Slide 1
... 2. If you have STILL not finished your hand, do so now. 3. I’m throwing away all the papers left in the room this afternoon ...
... 2. If you have STILL not finished your hand, do so now. 3. I’m throwing away all the papers left in the room this afternoon ...
CELL TRANSPORT - Oncourse : Gateway : Home
... difference between concentrations in space Simple diffusion only allows certain molecules across a membrane ...
... difference between concentrations in space Simple diffusion only allows certain molecules across a membrane ...
Cell Structure
... Chromatin is DNA bound to protein During cell division, chromosomes form when chromatin condenses. Chromosomes hold genetic info which pass from one generation to another ...
... Chromatin is DNA bound to protein During cell division, chromosomes form when chromatin condenses. Chromosomes hold genetic info which pass from one generation to another ...
CHAPTER 7 THE CELL
... 4. Matthias Schleiden (1830’s) found that plants are composed of cells. 5. Theodore Schwann (1830’s) found that animals are composed of cells. 6. Rudolf Virchow (1855) stated that cells can only come from existing cells. ...
... 4. Matthias Schleiden (1830’s) found that plants are composed of cells. 5. Theodore Schwann (1830’s) found that animals are composed of cells. 6. Rudolf Virchow (1855) stated that cells can only come from existing cells. ...
Document
... acts to dilute! Example: Diffusion of water into a plant cell to create turgor pressure. c. Passive Transport - transport of molecules by way of diffusion (no energy required). Diffusion down a concentration gradient. Ex. Diffusion of oxygen into a cell. d. Active Transport - movement of molecules a ...
... acts to dilute! Example: Diffusion of water into a plant cell to create turgor pressure. c. Passive Transport - transport of molecules by way of diffusion (no energy required). Diffusion down a concentration gradient. Ex. Diffusion of oxygen into a cell. d. Active Transport - movement of molecules a ...
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
... 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? ...
... 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? ...
Cell Structures - cloudfront.net
... 21. Chloroplasts that contain the green pigment ____________, which makes a plant green. 22. In some cells, a cell ____________ is outside the plasma membrane, 23. The two layers of phospholipids in the plasma membrane are called a phospholipid ____________. 24. ____________ are organelles where pro ...
... 21. Chloroplasts that contain the green pigment ____________, which makes a plant green. 22. In some cells, a cell ____________ is outside the plasma membrane, 23. The two layers of phospholipids in the plasma membrane are called a phospholipid ____________. 24. ____________ are organelles where pro ...
Fungal Cells 02
... Golgi Apparatus – Sorts and processes proteins and lipids which are then transported around the cell. Lysosomes – These contain enzymes needed to destroy unwanted material in the cell. Mitochondria – These are the power stations of the cells as they provide the cell with all the energy it needs thro ...
... Golgi Apparatus – Sorts and processes proteins and lipids which are then transported around the cell. Lysosomes – These contain enzymes needed to destroy unwanted material in the cell. Mitochondria – These are the power stations of the cells as they provide the cell with all the energy it needs thro ...
Modern biology is guided by the cell theory, the view that ______.
... and ribosomes and divide by simple fission like bacteria do mitochondria can produce ATP using ...
... and ribosomes and divide by simple fission like bacteria do mitochondria can produce ATP using ...
Cells and Heredity
... Every living thing is made of one or more cells. Cells carry out the functions needed to support life. Cells come only from other living cells. ...
... Every living thing is made of one or more cells. Cells carry out the functions needed to support life. Cells come only from other living cells. ...
L 9 Myosin
... has a banded (striated) appearance when examined under a microscope. • It consists of multinucleated cells that are bounded by plasma membrane. • A muscle cell contains many parallel myofibrils, each about 1 mm in diameter. • The functional unit, called a sarcomere, typically repeats every 2.3 mm (2 ...
... has a banded (striated) appearance when examined under a microscope. • It consists of multinucleated cells that are bounded by plasma membrane. • A muscle cell contains many parallel myofibrils, each about 1 mm in diameter. • The functional unit, called a sarcomere, typically repeats every 2.3 mm (2 ...
Chapter 6 ppt 6 PDF
... - Function: the internal delivery system of the cell - Parts: - Rough ER - Function: helps make proteins, that's why it has ribosomes - Appearance: rough appearance because it has ribosomes - Smooth ER - No ribosomes - Function: makes fats or lipids ...
... - Function: the internal delivery system of the cell - Parts: - Rough ER - Function: helps make proteins, that's why it has ribosomes - Appearance: rough appearance because it has ribosomes - Smooth ER - No ribosomes - Function: makes fats or lipids ...
File
... 1. Various tissues that work together to perform a specific job constitute ORGANS. 2. The role of the cell’s MITOCHONDRIA is to release energy that can be used to power various cellular processes. 3. DNA, the genetic material in cells, is located in a eukaryotic cell’s NUCLEUS. 4. Cells that have no ...
... 1. Various tissues that work together to perform a specific job constitute ORGANS. 2. The role of the cell’s MITOCHONDRIA is to release energy that can be used to power various cellular processes. 3. DNA, the genetic material in cells, is located in a eukaryotic cell’s NUCLEUS. 4. Cells that have no ...
Plant and Animal Cells
... • Diffusion is when materials move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Osmosis is the movement of water across the cell membrane. ...
... • Diffusion is when materials move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. • Osmosis is the movement of water across the cell membrane. ...
Cell Theory
... Nuclear membrane: surrounds nucleus, controls material flow in and out of nucleus Nucleolus: makes the ribosome parts Chromosomes: contains DNA, passes on genetic info Nuclear membrane ...
... Nuclear membrane: surrounds nucleus, controls material flow in and out of nucleus Nucleolus: makes the ribosome parts Chromosomes: contains DNA, passes on genetic info Nuclear membrane ...
Cell Structure and Function Dr. Ehan Abdulhadi PhD in Microbology
... – differences in concentration, pressure, charge – High moves toward low Types of Passive Transport ...
... – differences in concentration, pressure, charge – High moves toward low Types of Passive Transport ...
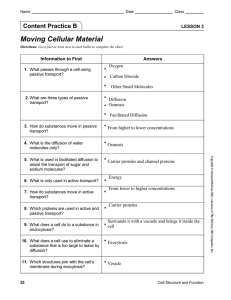
Moving Cellular Material
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
Cell Biology Form and Function - This area is password protected
... fills the interior of the cell. It consists of a liquid (called the cytosol that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical reactions occur. ...
... fills the interior of the cell. It consists of a liquid (called the cytosol that contains water, proteins and dissolved ions) and cell organelles. It is used to transport substances throughout the cell and create internal pressure and is where most chemical reactions occur. ...
The Cell - Texarkana Independent School District
... that controls cellular traffic - Contains proteins (left, gray) that span through the membrane and allow passage of materials - Proteins are surrounded by a phospholipid bi-layer. ...
... that controls cellular traffic - Contains proteins (left, gray) that span through the membrane and allow passage of materials - Proteins are surrounded by a phospholipid bi-layer. ...
Cell Organelles - Ms. Nevel's Biology Website
... coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules for the cell • The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave See? ...
... coded instructions for making proteins and other molecules for the cell • The nuclear envelope has nuclear pores, where things can enter or leave See? ...
Cytoplasmic streaming

Cytoplasmic streaming, also called protoplasmic streaming and cyclosis, is the directed flow of cytosol (the liquid component of the cytoplasm) and organelles around large fungal and plant cells through the mediation of actin. This movement aids in the delivery of organelles, nutrients, metabolites, genetic information, and other materials to all parts of the cell. Cytoplasmic streaming occurs along actin filaments in the cytoskeleton of the cell.Cytoplasmic streaming was first discovered in the 1830s. The scientific breakthrough assisted scientists in developing an understanding of the different roles of cells and how they function as the basic operating systems of life.This process occurs through the operation of motor proteins called myosins.These proteins use energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to act as a molecular motor, which slides along actin filaments. This works in a manner that tows the organelles and other cytoplasmic contents in the same direction. Myosin proteins consist of two conjoined proteins. If one protein remains attached to the substrate, the substance acted upon by the protein, such as a microfilament, has the ability to move organelles through the cytoplasm.The green alga genus Chara and other genera in the Division Charophyta, such as Coleochaete, are thought to be the closest relatives of land plants. These haploid organisms contain some of the largest plant cells on earth, a single cell of which can reach up to 10 cm in length. The large size of these cells demands an efficient means to distribute resources, which is enabled via cytoplasmic streaming.Cytoplasmic streaming is strongly dependent upon intracellular pH and temperature. It has been observed that the effect of temperature on cytoplasmic streaming created linear variance and dependence at different high temperatures in comparison to low temperatures. This process is complicated, with temperature alterations in the system increasing its efficiency, with other factors such as the transport of ions across the membrane being simultaneously affected. This is due to cells homeostasis depending upon active transport which may be affected at some critical temperatures.In plant cells, chloroplasts may be moved around with the stream, possibly to a position of optimum light absorption for photosynthesis. The rate of motion is usually affected by light exposure, temperature, and pH levels.In reference to pH, because actin and myosin are both proteins, strong dependence on pH is expected. The optimal pH at which cytoplasmic streaming is highest, is achieved at neutral pH and decreases at both low and high pH.The flow of cytoplasm may be stopped by:Adding Lugol's iodine solutionAdding Cytochalasin D (dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide)↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑