central concepts of economics
... Economic goods are scarce and therefore have a cost. Economic goods can be subdivided into either consumer goods or capital (producer) goods. Consumer goods are for consumption by individuals or households (a group of individuals) for their own private satisfaction (use), for example, DVDs, designe ...
... Economic goods are scarce and therefore have a cost. Economic goods can be subdivided into either consumer goods or capital (producer) goods. Consumer goods are for consumption by individuals or households (a group of individuals) for their own private satisfaction (use), for example, DVDs, designe ...
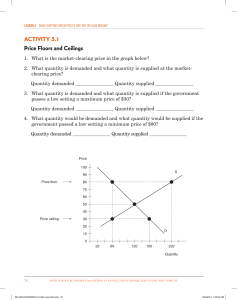
Price Floors and Ceilings - HS Economics
... the biggest arenas, but she prefers smaller venues for a more intimate concert experience. Yes, she can charge hundreds of dollars for seats, but she would rather keep ticket prices low for her legion of blue-collar followers. Her heart may be in the right place, but ticket scalpers are salivating a ...
... the biggest arenas, but she prefers smaller venues for a more intimate concert experience. Yes, she can charge hundreds of dollars for seats, but she would rather keep ticket prices low for her legion of blue-collar followers. Her heart may be in the right place, but ticket scalpers are salivating a ...
Economic - Choithram School
... 1. An economy always manages to meet all the needs of people living in the country. 2. In the context of economy when we talk about scarcity, we refer to short supply of money. 3. A PPF is always represented as a downward sloping curve. 4. Government should rise taxes on industries that causes pollu ...
... 1. An economy always manages to meet all the needs of people living in the country. 2. In the context of economy when we talk about scarcity, we refer to short supply of money. 3. A PPF is always represented as a downward sloping curve. 4. Government should rise taxes on industries that causes pollu ...
Consumer Choice and Demand
... • Total utility – total amount of satisfaction or pleasure from consuming some specific quantity of a good • Marginal utility – the extra utility from consuming one more unit of the good ...
... • Total utility – total amount of satisfaction or pleasure from consuming some specific quantity of a good • Marginal utility – the extra utility from consuming one more unit of the good ...
economics paper i
... 3. Explain the factors which determine the price elasticity of demand. 4. Briefly explain the law of diminishing marginal utility. 5. Briefly explain the structure of balance of payments. 6. What is National Income? Explain briefly the methods of measuring national income. ...
... 3. Explain the factors which determine the price elasticity of demand. 4. Briefly explain the law of diminishing marginal utility. 5. Briefly explain the structure of balance of payments. 6. What is National Income? Explain briefly the methods of measuring national income. ...
Fundamentals of Microeconomics Johns Hopkins University Center for Talented Youth
... Market entry-market exit Competitive Markets in the real world: economic applications in business ...
... Market entry-market exit Competitive Markets in the real world: economic applications in business ...
Chapter 6
... Consumer surplus is the net benefit a consume receives from participating in the market for some good and, the amount of money that would compensate the consumer for losing access to the market, compensating variation Consumer’s D curve measures the gross benefit of consuming a good Consumer sur ...
... Consumer surplus is the net benefit a consume receives from participating in the market for some good and, the amount of money that would compensate the consumer for losing access to the market, compensating variation Consumer’s D curve measures the gross benefit of consuming a good Consumer sur ...
Consumer and Producer Surplus
... So to graph we say how much is the price when the quantity demanded (or supplied) is zero in both equations Ps = 40 + 4(0)= 40 Pd = 100 – 2(0) = 100. These are the intercepts at the Y axis. To calculate the intercept at the X axis we say how much is the quantity demanded when the price is zero, so 0 ...
... So to graph we say how much is the price when the quantity demanded (or supplied) is zero in both equations Ps = 40 + 4(0)= 40 Pd = 100 – 2(0) = 100. These are the intercepts at the Y axis. To calculate the intercept at the X axis we say how much is the quantity demanded when the price is zero, so 0 ...
ME11_Ch04
... income effect substitution effect price-consumption curve income-consumption curve Engle curve normal goods inferior goods consumer surplus two-part pricing bundle pricing optimal market basket revealed preference marginal rate of substitution consumption path ...
... income effect substitution effect price-consumption curve income-consumption curve Engle curve normal goods inferior goods consumer surplus two-part pricing bundle pricing optimal market basket revealed preference marginal rate of substitution consumption path ...
Problem Set 2 Solutions
... people don’t understand how the EITC is phased in or phased out, so they don’t know that they should reduce hours to maximize utility. c) How would the effect on hours of labor differ if the individual initially did not work? For someone who initially chose zero hours of labor, the EITC could only h ...
... people don’t understand how the EITC is phased in or phased out, so they don’t know that they should reduce hours to maximize utility. c) How would the effect on hours of labor differ if the individual initially did not work? For someone who initially chose zero hours of labor, the EITC could only h ...
When Rewards Backfire: Customer Resistance to Loyalty Programs
... this study explores the negative elements perceived by customers informants’ alleged resistance do not solely derives from previthat may lead them reject membership in such programs. Using an ous bad experiences and feelings about the program, but from an exploratory study of 15 customers who resist ...
... this study explores the negative elements perceived by customers informants’ alleged resistance do not solely derives from previthat may lead them reject membership in such programs. Using an ous bad experiences and feelings about the program, but from an exploratory study of 15 customers who resist ...
University of Vermont Department of Economics Course Outline
... Dahne Duffy will be your T.A. He will hold supplemental instruction sessions to help you grasp the material. The supplemental instruction sessions are an opportunity for students to review the class’ material and improve their understanding of the course. These review sessions will include problem s ...
... Dahne Duffy will be your T.A. He will hold supplemental instruction sessions to help you grasp the material. The supplemental instruction sessions are an opportunity for students to review the class’ material and improve their understanding of the course. These review sessions will include problem s ...
Supply - Cloudfront.net
... Role of Profit • Over time, total revenue must cover total cost for the firm to survive. • When firms break even, total revenue just covers total cost. ...
... Role of Profit • Over time, total revenue must cover total cost for the firm to survive. • When firms break even, total revenue just covers total cost. ...
Chapter 4a
... producers are willing to sell during a particular time period, all else being equal. ...
... producers are willing to sell during a particular time period, all else being equal. ...
Ordering America: How the Progressive Era and the Eugenics
... teachers, philanthropists, journalists and ordinary citizens. Eugenicists believed that some “races,” classes and individuals were superior to others. They advocated for policies that created an “orderly society” based on who should be treated as superior and inferior. By examining events from this ...
... teachers, philanthropists, journalists and ordinary citizens. Eugenicists believed that some “races,” classes and individuals were superior to others. They advocated for policies that created an “orderly society” based on who should be treated as superior and inferior. By examining events from this ...
Friend, Anthony M. "Economics, Ecology and Sustainable
... control, so seductively described in Adam Smith’s metaphor of the ‘invisible hand’. The Polanyi thesis suggests that dominance of market values in human intercourse is of recent origin stemming from the machine age and the globalization of markets. Thus, what appeared as natural laws might be merely ...
... control, so seductively described in Adam Smith’s metaphor of the ‘invisible hand’. The Polanyi thesis suggests that dominance of market values in human intercourse is of recent origin stemming from the machine age and the globalization of markets. Thus, what appeared as natural laws might be merely ...
Demand PowerPoint
... • If the price changes, the law of demand says that the quantity will change. This is known as the Price Effect. It is NOT a change in demand to have the quantity change when the price changes, it is merely a movement along the curve. ...
... • If the price changes, the law of demand says that the quantity will change. This is known as the Price Effect. It is NOT a change in demand to have the quantity change when the price changes, it is merely a movement along the curve. ...
activities that support the Nature of Science strand
... ‘It is our view that developing an understanding of the NOS (Nature OF Science) does not come naturally. It is highly unlikely that students and their teachers will come to understand that science is tentative, empirically-based, partly the product of human imagination and creativity, and is influen ...
... ‘It is our view that developing an understanding of the NOS (Nature OF Science) does not come naturally. It is highly unlikely that students and their teachers will come to understand that science is tentative, empirically-based, partly the product of human imagination and creativity, and is influen ...
Midterm Two from the Morning Lecture
... How to fill in the special codes section of the scantron: 1) Write the number of the section YOU ATTEND in the special codes spaces ABC and fill in the bubbles. The discussion sections are listed on the back of the exam. 2) Write the VERSION NUMBER of the exam under special codes space D and fill in ...
... How to fill in the special codes section of the scantron: 1) Write the number of the section YOU ATTEND in the special codes spaces ABC and fill in the bubbles. The discussion sections are listed on the back of the exam. 2) Write the VERSION NUMBER of the exam under special codes space D and fill in ...
AP Microeconomics
... 6.) Know how to apply the Optimal Purchase Rule (allows you to determine the number of units of a particular product a consumer will buy to maximize consumer surplus). 7.) Know how to calculate a consumer’s optimal consumption bundle (Module 51 -states that a consumer will maximize her satisfaction ...
... 6.) Know how to apply the Optimal Purchase Rule (allows you to determine the number of units of a particular product a consumer will buy to maximize consumer surplus). 7.) Know how to calculate a consumer’s optimal consumption bundle (Module 51 -states that a consumer will maximize her satisfaction ...
EC 332U: Economics of Environmental Issues Department of
... ISBN–9781597260473: Markets and the Environment by Nathaniel Keohane & Sheila Olmstead (June 2007, Island Press). This book is abbreviated as “KO” on the next page. ISBN–9781121935631: Custom Reader (2013, McGraw-Hill Online). This is book is abbreviated as “CR”. The first book is available at PSU B ...
... ISBN–9781597260473: Markets and the Environment by Nathaniel Keohane & Sheila Olmstead (June 2007, Island Press). This book is abbreviated as “KO” on the next page. ISBN–9781121935631: Custom Reader (2013, McGraw-Hill Online). This is book is abbreviated as “CR”. The first book is available at PSU B ...
Summation of Demand, Consumer Surplus and Network Externality
... The idea of Externality The idea of externality is that what an agent—could be an individual or a firm— does have effect on others; since the agent acts according to her private benefit and cost, this effect on others is not taken into consideration in her choice. If the effect is positive we call i ...
... The idea of Externality The idea of externality is that what an agent—could be an individual or a firm— does have effect on others; since the agent acts according to her private benefit and cost, this effect on others is not taken into consideration in her choice. If the effect is positive we call i ...
Lecture notes
... FIGURE 3-1 Production Frontiers of Nation 1 and Nation 2 with Increasing Costs. Salvatore: International Economics, 10th Edition © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
... FIGURE 3-1 Production Frontiers of Nation 1 and Nation 2 with Increasing Costs. Salvatore: International Economics, 10th Edition © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ...
Chpt8
... The position of the short-run average total cost curve for a firm depends on the size of the plant. Each plant size can be represented by a U-shaped shortrun average total cost curve. The firm’s long-run average cost curve is the “envelope” of these and other possible short-run average total cost ...
... The position of the short-run average total cost curve for a firm depends on the size of the plant. Each plant size can be represented by a U-shaped shortrun average total cost curve. The firm’s long-run average cost curve is the “envelope” of these and other possible short-run average total cost ...