Lecture 16: Spherical Virus Structures
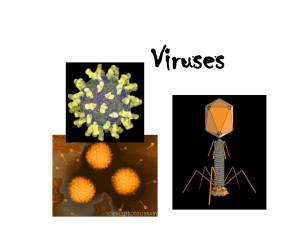
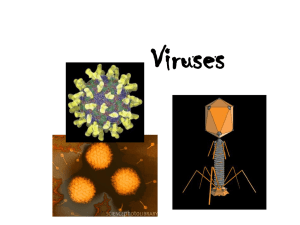
... Viruses come in many shapes, sizes and compositions All carry genomic nucleic acid (RNA or DNA) ...
... Viruses come in many shapes, sizes and compositions All carry genomic nucleic acid (RNA or DNA) ...
Viruses: Bacterial and Animal
... • Replication of viral nucleic acid (remember eukaryotic cells have a nucleus) • Uncoating step is required by animal viruses • Exit the host cell by budding or shedding ...
... • Replication of viral nucleic acid (remember eukaryotic cells have a nucleus) • Uncoating step is required by animal viruses • Exit the host cell by budding or shedding ...
Viral Disease - School Portal
... enters the nucleus of the host cell. The viral RNA polymerase is activated, and viral mRNA is formed – these move into the cytoplasm where they form new viral coats from proteins and lipids. The new virus particles are self-assembled. Finally, a late-produced enzyme causes cell lysis, and releases t ...
... enters the nucleus of the host cell. The viral RNA polymerase is activated, and viral mRNA is formed – these move into the cytoplasm where they form new viral coats from proteins and lipids. The new virus particles are self-assembled. Finally, a late-produced enzyme causes cell lysis, and releases t ...
Viruses - Chap 13 partI
... Plating efficiency - counts made by plaque assays are always lower than counts made with electron microscope. Plating efficiency with bacteriophage is usually > 50% but with some animal viruses may be <1% The plaque procedure may be used to prepare pure viral strains Cell cultures may also be ...
... Plating efficiency - counts made by plaque assays are always lower than counts made with electron microscope. Plating efficiency with bacteriophage is usually > 50% but with some animal viruses may be <1% The plaque procedure may be used to prepare pure viral strains Cell cultures may also be ...
Virus Webquest - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 3. Without a ____________________________, viruses cannot carry out their life-sustaining functions or reproduce. 4. Viruses are generally ____________________________by the organisms they ________________, animals, plants, or bacteria. 5. Viruses are further classified into families and genera base ...
... 3. Without a ____________________________, viruses cannot carry out their life-sustaining functions or reproduce. 4. Viruses are generally ____________________________by the organisms they ________________, animals, plants, or bacteria. 5. Viruses are further classified into families and genera base ...
Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus
... There may be nausea, vomiting and sore throat earlier on which may lead to diarrhea and generalized abdominal pain. ...
... There may be nausea, vomiting and sore throat earlier on which may lead to diarrhea and generalized abdominal pain. ...
tus Scrupps RrsnaRcu Ixsrrrurn - The Scripps Research Institute
... Scripps ScientistsDiscoverNew Pathway to Inhibit Spread of Viral Plant Disease ...
... Scripps ScientistsDiscoverNew Pathway to Inhibit Spread of Viral Plant Disease ...
Chapter 21 Viruses
... Living things vs Viruses Both contain protein, genetic material, and they can reproduce. Viruses cannot eat, grow, break-down food, or use oxygen. They must depend on their HOST Cell ...
... Living things vs Viruses Both contain protein, genetic material, and they can reproduce. Viruses cannot eat, grow, break-down food, or use oxygen. They must depend on their HOST Cell ...
Created with Sketch. Make an adenovirus
... 4. Before you glue the last tab, coil up the string and put it inside the virus capsid. This represents the viral DNA. 5. Cut the straws into 5 centimetre sections – you need a total of 12 for each virus. 6. Cut two slits about 2 centimetres into one end of each straw, and spread out the three ‘legs ...
... 4. Before you glue the last tab, coil up the string and put it inside the virus capsid. This represents the viral DNA. 5. Cut the straws into 5 centimetre sections – you need a total of 12 for each virus. 6. Cut two slits about 2 centimetres into one end of each straw, and spread out the three ‘legs ...
review worksheet... Comm disease
... 2. ________ A cold is caused by bacteria? 3. ________ Antigens produce a “code” that allows the body to detect certain pathogens? 4. ________ T cells and B cells are part of specific resistance? 5. ________ Ringworm is caused by a fungus? 6. ________ The rabies virus attacks the brain? 7. ________ A ...
... 2. ________ A cold is caused by bacteria? 3. ________ Antigens produce a “code” that allows the body to detect certain pathogens? 4. ________ T cells and B cells are part of specific resistance? 5. ________ Ringworm is caused by a fungus? 6. ________ The rabies virus attacks the brain? 7. ________ A ...
Viruses - SaddleSpace/Haiku
... an infectious disease at a specific time. Pandemic – a worldwide or multiple continent outbreak of an infectious disease. ...
... an infectious disease at a specific time. Pandemic – a worldwide or multiple continent outbreak of an infectious disease. ...
VIROLOGY - MCB 5505 VIRUS FAMILY: RHABDOVIRIDAE I
... capped and polyadenylated. Glycoprotein (G) and Matrix protein (M) are both involved in the envelope. The viral core is found to be infectious, which shows that transcript activity is associated with the Largest protein (L), the Nucleocapsid protein (N) and the P protein. This makes the 3 internal p ...
... capped and polyadenylated. Glycoprotein (G) and Matrix protein (M) are both involved in the envelope. The viral core is found to be infectious, which shows that transcript activity is associated with the Largest protein (L), the Nucleocapsid protein (N) and the P protein. This makes the 3 internal p ...
Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Ag Rapid Test
... sandwich lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for the qualitative detection of Infectious bursal disease virus (IBD Ag) in avian secretions. Assay Time: 5 - 10 min Sample: secretions ...
... sandwich lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for the qualitative detection of Infectious bursal disease virus (IBD Ag) in avian secretions. Assay Time: 5 - 10 min Sample: secretions ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 2. All membranes of free-living organisms have phospholipid bilayers, with the expection of a) Bacteria b) Fungi c) Archaebacteria d) Algae 3. Which of the following nucleoside diphosphates is used most often in carbohydrate anabolism? a) Uridine b) Thymosine c) Guanosine d) Adenosine 4. The transdu ...
... 2. All membranes of free-living organisms have phospholipid bilayers, with the expection of a) Bacteria b) Fungi c) Archaebacteria d) Algae 3. Which of the following nucleoside diphosphates is used most often in carbohydrate anabolism? a) Uridine b) Thymosine c) Guanosine d) Adenosine 4. The transdu ...
Viruses: viruses are not considered to be living organisms do not
... viruses invade the cells of organisms and use the metabolism of a host cell to reproduce ...
... viruses invade the cells of organisms and use the metabolism of a host cell to reproduce ...
General Virology - California State University, Fullerton
... • Small genome positive strand RNA - sequence known • Synthesized small DNA segments (~ 69 nucleotides) with ...
... • Small genome positive strand RNA - sequence known • Synthesized small DNA segments (~ 69 nucleotides) with ...
19-3 Viruses
... into the cell and is replicated along with the host cell’s DNA. Do NOT lyse the host cell away. Viral DNA becomes part of the hosts DNA…(prophage.) The prophage will remain this way for a varied amount of time. Some “factors” will activate the prophage, and the cell will start making viruses ...
... into the cell and is replicated along with the host cell’s DNA. Do NOT lyse the host cell away. Viral DNA becomes part of the hosts DNA…(prophage.) The prophage will remain this way for a varied amount of time. Some “factors” will activate the prophage, and the cell will start making viruses ...
24 Hour Fluorescent Virus Titration Assay (96
... Now remove medium from Row D 1-6 up to Row A 1-6; then add the virus from the dilution plate. Use the same tips to add the virus when moving up from Row H 1-6 to Row A 1-6, then change tips for Row H 7-12 through Row A 7-12. Take note of the time the plate is put back into the incubator. Incubate th ...
... Now remove medium from Row D 1-6 up to Row A 1-6; then add the virus from the dilution plate. Use the same tips to add the virus when moving up from Row H 1-6 to Row A 1-6, then change tips for Row H 7-12 through Row A 7-12. Take note of the time the plate is put back into the incubator. Incubate th ...
Virus/Bacterial Worksheet
... 1. Where is the genetic material in a T4 bacteriophage located? 2. In general, is the genetic material in a virus inside or outside the protein parts? 3. Why do you think the word virus, based on the Latin word for poison, was used for these structures? ...
... 1. Where is the genetic material in a T4 bacteriophage located? 2. In general, is the genetic material in a virus inside or outside the protein parts? 3. Why do you think the word virus, based on the Latin word for poison, was used for these structures? ...
Master/PhD position in cell biology of virus infection at the University
... Master/PhD position in cell biology of virus infection at the University of Cologne We offer a master and/or PhD position to join the DFG-project “Herpes simplex virus entry into skin or mucosa” with the possibility to study at the Graduate School for Biological Sciences at the Faculty of Mathematic ...
... Master/PhD position in cell biology of virus infection at the University of Cologne We offer a master and/or PhD position to join the DFG-project “Herpes simplex virus entry into skin or mucosa” with the possibility to study at the Graduate School for Biological Sciences at the Faculty of Mathematic ...
Virus quantification

Virus quantification involves counting the number of viruses in a specific volume to determine the virus concentration. It is utilized in both research and development (R&D) in commercial and academic laboratories as well as production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable. For example, the production of viral vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually adapt and monitor the process in order to optimize production yields and respond to ever changing demands and applications. Examples of specific instances where known viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization and adaptation of methods to cell culture. This page discusses various techniques currently used to quantify viruses in liquid samples. These methods are separated into two categories, traditional vs. modern methods. Traditional methods are industry-standard methods that have been used for decades but are generally slow and labor-intensive. Modern methods are relatively new commercially available products and kits that greatly reduce quantification time. This is not meant to be an exhaustive review of all potential methods, but rather a representative cross-section of traditional methods and new, commercially available methods. While other published methods may exist for virus quantification, non-commercial methods are not discussed here.