transport Cells may need to move molecules against concentration gradient ...
... Active Transport Cells may need to move molecules against concentration gradient ...
The Euglena
... The Euglena Euglena are unicellular organisms classified into the Kingdom Protista, and the Phylum Euglenophyta. All euglena have chloroplasts and can make their own food by photosynthesis. They are not completely autotrophic though, euglena can also absorb food from their environment; euglena usual ...
... The Euglena Euglena are unicellular organisms classified into the Kingdom Protista, and the Phylum Euglenophyta. All euglena have chloroplasts and can make their own food by photosynthesis. They are not completely autotrophic though, euglena can also absorb food from their environment; euglena usual ...
241083_Cell_City
... between cell structures and their functions in order to better understand the role of the various organelles and how they interact. How we will do this - Make analogies between the functional parts of a city and the functional parts of a cell. ...
... between cell structures and their functions in order to better understand the role of the various organelles and how they interact. How we will do this - Make analogies between the functional parts of a city and the functional parts of a cell. ...
L-form bacteria, cell walls and the origins of life
... shell that serves several critical roles for those organisms that possess it. Traditionally, bacteria have been divided into two major subdivisions depending on whether they possess a second membrane (the outer membrane, OM) outside the PG wall. Gram-negatives or ‘diderms’ (red in figure 1a) have an ...
... shell that serves several critical roles for those organisms that possess it. Traditionally, bacteria have been divided into two major subdivisions depending on whether they possess a second membrane (the outer membrane, OM) outside the PG wall. Gram-negatives or ‘diderms’ (red in figure 1a) have an ...
Monera: Eubacteria
... fibrils inside the cells. • Round eubacteria that live underwater can move by release gas. • The most common type of locomotion is by a flagella. Flagella are protein filaments powered by a molecular motor. They spin rapidly and allow the cell to move the cell through the environment. The flagella a ...
... fibrils inside the cells. • Round eubacteria that live underwater can move by release gas. • The most common type of locomotion is by a flagella. Flagella are protein filaments powered by a molecular motor. They spin rapidly and allow the cell to move the cell through the environment. The flagella a ...
Osmosis and Diffusion
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Question Bank The cell
... structures in a thin section of cork under simple microscope. What did he mean by these structures? Ans. Robert Hooke He observed that cork consisted of box-like compartments which formed a honey-comb structure. The compartments were named as cells by him. 2. Define a cell. Ans. A cell is the struct ...
... structures in a thin section of cork under simple microscope. What did he mean by these structures? Ans. Robert Hooke He observed that cork consisted of box-like compartments which formed a honey-comb structure. The compartments were named as cells by him. 2. Define a cell. Ans. A cell is the struct ...
Organelle Name: Nucleus - Fall River Public Schools
... All over the cell, we’re finding lots of round containers filled with stuff. These must be vacuoles (vak-you-ohl). The vacuoles are large sacs within a cell that are used to store food, water and other important substances. Vacuoles often store raw materials the cell needs to live, like food (which ...
... All over the cell, we’re finding lots of round containers filled with stuff. These must be vacuoles (vak-you-ohl). The vacuoles are large sacs within a cell that are used to store food, water and other important substances. Vacuoles often store raw materials the cell needs to live, like food (which ...
Cell membrane - Holy Family Regional School
... ‘The diffusion of water from an area of high concentration of water molecules to an area of low concentration of water across a partially permeable membrane.’ ...
... ‘The diffusion of water from an area of high concentration of water molecules to an area of low concentration of water across a partially permeable membrane.’ ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... molecules across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient (low to high solute concentration areas). It requires a boost of energy (ATP) to occur. As facilitated diffusion, is very selective • Glucose is actively transported through the plasma membrane of intestinal cells ...
... molecules across the cell membrane against a concentration gradient (low to high solute concentration areas). It requires a boost of energy (ATP) to occur. As facilitated diffusion, is very selective • Glucose is actively transported through the plasma membrane of intestinal cells ...
9th CBSE {SA - 1} Revision Pack Booklet-5
... (b) What is the relationship between chromatin material and chromosomes. Sol. (a) Chromosomes are rod-shaped structure present in nucleus. They contain information for inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA. Chromosomes are made up of DNA and protein. (b) When the ...
... (b) What is the relationship between chromatin material and chromosomes. Sol. (a) Chromosomes are rod-shaped structure present in nucleus. They contain information for inheritance of features from parents to next generation in the form of DNA. Chromosomes are made up of DNA and protein. (b) When the ...
Ch7 - kespinosa
... ONE CELL DIVIDES TO FORM TWO IDENTICAL CELLS • BINARY FISSION IS A FORM OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION, WHICH IS A PROCESS THAT INVOLVES ONLY ONE PARENT AND PRODUCES OFFSPRING THAT ARE IDENTICAL TO THE PARENT • DURING BINARY FISSION, A CELL FIRST DUPLICATES ITS GENETIC MATERIAL AND THEN DIVIDES INTO TWO SE ...
... ONE CELL DIVIDES TO FORM TWO IDENTICAL CELLS • BINARY FISSION IS A FORM OF ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION, WHICH IS A PROCESS THAT INVOLVES ONLY ONE PARENT AND PRODUCES OFFSPRING THAT ARE IDENTICAL TO THE PARENT • DURING BINARY FISSION, A CELL FIRST DUPLICATES ITS GENETIC MATERIAL AND THEN DIVIDES INTO TWO SE ...
Slide 1
... •Most reproduce by binary fission. •Move by two flagella •Algae that is usually found in oceans ...
... •Most reproduce by binary fission. •Move by two flagella •Algae that is usually found in oceans ...
Six Instructional Shifts
... Under the microscope, a cell looks a lot like a fried egg: It has a white (the cytoplasm) that’s full of water and proteins to keep it fed, and a yolk (the nucleus) that holds all the genetic information that makes you you. The cytoplasm buzzes like a New York City street. It’s crammed full of molec ...
... Under the microscope, a cell looks a lot like a fried egg: It has a white (the cytoplasm) that’s full of water and proteins to keep it fed, and a yolk (the nucleus) that holds all the genetic information that makes you you. The cytoplasm buzzes like a New York City street. It’s crammed full of molec ...
If I Were the Most Important Cell Organelle…. For nearly 1.5 billion
... If I Were the Most Important Cell Organelle…. For nearly 1.5 billion years, the nucleus has boasted its ability to direct cell activities. But now, all of the other cell organelles have called for an “organelle election.” The organelles have hired you to organize and run their individual election ca ...
... If I Were the Most Important Cell Organelle…. For nearly 1.5 billion years, the nucleus has boasted its ability to direct cell activities. But now, all of the other cell organelles have called for an “organelle election.” The organelles have hired you to organize and run their individual election ca ...
Flagellum
A flagellum (/fləˈdʒɛləm/; plural: flagella) is a lash-like appendage that protrudes from the cell body of certain prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The word flagellum in Latin means whip. The primary role of the flagellum is locomotion but it also often has function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to chemicals and temperatures outside the cell. Flagella are organelles defined by function rather than structure. There are large differences between different types of flagella; the prokaryotic and eukaryotic flagella differ greatly in protein composition, structure, and mechanism of propulsion. However, both are used for swimming.An example of a flagellate bacterium is the ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. An example of a eukaryotic flagellate cell is the mammalian sperm cell, which uses its flagellum to propel itself through the female reproductive tract. Eukaryotic flagella are structurally identical to eukaryotic cilia, although distinctions are sometimes made according to function and/or length.