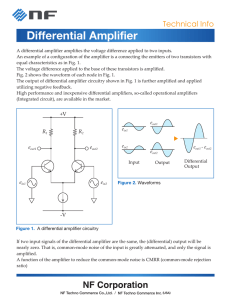
Speed Control of PMBLDC Motor Using PFC Cuk Converter
... within the power factor correction (PFC) converter circuit. The permanent magnet brushless DC motor (PMBLDCM) is controlled with the help of DC – DC cuk converter input fed to the three phase voltage – source inverter (VSI) bridge circuit which in–turn to regulate the motor. The electronic commutato ...
... within the power factor correction (PFC) converter circuit. The permanent magnet brushless DC motor (PMBLDCM) is controlled with the help of DC – DC cuk converter input fed to the three phase voltage – source inverter (VSI) bridge circuit which in–turn to regulate the motor. The electronic commutato ...
2011.05.31 DHF R01 Earthing and supply of control circuits
... RCD is designed to work only with an earthed supply. An insulation monitoring relay is required. Earthing a previously unearthed control circuit at one point will not cause any earth fault current and would therefore not trip a conventional RCD. Unearthed control circuits are confusing to work on be ...
... RCD is designed to work only with an earthed supply. An insulation monitoring relay is required. Earthing a previously unearthed control circuit at one point will not cause any earth fault current and would therefore not trip a conventional RCD. Unearthed control circuits are confusing to work on be ...
dali wall plate controller
... using any of the zones. To do this touch Zone button Z1/Z2/Z3/Z4 separately over 2 seconds. When the blue backlight is illuminated, it signifies the zone is active. When the backlight is amber it signifies that the zone is OFF. ...
... using any of the zones. To do this touch Zone button Z1/Z2/Z3/Z4 separately over 2 seconds. When the blue backlight is illuminated, it signifies the zone is active. When the backlight is amber it signifies that the zone is OFF. ...
Design of Three Phase Inverter Fed Induction Motor Drive Using PID
... On the other hand, in electric traction, the use of power is either DC or AC. Three phase DC/AC inverter is the only possible interface due to their flexible voltage and frequency variation. As mentioned above, a three phase DC/AC inverter used in traction is supplied by power either in AC or DC. In ...
... On the other hand, in electric traction, the use of power is either DC or AC. Three phase DC/AC inverter is the only possible interface due to their flexible voltage and frequency variation. As mentioned above, a three phase DC/AC inverter used in traction is supplied by power either in AC or DC. In ...
based discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) detection technique
... detection method to provide simple MCM control of the boost PFC converter. By using integrated high-speed comparators so the need for a costly auxiliary winding to detect zero inductor current is eliminated, as well as providing detection of DCM operation without knowledge of the power converter com ...
... detection method to provide simple MCM control of the boost PFC converter. By using integrated high-speed comparators so the need for a costly auxiliary winding to detect zero inductor current is eliminated, as well as providing detection of DCM operation without knowledge of the power converter com ...
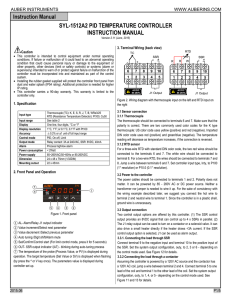
SYL-1512A Instruction Manual
... 1 - Relay J1 as PID controlled relay contact output; SSR output disabled. 2 - Relay J1 as alarm output; SSR PID control output. 3 - Relay J1 as alarm output; SSR On/off control output. 4 - J1 as On/off control relay contactor output. SSR output disabled. 5 - J1 as Limit control output. 6 – Relay J1 ...
... 1 - Relay J1 as PID controlled relay contact output; SSR output disabled. 2 - Relay J1 as alarm output; SSR PID control output. 3 - Relay J1 as alarm output; SSR On/off control output. 4 - J1 as On/off control relay contactor output. SSR output disabled. 5 - J1 as Limit control output. 6 – Relay J1 ...
Final Annexures -VI 2015
... Control Systems: Basic control system components; block diagrammatic description, reduction of block diagrams. Open loop and closed loop (feedback) systems and stability analysis of these systems. Signal flow graphs and their use in determining transfer functions of systems; transient and steady sta ...
... Control Systems: Basic control system components; block diagrammatic description, reduction of block diagrams. Open loop and closed loop (feedback) systems and stability analysis of these systems. Signal flow graphs and their use in determining transfer functions of systems; transient and steady sta ...
ANNEXURE - VI M.E./M.Tech. Admissions (2015-2016) SYLLABUS FOR M.E. (CIVIL) ENTRANCE TEST
... Control Systems: Basic control system components; block diagrammatic description, reduction of block diagrams. Open loop and closed loop (feedback) systems and stability analysis of these systems. Signal flow graphs and their use in determining transfer functions of systems; transient and steady sta ...
... Control Systems: Basic control system components; block diagrammatic description, reduction of block diagrams. Open loop and closed loop (feedback) systems and stability analysis of these systems. Signal flow graphs and their use in determining transfer functions of systems; transient and steady sta ...
Technical Teaching Equipment
... ESL-SOF is the application addressed to the Students that helps them to understand theoretical concepts by means of practical exercises and to prove their knowledge and progression by performing tests and calculations in addition to Multimedia Resources. Default planned tasks and an Open workgroup a ...
... ESL-SOF is the application addressed to the Students that helps them to understand theoretical concepts by means of practical exercises and to prove their knowledge and progression by performing tests and calculations in addition to Multimedia Resources. Default planned tasks and an Open workgroup a ...
Digital Control
... the response against sinusoids, is unclear in such a sampled-data control setup. Another way of seeing this is to note that e−jωh = ejωh and hence C(ej(2π/h−ω)h ) = C(ejωh ). This means that beyond the frequency π/h, the same gain characteristic repeats and C(ejωh ) cannot be treated as the same fr ...
... the response against sinusoids, is unclear in such a sampled-data control setup. Another way of seeing this is to note that e−jωh = ejωh and hence C(ej(2π/h−ω)h ) = C(ejωh ). This means that beyond the frequency π/h, the same gain characteristic repeats and C(ejωh ) cannot be treated as the same fr ...
Section 26 09 00 - Wired Control System
... All cables supplied by SAGE Electrochromics should be conditioned for 24 hours at room temperature prior to installation and never installed below 32 degrees F (0 degrees C) ambient temperature. ...
... All cables supplied by SAGE Electrochromics should be conditioned for 24 hours at room temperature prior to installation and never installed below 32 degrees F (0 degrees C) ambient temperature. ...
PDF
... proposed controller used an SRF proportionalintegral controller to regulate the instantaneous output voltage, a capacitor current shaping loop in the stationary reference frame to provide active damping and improve both transient and steady-state performances, a voltage decoupling feed forward to im ...
... proposed controller used an SRF proportionalintegral controller to regulate the instantaneous output voltage, a capacitor current shaping loop in the stationary reference frame to provide active damping and improve both transient and steady-state performances, a voltage decoupling feed forward to im ...
Ho Control of System With I/O Delay: A Review of
... framework of distributed parameter systems [67, 9, 70, 76, 32, 37]. A feature that facilitates design in systems with input (or output) delays is that their distributed component has very simple dynamics (essentially, an FIR). Indeed, in “classical” and some robust stabilization problems, this featu ...
... framework of distributed parameter systems [67, 9, 70, 76, 32, 37]. A feature that facilitates design in systems with input (or output) delays is that their distributed component has very simple dynamics (essentially, an FIR). Indeed, in “classical” and some robust stabilization problems, this featu ...
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems with inputs, and how their behavior is modified by feedback. The usual objective of control theory is to control a system, often called the plant, so its output follows a desired control signal, called the reference, which may be a fixed or changing value. To do this a controller is designed, which monitors the output and compares it with the reference. The difference between actual and desired output, called the error signal, is applied as feedback to the input of the system, to bring the actual output closer to the reference. Some topics studied in control theory are stability (whether the output will converge to the reference value or oscillate about it), controllability and observability.Extensive use is usually made of a diagrammatic style known as the block diagram. The transfer function, also known as the system function or network function, is a mathematical representation of the relation between the input and output based on the differential equations describing the system.Although a major application of control theory is in control systems engineering, which deals with the design of process control systems for industry, other applications range far beyond this. As the general theory of feedback systems, control theory is useful wherever feedback occurs. A few examples are in physiology, electronics, climate modeling, machine design, ecosystems, navigation, neural networks, predator-prey interaction, gene expression, and production theory.