Galaxies • Test 3 (New date) – Thurs, 9 April
... There is little light beyond 7 kpc. Where there is mass there is not necessarily light from stars & gas. Extrapolate M(R) is linear beyond visible part of ...
... There is little light beyond 7 kpc. Where there is mass there is not necessarily light from stars & gas. Extrapolate M(R) is linear beyond visible part of ...
PC2491 Examples 2
... (9) The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) has a mass of 1010 Mo and is 50kpc from the centre of the Milky Way. Assume it is a circular orbit around the Milky Way with a circular velocity of 200 km/s and estimate the distance from the centre of the LMC that stars and gas will be significantly tidally affe ...
... (9) The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) has a mass of 1010 Mo and is 50kpc from the centre of the Milky Way. Assume it is a circular orbit around the Milky Way with a circular velocity of 200 km/s and estimate the distance from the centre of the LMC that stars and gas will be significantly tidally affe ...
Measuring the Stars
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
Astronomy Club of Asheville June 2016 Sky Events
... away (about half the Earth-Sun distance), and it shines at an average magnitude of -1.7 almost as bright as Jupiter! Located in the constellation Libra this month, this is a great time to look for telescopic details on the red planet. ...
... away (about half the Earth-Sun distance), and it shines at an average magnitude of -1.7 almost as bright as Jupiter! Located in the constellation Libra this month, this is a great time to look for telescopic details on the red planet. ...
JPL Small-Body Database Browser
... Proper Motion Proper motion was discovered by Edmund Halley. He compared the positions of bright stars that had been recorded by (Ptolemy). http://www.hwy.com.au/~sjquirk/images/film/barnard.html Barnard’s Star has the highest known proper motion of 10.3”/year. Even at that rate, Barnard’s Star wil ...
... Proper Motion Proper motion was discovered by Edmund Halley. He compared the positions of bright stars that had been recorded by (Ptolemy). http://www.hwy.com.au/~sjquirk/images/film/barnard.html Barnard’s Star has the highest known proper motion of 10.3”/year. Even at that rate, Barnard’s Star wil ...
The Universe and Galaxies - West Jefferson Local Schools
... might be causing accelerated expansion of the universe ...
... might be causing accelerated expansion of the universe ...
Suns .n. Stars
... The Sun! • The sun is 150 million kilometres away from Earth. • The sun rises in the east every morning. • The sun gives us light and heat. • The sun has a core in the centre of it. • The sun is about 5,000 degrees but the core is 3 times as hot. • It takes light about 8 minutes 70 seconds to get f ...
... The Sun! • The sun is 150 million kilometres away from Earth. • The sun rises in the east every morning. • The sun gives us light and heat. • The sun has a core in the centre of it. • The sun is about 5,000 degrees but the core is 3 times as hot. • It takes light about 8 minutes 70 seconds to get f ...
Earth
... hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silicon, magnesium and sulfur. The sun shines because it is burning hydrogen into helium in its extremely hot core. This mea ...
... hydrogen (about 70%) and helium (about 28%). Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen make up 1.5% and the other 0.5% is made up of small amounts of many other elements such as neon, iron, silicon, magnesium and sulfur. The sun shines because it is burning hydrogen into helium in its extremely hot core. This mea ...
Review 2
... Internal structure of our Sun and its chemical composition. What is the convection zone on the Sun and what are the granules and supergranules? What is the temperature in the Sun’s core? What is the photosphere, chromosphere and corona? What is their temperature and what causes their color? What is ...
... Internal structure of our Sun and its chemical composition. What is the convection zone on the Sun and what are the granules and supergranules? What is the temperature in the Sun’s core? What is the photosphere, chromosphere and corona? What is their temperature and what causes their color? What is ...
Antares - Emmi
... the suns 5700 degrees Kelvin.( Kelvin is unit used to measure incredibly hot objects or stars Kelvin is 272 degrees Celsius) Even though Antares is much colder it is brighter because it is much larger ...
... the suns 5700 degrees Kelvin.( Kelvin is unit used to measure incredibly hot objects or stars Kelvin is 272 degrees Celsius) Even though Antares is much colder it is brighter because it is much larger ...
1201 Discussion Notes
... hydrogen supply?" are: "Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger and brighter," which is true for LOW-mass stars, and "Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger but cooler and therefore remains at the same brightness," which is tru ...
... hydrogen supply?" are: "Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger and brighter," which is true for LOW-mass stars, and "Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger but cooler and therefore remains at the same brightness," which is tru ...
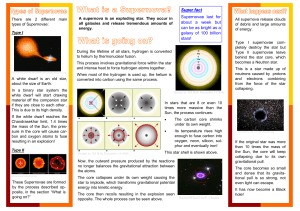
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
Chapter 28 Stars and Galaxies Reading Guide
... 15. The Sun has an apparent magnitude of –26.7. A friend tells you about a star that also has a magnitude of –26.7. How could this be true? The friend can be referring to absolute magnitude and not apparent magnitude ...
... 15. The Sun has an apparent magnitude of –26.7. A friend tells you about a star that also has a magnitude of –26.7. How could this be true? The friend can be referring to absolute magnitude and not apparent magnitude ...
After Dark in Allenspark
... Jupiter) orbits Ed. Ed tugs on the planet, but the planet tugs on Ed a little too, so both Ed and the planet orbit around an imaginary point called the "center of mass." Ed is about one million times more massive than its planet, so the center of mass is almost at Ed's center, but shifted a little b ...
... Jupiter) orbits Ed. Ed tugs on the planet, but the planet tugs on Ed a little too, so both Ed and the planet orbit around an imaginary point called the "center of mass." Ed is about one million times more massive than its planet, so the center of mass is almost at Ed's center, but shifted a little b ...
Multiple Choice, continued
... come from Latin. • Some constellations are named for real or imaginary animals, such as Ursa Major (the great bear) or ancient gods or legendary heroes, such as Hercules or Orion. ...
... come from Latin. • Some constellations are named for real or imaginary animals, such as Ursa Major (the great bear) or ancient gods or legendary heroes, such as Hercules or Orion. ...
WebQuest-The-Life-Cycle-of-Stars-1
... 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
... 3. You will also begin to understand the forces involved in stars that maintain this nuclear reaction and how these forces change as the star ages. 4. You will explore the stages stars progress through from birth to death and how the death of a star depends on its initial mass. ...
Quiz Chapter 10 Answers
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
... Quiz Chapter 10 Answers 10-1. Protostars are not seen in visible light telescopes because: a) they don’t emit any radiation b) they are surrounded by clouds of gas and dust X c) they only emit infrared radiation d) they are all moving away from Earth so fast that their visible light is Doppler shift ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.