Calibrating Standard Conductivity
... However, we make no warranty of merchantability, or fitness for any particular use, or any other warranty, express or implied, with respect to this information, and we assume no liability resulting from the use of this information. Users should make their own investigations to determine the suitabil ...
... However, we make no warranty of merchantability, or fitness for any particular use, or any other warranty, express or implied, with respect to this information, and we assume no liability resulting from the use of this information. Users should make their own investigations to determine the suitabil ...
Lecture No. 12+13
... Organophosphates - insecticides - antiparasitics Mechanism of toxic action – irreversible inhibition of enzymes, particularly of acetylcholinesterase on nerve synapses (by phosphorylation of hydroxyl group of serine bound in the active centre of ACHE). ...
... Organophosphates - insecticides - antiparasitics Mechanism of toxic action – irreversible inhibition of enzymes, particularly of acetylcholinesterase on nerve synapses (by phosphorylation of hydroxyl group of serine bound in the active centre of ACHE). ...
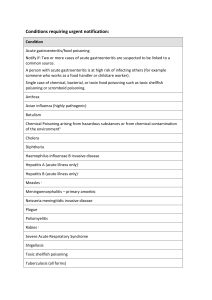
Conditions requiring urgent notification:
... Rabies 3 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Shigellosis Toxic shellfish poisoning Tuberculosis (all forms) ...
... Rabies 3 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Shigellosis Toxic shellfish poisoning Tuberculosis (all forms) ...
Types of Pesticides
... There is evidence that pollinators may be exposed via the resources they collect, but further research is required to determine the details and how problems might be mitigated. Neonicotinoid compounds may also pose a hazard if used as a seed treatment or sprayed before bloom, as they can be present ...
... There is evidence that pollinators may be exposed via the resources they collect, but further research is required to determine the details and how problems might be mitigated. Neonicotinoid compounds may also pose a hazard if used as a seed treatment or sprayed before bloom, as they can be present ...
POWER_AND_TECH_files/Unit 3
... kills insect when it ingests plant Gas poisons that enter insect’s respiratory system ...
... kills insect when it ingests plant Gas poisons that enter insect’s respiratory system ...
Epilepsy and Lead Poisoning
... After months of exposure unless large amount Faster absorption with inhalation ...
... After months of exposure unless large amount Faster absorption with inhalation ...
Document
... been used in the past 50 years than were used in the entire previous history of the ...
... been used in the past 50 years than were used in the entire previous history of the ...
Presentation
... gasoline, pipes containing water for a long time Causes anemia, neurological damage, chronic renal disease Completely decays Daphnia in 15 days and is toxic to algae in 30 days Lead air pollution in ecosystems causes loss in biodiversity, change in community composition, and decrease in growth ...
... gasoline, pipes containing water for a long time Causes anemia, neurological damage, chronic renal disease Completely decays Daphnia in 15 days and is toxic to algae in 30 days Lead air pollution in ecosystems causes loss in biodiversity, change in community composition, and decrease in growth ...
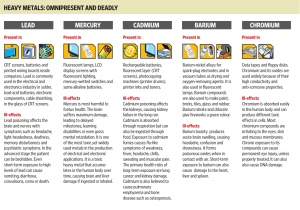
lead mercury cadmium barium chromium heavy metals
... disabilities or even gross mental retardation. It is one of the most toxic yet widely used metals in the production of electrical and electronic applications. It is a toxic heavy metal that accumulates in the human body over time, causing brain and liver damage if ingested or inhaled. ...
... disabilities or even gross mental retardation. It is one of the most toxic yet widely used metals in the production of electrical and electronic applications. It is a toxic heavy metal that accumulates in the human body over time, causing brain and liver damage if ingested or inhaled. ...
Ch 14 Env Health 2013 - Pendleton
... • Dosage: Amount of substance ingested, inhaled or absorbed through skin ...
... • Dosage: Amount of substance ingested, inhaled or absorbed through skin ...
Chapter 8
... • Viruses cannot be attacked in cells • Being non-living, can’t be killed by antibiotics in blood stream • Only defenses are immunization or prevention • Antibiotics do not work against viruses ...
... • Viruses cannot be attacked in cells • Being non-living, can’t be killed by antibiotics in blood stream • Only defenses are immunization or prevention • Antibiotics do not work against viruses ...
Forensic Toxicology
... – Ethanol – produced by fermentation of sugar in fruits, grains, and vegetables • The body converts ethanol into acetaldehyde which causes dehydration when it accumulates in the blood (causing hangover symptoms) • Chronic abuse causes liver damage, dangerous behavior, depression of CNS, and permanen ...
... – Ethanol – produced by fermentation of sugar in fruits, grains, and vegetables • The body converts ethanol into acetaldehyde which causes dehydration when it accumulates in the blood (causing hangover symptoms) • Chronic abuse causes liver damage, dangerous behavior, depression of CNS, and permanen ...
TOXICOLOGY
... • Toxic effects: is related to hypoxia within the brain and heart. Dyspnea, lethargy, confusion, headache, drowsiness, seizures, coma & death. • antidote: removal of patient from source, 100% oxygen by face mask or endotracheal tube. ...
... • Toxic effects: is related to hypoxia within the brain and heart. Dyspnea, lethargy, confusion, headache, drowsiness, seizures, coma & death. • antidote: removal of patient from source, 100% oxygen by face mask or endotracheal tube. ...
TOXICOLOGICAL HIGHLIGHT Organophosphates, Serine Esterase
... group of the esterase or protease. Thus during this phosphorylation reaction, the organophosphate molecule is destroyed through stoichiometric reaction with the enzyme. The inhibition from organophosphates is persistent, lasting hours to days, and potentially may not be reversible if a nonenzymatica ...
... group of the esterase or protease. Thus during this phosphorylation reaction, the organophosphate molecule is destroyed through stoichiometric reaction with the enzyme. The inhibition from organophosphates is persistent, lasting hours to days, and potentially may not be reversible if a nonenzymatica ...
lecture text - UNC
... lesion. Inhibition of the enzyme permits an abnormal accumulation of acetylcholine; minimal excess causes (1) excessive activity of the parasympathetic system (miosis, sweating, profuse secretions in the upper respiratory tract, abdominal cramps and discomfort in chest from overactivity of smooth mu ...
... lesion. Inhibition of the enzyme permits an abnormal accumulation of acetylcholine; minimal excess causes (1) excessive activity of the parasympathetic system (miosis, sweating, profuse secretions in the upper respiratory tract, abdominal cramps and discomfort in chest from overactivity of smooth mu ...
Chlorpyrifos/Dursban
... collected by the National Pesticide Telecommunications Network and ranks second in the precipitation of peripheral neuropathy. Other organophosphates were also involved with 104 suspect cases attributed to diazinon exposure and 51 cases attributed to malathion. DowElanco for years withheld informati ...
... collected by the National Pesticide Telecommunications Network and ranks second in the precipitation of peripheral neuropathy. Other organophosphates were also involved with 104 suspect cases attributed to diazinon exposure and 51 cases attributed to malathion. DowElanco for years withheld informati ...
Marion Ehrich – Pesticide Neurotoxicity More or Less
... What are the problems of oximes for the treatment of organophosphates? Describe how scavengers might be used to treat organophosphate exposure. What are the features of delayed neuropathy that occur in humans and animals following exposure to organophosphates? What are some of the risk factors that ...
... What are the problems of oximes for the treatment of organophosphates? Describe how scavengers might be used to treat organophosphate exposure. What are the features of delayed neuropathy that occur in humans and animals following exposure to organophosphates? What are some of the risk factors that ...
Insecticides: Cholinesterase Inhibitors
... Give atropine in escalating doses until clinical improvement is evident. Begin with 2–5 mg IV initially Double the dose administered every 5 minutes until respiratory secretions have cleared. Note: Atropine will reverse muscarinic but not nicotinic effects ...
... Give atropine in escalating doses until clinical improvement is evident. Begin with 2–5 mg IV initially Double the dose administered every 5 minutes until respiratory secretions have cleared. Note: Atropine will reverse muscarinic but not nicotinic effects ...
Organophosphate poisoning
Organophosphate poisoning results from exposure to organophosphates (OPs), which cause the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), leading to the accumulation of acetylcholine (ACh) in the body. Organophosphate poisoning most commonly results from exposure to insecticides or nerve agents. OPs are one of the most common causes of poisoning worldwide, and are frequently intentionally used in suicides in agrarian areas. There are around 1 million OP poisonings per year with several hundred thousand resulting in fatalities annually.Organophosphates inhibit AChE, causing OP poisoning by phosphorylating the serine hydroxyl residue on AChE, which inactivates AChE. AChE is critical for nerve function, so the irreversible blockage of this enzyme, which causes acetylcholine accumulation, results in muscle overstimulation. This causes disturbances across the cholinergic synapses and can only be reactivated very slowly, if at all. Paraoxonase (PON1) is a key enzyme involved in OP pesticides and has been found to be critical in determining an organism's sensitivity to OP exposure.