The Galaxy–Dark Matter Connection
... Satellites more concentrated than centrals @ fixed stellar mass. However: Fraction of galaxies with C>3 ~ is the same! Ellipticals are not produced by environmental processes acting on satellites ...
... Satellites more concentrated than centrals @ fixed stellar mass. However: Fraction of galaxies with C>3 ~ is the same! Ellipticals are not produced by environmental processes acting on satellites ...
The Milky Way: Spiral galaxies:
... atoms become frequent enough to form molecules. •! The most common molecule is H2, but since H2 is a symmetric molecule, it has no rotational quantum transitions. It is therefore extremely difficult to detect. •! As a tracer of H2, astronomers usually use CO •! Ratio of CO/H2 is ~6 x 10-5 •! CO is g ...
... atoms become frequent enough to form molecules. •! The most common molecule is H2, but since H2 is a symmetric molecule, it has no rotational quantum transitions. It is therefore extremely difficult to detect. •! As a tracer of H2, astronomers usually use CO •! Ratio of CO/H2 is ~6 x 10-5 •! CO is g ...
Triple Conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn
... Everything in the wide universe, except the Paradise, is nonstationary and constantly moving. Our Superuniverse, Orvonton, together with all its components, including Nebadon, are moving. However, the conjunctions of planets are relative to the earth. Thus, in these diagrams the earth is held statio ...
... Everything in the wide universe, except the Paradise, is nonstationary and constantly moving. Our Superuniverse, Orvonton, together with all its components, including Nebadon, are moving. However, the conjunctions of planets are relative to the earth. Thus, in these diagrams the earth is held statio ...
+(J - cloudfront.net
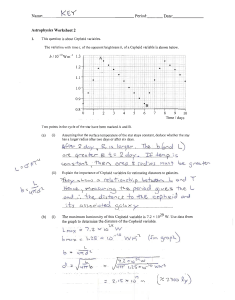
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
... spectrum and temperature of a certain star are used to determine its luminosity to be approximately 5.0 x 1031 W. The '!Pparent brightness of the star is 1.4 x 10-9 W m-2. These data can be used to detennine the distance ofihe'staifromEarth~------""----..-.--..---- - - ..(i) ...
Celestial Distances
... Their periods are always less than one day, and their changes in brightness are typically less than about a factor of 2 From observations, astronomers have concluded that RR Lyrae variables all have nearly the same intrinsic luminosity, of about 50 times that of the Sun Thus, they are like standard ...
... Their periods are always less than one day, and their changes in brightness are typically less than about a factor of 2 From observations, astronomers have concluded that RR Lyrae variables all have nearly the same intrinsic luminosity, of about 50 times that of the Sun Thus, they are like standard ...
TMSP Stellar Evolution & Life
... laboratories with elements heated to gaseous states, we now have a catalog of elemental spectra. •Using this catalog, we now look at stars through a spectroscope and see what they’re made of… ...
... laboratories with elements heated to gaseous states, we now have a catalog of elemental spectra. •Using this catalog, we now look at stars through a spectroscope and see what they’re made of… ...
Compact stars
... 3. Neutron stars The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant containing the Crab Pulsar, a neutron star. Main article: Neutron star In certain binary stars containing a white dwarf, mass is transferred from the companion star onto the white dwarf, eventually pushing it over the Chandrasekhar limit. Elect ...
... 3. Neutron stars The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant containing the Crab Pulsar, a neutron star. Main article: Neutron star In certain binary stars containing a white dwarf, mass is transferred from the companion star onto the white dwarf, eventually pushing it over the Chandrasekhar limit. Elect ...
HR DIAGRAM[1] Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same
... HR DIAGRAM1 Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same? Not in the least! Some stars are just beginning to form in nebulae, others are enjoying middle age along the main sequence, and some have begun to die. The life cycle of a star can be compared to the life cycle of humans. Before you were born ...
... HR DIAGRAM1 Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same? Not in the least! Some stars are just beginning to form in nebulae, others are enjoying middle age along the main sequence, and some have begun to die. The life cycle of a star can be compared to the life cycle of humans. Before you were born ...
Robert_Minchin_Galaxies_2011_REU
... tells us how gas-rich a galaxy is. – Gas-rich galaxies are often blue, late-type galaxies with active star formation. – Some are more intriguing objects with low SF rates. A number of these have been turned up by HI surveys. ...
... tells us how gas-rich a galaxy is. – Gas-rich galaxies are often blue, late-type galaxies with active star formation. – Some are more intriguing objects with low SF rates. A number of these have been turned up by HI surveys. ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
... • Stars “move” East to West over the course of one Night (in circle about the North Star) • Stars “move” East to West by 2 hours per month and “return” to the same position after one Year • It’s just caused by Earth’s daily spin and yearly orbit about the Sun • Star wheel depends on latitude: northe ...
Chap. 02
... • The apparent displacement of a nearby object against a distant fixed background from two different viewpoints. ...
... • The apparent displacement of a nearby object against a distant fixed background from two different viewpoints. ...
The supernova of AD1181 – an update
... Recently it has become clear that not only is 3C 58 much less luminous than the Crab nebula, despite being about the same age, but also that (see Green and Scheuer 1993 or Woltjer et al. 1997) the form of its synchrotron spectrum is quite different from that of the Crab. The flat radio spectra of th ...
... Recently it has become clear that not only is 3C 58 much less luminous than the Crab nebula, despite being about the same age, but also that (see Green and Scheuer 1993 or Woltjer et al. 1997) the form of its synchrotron spectrum is quite different from that of the Crab. The flat radio spectra of th ...
thefixedstarsinnatal.. - Saptarishis Astrology
... The fixed stars operate by position and are said to "cast no rays," or in other words their aspects are said to be ineffective and their influence to be exerted only by conjunction and parallel. As in the case of the planets they are most powerful when in angles and weak when cadent, their effect b ...
... The fixed stars operate by position and are said to "cast no rays," or in other words their aspects are said to be ineffective and their influence to be exerted only by conjunction and parallel. As in the case of the planets they are most powerful when in angles and weak when cadent, their effect b ...
Additional Cosmology Images
... Why is this galaxy, NGC 5866, so thin? Many disk galaxies are actually just as thin as NGC 5866, but are not seen edge-on from our vantage point. One galaxy that is situated edge-on is the Milky Way. Classified as a lenticular galaxy, NGC 5866 has numerous and complex dust lanes appearing dark and r ...
... Why is this galaxy, NGC 5866, so thin? Many disk galaxies are actually just as thin as NGC 5866, but are not seen edge-on from our vantage point. One galaxy that is situated edge-on is the Milky Way. Classified as a lenticular galaxy, NGC 5866 has numerous and complex dust lanes appearing dark and r ...
Globular Clusters - Lick Observatory
... Picking and Choosing We have a big pile of stars, now what? ...
... Picking and Choosing We have a big pile of stars, now what? ...
2012-13_1st_Sem_Final_ SG
... Use the chapters in the textbook The Cosmos: Astronomy in the New Millennium by Pasachoff & Filippenko as a resource, either 2nd or 3rd edition. Not everything in every chapter will be on the final. Constellations (Chp 1; Chp 4 pg 63-67; A Walk Through the Sky (small textbook); Star Charts) Why aren ...
... Use the chapters in the textbook The Cosmos: Astronomy in the New Millennium by Pasachoff & Filippenko as a resource, either 2nd or 3rd edition. Not everything in every chapter will be on the final. Constellations (Chp 1; Chp 4 pg 63-67; A Walk Through the Sky (small textbook); Star Charts) Why aren ...
Lecture 9a: More on Star formation and evolution 10/22
... stars with the same age but different masses • Birth ! Main Sequence " Red Giant ! “live+die” faster if higher mass • Tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
... stars with the same age but different masses • Birth ! Main Sequence " Red Giant ! “live+die” faster if higher mass • Tell age of cluster by most massive star still on Main Sequence ...
ph512-11-lec5
... This gives a biased estimate of the centroid in the presence of an asymmetric PSF. PSP uses bright stars to determine the shape of the PSF as a smoothly varying function of CCD column and row for each frame. Thus, the PSF at the position of each object is determined to high accuracy. The centroid of ...
... This gives a biased estimate of the centroid in the presence of an asymmetric PSF. PSP uses bright stars to determine the shape of the PSF as a smoothly varying function of CCD column and row for each frame. Thus, the PSF at the position of each object is determined to high accuracy. The centroid of ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... being able to penetrate through dust and gas. Thus, even though the protostars are invisible behind a cloud of gas and dust, their IR radiation penetrates the gas and dust and they can been “seen” at IR wavelengths. 4. How do T-Tauri stars get rid of the surrounding gas and dust from which they form ...
... being able to penetrate through dust and gas. Thus, even though the protostars are invisible behind a cloud of gas and dust, their IR radiation penetrates the gas and dust and they can been “seen” at IR wavelengths. 4. How do T-Tauri stars get rid of the surrounding gas and dust from which they form ...
The Hubble Redshift Distance Relation
... background noise. The higher the Signal/Noise, the stronger the signal. Record the relavent data in the chart at the end of the lab. • Continue collecting photons until you reach a Signal/Noise of at least 10.0. Once you have reached this value, click Stop Count. If at any time you need to collect m ...
... background noise. The higher the Signal/Noise, the stronger the signal. Record the relavent data in the chart at the end of the lab. • Continue collecting photons until you reach a Signal/Noise of at least 10.0. Once you have reached this value, click Stop Count. If at any time you need to collect m ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.






![HR DIAGRAM[1] Star Human Comparison Are all stars the same](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010665051_1-e4f26b4aee29f3f3aaab891d368963d6-300x300.png)