electric motor - Madison County Schools
... magnetic field. The electrical energy produces the magnetic field in the wire with a current. The movement that results is mechanical energy. ...
... magnetic field. The electrical energy produces the magnetic field in the wire with a current. The movement that results is mechanical energy. ...
Handout for ALTIVAR 18 AC Drives
... deceleration ramps: Linear ramps which can be adjusted separately from 0.1 to 3,600 seconds. Automatic adaptation of ramp times if the torque capacity is exceeded. Voltage/frequency ratio: Factory set for most constant torque applications with sensorless flux vector control. Adjustment possible: spe ...
... deceleration ramps: Linear ramps which can be adjusted separately from 0.1 to 3,600 seconds. Automatic adaptation of ramp times if the torque capacity is exceeded. Voltage/frequency ratio: Factory set for most constant torque applications with sensorless flux vector control. Adjustment possible: spe ...
Motor-Generator Sets
... the synchronous motor to adjust motor input power factor independently of the generator. ...
... the synchronous motor to adjust motor input power factor independently of the generator. ...
Unit 6 Magnetism
... • Gauges are your dashboard of your car are galvanometers • They measure the current being sent from sensors which in turn register the amount of ex: gasoline you have left ...
... • Gauges are your dashboard of your car are galvanometers • They measure the current being sent from sensors which in turn register the amount of ex: gasoline you have left ...
World`s Simplest Motor
... Try the experiment to view the magnetic field lines seen on the video. You will need white paper, iron filings, and several different magnets for each group. Make sure to record your findings and to draw pictures of what you observe in your science notebooks! View the How does electricity create a m ...
... Try the experiment to view the magnetic field lines seen on the video. You will need white paper, iron filings, and several different magnets for each group. Make sure to record your findings and to draw pictures of what you observe in your science notebooks! View the How does electricity create a m ...
Basics on electric motors
... was initiated by accident when one DC generator was accidentally connected to another in 1873, producing motion and leading Zenobe Gramme to realize that his generators could also be used as motors. The first AC motors (synchronous and then induction) were invented by Tesla in the 1880s. Electric mo ...
... was initiated by accident when one DC generator was accidentally connected to another in 1873, producing motion and leading Zenobe Gramme to realize that his generators could also be used as motors. The first AC motors (synchronous and then induction) were invented by Tesla in the 1880s. Electric mo ...
DC shunt motor DC series motor
... The method is often used in electric traction and is shown in fig. The number of series field turns in the circuit can be changed at will as shown. With full field, the motor runs at its minimum speed which can be raised in steps by cutting out some of the series turns. ...
... The method is often used in electric traction and is shown in fig. The number of series field turns in the circuit can be changed at will as shown. With full field, the motor runs at its minimum speed which can be raised in steps by cutting out some of the series turns. ...
SMJE 2103
... A 480V, 60Hz, 50hp, 3 phase induction motor is drawing 60A at 0.85 Pf lagging. The stator copper losses are 2 kW, and the rotor losses are 700W. The friction and windage losses re 600W, the core losses are 180W, and the stray losses are negligible. Find: a) The air gap power PAG b) The power convert ...
... A 480V, 60Hz, 50hp, 3 phase induction motor is drawing 60A at 0.85 Pf lagging. The stator copper losses are 2 kW, and the rotor losses are 700W. The friction and windage losses re 600W, the core losses are 180W, and the stray losses are negligible. Find: a) The air gap power PAG b) The power convert ...
Advanced Dissectable and Configurable Electrical Machines AEL-EMT-KIT Technical Teaching Equipment
... apart from assembling the machine, both the velocity and torque of the machine can be controlled. It includes: • Rotor. This element consists of a set of ferromagnetic pieces that constitute the rotor of the two-pole synchronous generator. Such poles consist of sheets to reduce the parasitic current ...
... apart from assembling the machine, both the velocity and torque of the machine can be controlled. It includes: • Rotor. This element consists of a set of ferromagnetic pieces that constitute the rotor of the two-pole synchronous generator. Such poles consist of sheets to reduce the parasitic current ...
MEEPP 202 Electric Drives
... drive. Get the expression for the average output voltage and speed. Draw the speedtorque characteristics. (10 marks) 5. (a) Analyze and compare the operation of an induction motor with balanced and unbalanced source voltages. (10 marks) (b) A 440V,50Hz,6 pole,950 rpm,Y-connected induction motor has ...
... drive. Get the expression for the average output voltage and speed. Draw the speedtorque characteristics. (10 marks) 5. (a) Analyze and compare the operation of an induction motor with balanced and unbalanced source voltages. (10 marks) (b) A 440V,50Hz,6 pole,950 rpm,Y-connected induction motor has ...
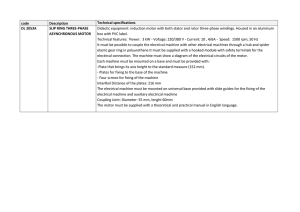
code Description Technical specifications DL 2053A SLIP RING
... Didactic equipment: induction motor with both stator and rotor three-phase windings. Housed in an aluminum box with PVC label. Technical features: Power: 3 kW - Voltage: 220/380 V - Current: 10 , 4/6A - Speed: 1500 rpm, 50 Hz It must be possible to couple the electrical machine with other electrical ...
... Didactic equipment: induction motor with both stator and rotor three-phase windings. Housed in an aluminum box with PVC label. Technical features: Power: 3 kW - Voltage: 220/380 V - Current: 10 , 4/6A - Speed: 1500 rpm, 50 Hz It must be possible to couple the electrical machine with other electrical ...
MOH Goat Autonomous Operation
... The more basic Basics… • Torque “twisting effort” – EG: shaft turning, force at the end of an arm, force at the circumference of wheel… “pushing/pulling strength” – Unlimited torque available through any motor with appropriate transmission ...
... The more basic Basics… • Torque “twisting effort” – EG: shaft turning, force at the end of an arm, force at the circumference of wheel… “pushing/pulling strength” – Unlimited torque available through any motor with appropriate transmission ...
Electric motor

An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The reverse of this would be the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy and is done by an electric generator.In normal motoring mode, most electric motors operate through the interaction between an electric motor's magnetic field and winding currents to generate force within the motor. In certain applications, such as in the transportation industry with traction motors, electric motors can operate in both motoring and generating or braking modes to also produce electrical energy from mechanical energy.Found in applications as diverse as industrial fans, blowers and pumps, machine tools, household appliances, power tools, and disk drives, electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, motor vehicles or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as from the power grid, inverters or generators. Small motors may be found in electric watches. General-purpose motors with highly standardized dimensions and characteristics provide convenient mechanical power for industrial use. The largest of electric motors are used for ship propulsion, pipeline compression and pumped-storage applications with ratings reaching 100 megawatts. Electric motors may be classified by electric power source type, internal construction, application, type of motion output, and so on.Electric motors are used to produce linear or rotary force (torque), and should be distinguished from devices such as magnetic solenoids and loudspeakers that convert electricity into motion but do not generate usable mechanical powers, which are respectively referred to as actuators and transducers.