_____ 1. Which of the following statements is NOT true about stars
... a. A star begins its life as a ball of gas and dust. b. As stars get older, they lose some of their material. c. Stars last forever. d. New stars form from the material of old stars. 2. During a star’s life cycle, hydrogen changes to helium in a process called __________________ __________________. ...
... a. A star begins its life as a ball of gas and dust. b. As stars get older, they lose some of their material. c. Stars last forever. d. New stars form from the material of old stars. 2. During a star’s life cycle, hydrogen changes to helium in a process called __________________ __________________. ...
The Life of a Star - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
... Young star clusters give insight into star formation and evolution • Newborn stars may form an open or galactic cluster • Stars are held together in such a cluster by gravity • Occasionally a star moving more rapidly than average will escape, or leave the cluster • A stellar association is a group ...
Astronomy
... pull on their stars, making them wobble like a large dog who walks its owner. You can often tell that a dog is walking it’s owner without seeing the dog, as you watch the person being pulled this way and that. This is how scientists detect massive planet that are far away. They look for stars that a ...
... pull on their stars, making them wobble like a large dog who walks its owner. You can often tell that a dog is walking it’s owner without seeing the dog, as you watch the person being pulled this way and that. This is how scientists detect massive planet that are far away. They look for stars that a ...
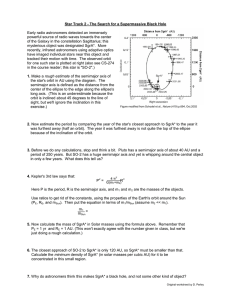
Star Track 2 - The Search for a Supermassive Black... Early radio astronomers detected an immensely
... powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tracked their motion with time. The observed orbi ...
... powerful source of radio waves towards the center of the Galaxy in the constellation Sagittarius; this mysterious object was designated SgrA*. More recently, infrared astronomers using adaptive optics have imaged individual stars near this object and tracked their motion with time. The observed orbi ...
Star Life Cycle
... Helium fuses to form Carbon, and the core shrinks. It begins losing outer layers ...
... Helium fuses to form Carbon, and the core shrinks. It begins losing outer layers ...
PHYSICS 1500 - ASTRONOMY TOTAL: 100 marks Section A Please
... (a) These are clearly the most common type of planet. (b) Smaller, rocky planets always lie closer to the star but are undetectable. (c) Few planetary systems have giant planets more than 1 AU from the star. (d) Detection of less massive planets is currently very difficult. (e) Detection of planets ...
... (a) These are clearly the most common type of planet. (b) Smaller, rocky planets always lie closer to the star but are undetectable. (c) Few planetary systems have giant planets more than 1 AU from the star. (d) Detection of less massive planets is currently very difficult. (e) Detection of planets ...
Lecture5 - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... Also Sun • “Spiral Nebulae” are outside our Galaxy • “Spiral Nebulae” are systems of stars, i.e., other galaxies • Slipher’s spectroscopic measurements high radial velocities • Showed photos of spiral nebulae – with absorbing bands ...
... Also Sun • “Spiral Nebulae” are outside our Galaxy • “Spiral Nebulae” are systems of stars, i.e., other galaxies • Slipher’s spectroscopic measurements high radial velocities • Showed photos of spiral nebulae – with absorbing bands ...
part 2 - Stardome
... layers will spread out, form size of Earth). the out (ab white dwarf star Sun will become a dense rs, but the yea of disperse over thousands universe. The planetary nebula will the in of w kno we ger than anything white dwarf will last lon can continue times larger than the Sun Stars that are about ...
... layers will spread out, form size of Earth). the out (ab white dwarf star Sun will become a dense rs, but the yea of disperse over thousands universe. The planetary nebula will the in of w kno we ger than anything white dwarf will last lon can continue times larger than the Sun Stars that are about ...
Properties of Ellipticals and Spirals
... • They do Not have a Disk; • They are tri-axial (comparable to a football); • They do not have dust; • They do NOT have hot young stars; most stars have formed a long time ago; • Their colors are red not because of reddening by ...
... • They do Not have a Disk; • They are tri-axial (comparable to a football); • They do not have dust; • They do NOT have hot young stars; most stars have formed a long time ago; • Their colors are red not because of reddening by ...
Lecture 17 Review
... Interstellar extinction - When enough gas and dust is in the way, far away objects cannot be seen because light is scattered out of the line of sight. Thus, we cannot see the galactic center with visible light. That these clouds are the source of stars follows from several observations: ...
... Interstellar extinction - When enough gas and dust is in the way, far away objects cannot be seen because light is scattered out of the line of sight. Thus, we cannot see the galactic center with visible light. That these clouds are the source of stars follows from several observations: ...
Earth
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 •
... greater than the planets, so... G (Recall first week’s studio laboratory) ...
... greater than the planets, so... G (Recall first week’s studio laboratory) ...
About SDSS - Astro Projects
... SDSS mainly imaged the area around the North Galactic Pole (RA = 193 deg, Dec = 27 deg). This is a point directly 'above' our position in the Milky Way Galaxy. Because of this the survey includes hardly any supernova remnants or planetary nebulae. This is because these objects are remnants of dead s ...
... SDSS mainly imaged the area around the North Galactic Pole (RA = 193 deg, Dec = 27 deg). This is a point directly 'above' our position in the Milky Way Galaxy. Because of this the survey includes hardly any supernova remnants or planetary nebulae. This is because these objects are remnants of dead s ...
Exam Study Guide
... 66. • The absolute magnitude of Aldebaran B ❆ (See Reference Item 3.) 67. • The spectral type of Rigel B ❆ (See Reference Item 3.) 68. A Bright Giant star has a temperature of 10,000 K. Which of these is a best estimate of its luminosity? ❆ (See Reference Item 5.) 69. A binary star system might hav ...
... 66. • The absolute magnitude of Aldebaran B ❆ (See Reference Item 3.) 67. • The spectral type of Rigel B ❆ (See Reference Item 3.) 68. A Bright Giant star has a temperature of 10,000 K. Which of these is a best estimate of its luminosity? ❆ (See Reference Item 5.) 69. A binary star system might hav ...
5-E Galaxy T - McDonald Observatory
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
Chapter13
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
... dwarfs are found in the lower left corner of the HertzsprungRussell diagram. The more massive a white dwarf, the smaller it is! ...
Phobos
... similar to those of extra-solar giant planets, usually found in orbit around a star. The researchers discovered the companion candidate in an optical image taken with ESO's 3.5-m New Technology Telescope on La Silla, Chile,and investigated it further with the 8.2-m Very Large Telescope on Paranal. T ...
... similar to those of extra-solar giant planets, usually found in orbit around a star. The researchers discovered the companion candidate in an optical image taken with ESO's 3.5-m New Technology Telescope on La Silla, Chile,and investigated it further with the 8.2-m Very Large Telescope on Paranal. T ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E2
... As the stars rotate, their velocity changes direction. When they move at right angles to the line of sight there is no Doppler shift (first and third diagram). When the faster of the two stars approaches the earth it suffers a blueshift and the slow star a smaller redshift (second diagram). In the f ...
... As the stars rotate, their velocity changes direction. When they move at right angles to the line of sight there is no Doppler shift (first and third diagram). When the faster of the two stars approaches the earth it suffers a blueshift and the slow star a smaller redshift (second diagram). In the f ...
Cosmic context: stars and formation of heavy elements
... Classification of stars Mass of stars ranges from ~0.1 Solar masses up to ~100 Solar masses. Low mass stars are much more common than high mass stars. Low mass stars: M < 2 Solar masses Greatest interest for astrobiology as long lived: “main sequence” lifetime (while fusing H -> He in the core) is b ...
... Classification of stars Mass of stars ranges from ~0.1 Solar masses up to ~100 Solar masses. Low mass stars are much more common than high mass stars. Low mass stars: M < 2 Solar masses Greatest interest for astrobiology as long lived: “main sequence” lifetime (while fusing H -> He in the core) is b ...
1. absolute brightness -
... lines observed, originally the amount of Hydrogen the lines seemed to indicate. • Today they are ranked in order of surface temperature. O, B, A, F, G, K, M from ...
... lines observed, originally the amount of Hydrogen the lines seemed to indicate. • Today they are ranked in order of surface temperature. O, B, A, F, G, K, M from ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.