2 - O`donovan Academy
... ONE STEP EQUATIONS To solve one step equations, you need to ask three questions about the equation: • What is the variable? • What operation is performed on the variable? • What is the inverse operation? (The one that will undo what is being done to the variable) ...
... ONE STEP EQUATIONS To solve one step equations, you need to ask three questions about the equation: • What is the variable? • What operation is performed on the variable? • What is the inverse operation? (The one that will undo what is being done to the variable) ...
CONCORDIA DISCORS: Wave-Particle Duality in the 3rd Century BC?
... also for compound particles like atoms and even molecules. For interference experiments including fullerenes and c-60 molecules as shown in the above figure. Since every particle now has wave nature and every macro object consists of these quantum-scale objects, the same should be exhibited as wave ...
... also for compound particles like atoms and even molecules. For interference experiments including fullerenes and c-60 molecules as shown in the above figure. Since every particle now has wave nature and every macro object consists of these quantum-scale objects, the same should be exhibited as wave ...
Chapter 3. The Structure of the Atom
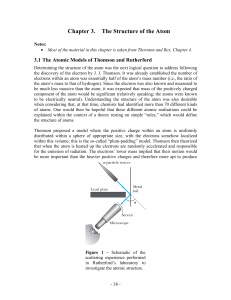
... could see through the challenges classical physics faced and came up with imaginative solutions based on the nascent quantum theory. When considering the failure of the atomic classical model Bohr proposed four general assumptions or postulates, which he could then use to explain much of the experim ...
... could see through the challenges classical physics faced and came up with imaginative solutions based on the nascent quantum theory. When considering the failure of the atomic classical model Bohr proposed four general assumptions or postulates, which he could then use to explain much of the experim ...
Section P.5
... polar axis at a distance p units to the left of the pole Directrix is perpendicular to the polar axis at a distance p units to the right of the pole Directrix is parallel to the polar axis at a distance p units above the pole Directrix is parallel to the polar axis at a distance p units below the po ...
... polar axis at a distance p units to the left of the pole Directrix is perpendicular to the polar axis at a distance p units to the right of the pole Directrix is parallel to the polar axis at a distance p units above the pole Directrix is parallel to the polar axis at a distance p units below the po ...
what is wave function?
... intensity profile is | 1 |2 If slit 2 is opened (slit 1 closed), then we can represent the wave function of the electrons passing through slit 1 as 2 and therefore the intensity profile is | 2 |2 ...
... intensity profile is | 1 |2 If slit 2 is opened (slit 1 closed), then we can represent the wave function of the electrons passing through slit 1 as 2 and therefore the intensity profile is | 2 |2 ...
Applications of the Schrodinger Wave Equation The free particle
... At x =0 At x =L A ≠ 0 because that would make Ψ(x) = 0 everywhere in the box. It would imply no particle at all! Therefore sin(ka) = 0. This will happen when ka = nπ; n = 1, 2, 3. Note n = 0 no good because again this would make Ψ(x) = 0 everywhere in the ...
... At x =0 At x =L A ≠ 0 because that would make Ψ(x) = 0 everywhere in the box. It would imply no particle at all! Therefore sin(ka) = 0. This will happen when ka = nπ; n = 1, 2, 3. Note n = 0 no good because again this would make Ψ(x) = 0 everywhere in the ...
Symbols “R” Us: Seismic Imaging, One-Way Wave Equations, Pseudodifferential
... numerical algorithms have been important issues in many industrial settings for many years. Mathematicians, physicists, and other applied scientisits, in fields as diverse as ocean acoustics, electromagnetics, medical imaging, optical design, and seismic exploration, have struggled with these issues ...
... numerical algorithms have been important issues in many industrial settings for many years. Mathematicians, physicists, and other applied scientisits, in fields as diverse as ocean acoustics, electromagnetics, medical imaging, optical design, and seismic exploration, have struggled with these issues ...
Solve the equation.
... An identity is an equation that is always true, no matter what value is substituted for the variable. The solution set of an identity is all real numbers. Some equations are always false. Their solution sets are empty. In other words, their solution sets contain no elements. ...
... An identity is an equation that is always true, no matter what value is substituted for the variable. The solution set of an identity is all real numbers. Some equations are always false. Their solution sets are empty. In other words, their solution sets contain no elements. ...