MESSIER - EarthLink
... His first own deep sky discovery of globular cluster M3, cataloged on May 3, probably causes him to undertake a systematical search for nebulous objects, leading to the observation and recording of the objects M3-M40, many of which were own discoveries, but several from old catalogs. Messier was mad ...
... His first own deep sky discovery of globular cluster M3, cataloged on May 3, probably causes him to undertake a systematical search for nebulous objects, leading to the observation and recording of the objects M3-M40, many of which were own discoveries, but several from old catalogs. Messier was mad ...
The Astronomical Unit and Parallax Laboratory Worksheet
... the Earth. The wavelength range shown is the same tiny portion of the spectrum shown in the bottom panel of the earlier figure, and the same two prominent iron lines are seen. From laboratory ...
... the Earth. The wavelength range shown is the same tiny portion of the spectrum shown in the bottom panel of the earlier figure, and the same two prominent iron lines are seen. From laboratory ...
Naked Eye, Binocular, or Small Backyard Telescope Night Sky
... Basic Scientific Content Information about what you can see in the night sky with your naked eye, binoculars, or a small telescope: 1.) The Moon – The Moon is the only natural satelli ...
... Basic Scientific Content Information about what you can see in the night sky with your naked eye, binoculars, or a small telescope: 1.) The Moon – The Moon is the only natural satelli ...
creation of a cosmology: big bang theory _eng
... that the Cosmic Background Radiation of the Big Bang should be about 3° above absolute zero. Dicke's colleague Jim Peebles also concluded that when the Fireball's remnants cooled to 3000° Kelvin nuclei would be able to form and helium was able to form from hydrogen. This left a universe with a mixtu ...
... that the Cosmic Background Radiation of the Big Bang should be about 3° above absolute zero. Dicke's colleague Jim Peebles also concluded that when the Fireball's remnants cooled to 3000° Kelvin nuclei would be able to form and helium was able to form from hydrogen. This left a universe with a mixtu ...
astrocoursespring2012lec4
... By now we have studied and observed clusters within the disk of our galaxy and in our western sky in the Spring. These clusters are thousand or so light years away. They also are known to be in the active process of star formation. Now it is time to go beyond the disk of the Milky way to observe Glo ...
... By now we have studied and observed clusters within the disk of our galaxy and in our western sky in the Spring. These clusters are thousand or so light years away. They also are known to be in the active process of star formation. Now it is time to go beyond the disk of the Milky way to observe Glo ...
aaswinter06
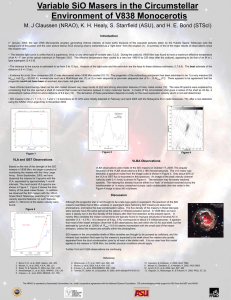
... • The detailed light curve is unlike that of a supernova, nova, or any other type of variable star (1,2,3). During the outburst, V838 Mon was found to have a maximum effective temperature of an A – F star at the optical maximum in February 2002. The effective temperature then cooled to a very low ~8 ...
... • The detailed light curve is unlike that of a supernova, nova, or any other type of variable star (1,2,3). During the outburst, V838 Mon was found to have a maximum effective temperature of an A – F star at the optical maximum in February 2002. The effective temperature then cooled to a very low ~8 ...
ADAS Simple Guide to Telescope Instrumentation and Operation
... terrestrial use, must be fitted with some kind of erector device which, by inverting the image again, erects it. But this disadvantage is amply compensated for by a much greater and more evenly illuminated field of view than that of the Galilean telescopes. ...
... terrestrial use, must be fitted with some kind of erector device which, by inverting the image again, erects it. But this disadvantage is amply compensated for by a much greater and more evenly illuminated field of view than that of the Galilean telescopes. ...
1. setting the scene 2. the cosmic dark ages and the first stars
... Max Pettini Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge Abstract. Astronomers have now at their disposal telescopes and instruments which allow them to look back in time over most of the history of the Universe, from the present epoch to less than a billion years after the Big Bang, when the Uni ...
... Max Pettini Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge Abstract. Astronomers have now at their disposal telescopes and instruments which allow them to look back in time over most of the history of the Universe, from the present epoch to less than a billion years after the Big Bang, when the Uni ...
ncam-program-2016 - Cline Observatory
... projected image looks as it should. This presentation will outline the design and construction process, and highlight what I would do differently if building another. ...
... projected image looks as it should. This presentation will outline the design and construction process, and highlight what I would do differently if building another. ...
VLT/FORS Surveys of Wolf-Rayet Stars beyond the
... slit loss corrected He ii λ 1640 line flux, in excellent agreement with optical results. Our HST/STIS result is however a factor of 35(!) times lower than that inferred from the same data set by Chandar et al. (2004). The discrepancy is primarily due to an anomalously high far-UV-derived extinction ...
... slit loss corrected He ii λ 1640 line flux, in excellent agreement with optical results. Our HST/STIS result is however a factor of 35(!) times lower than that inferred from the same data set by Chandar et al. (2004). The discrepancy is primarily due to an anomalously high far-UV-derived extinction ...
Mass Outflow in the Seyfert 1 Galaxy NGC 4151
... than estimated from luminosity – halos 10 to 20 times larger than visible parts of galaxies so, 10 x more mass ...
... than estimated from luminosity – halos 10 to 20 times larger than visible parts of galaxies so, 10 x more mass ...
The Cosmic Near-Infrared Background: Remnant light form
... The black data points between 1 and 300 microns on this graph come from the DIRBE experiment on the COBE satellite. The red data points are from Wright, E.L. 2001 (ApJ, 553, 538) which use a different zodiacal light model than the one used by Hauser et al. (1998, ApJ, 508, 25). The blue lower limit ...
... The black data points between 1 and 300 microns on this graph come from the DIRBE experiment on the COBE satellite. The red data points are from Wright, E.L. 2001 (ApJ, 553, 538) which use a different zodiacal light model than the one used by Hauser et al. (1998, ApJ, 508, 25). The blue lower limit ...
Unit 1
... of a single interstellar cloud of gas and dust • These groups are called star clusters • Open clusters have a low density of stars – there is lots of space between the cluster’s members • They can contain up to a few thousand stars in a volume 14 to 40 light years across • The Pleiades is a very fam ...
... of a single interstellar cloud of gas and dust • These groups are called star clusters • Open clusters have a low density of stars – there is lots of space between the cluster’s members • They can contain up to a few thousand stars in a volume 14 to 40 light years across • The Pleiades is a very fam ...
Black Holes & Quasars—18 Nov • Black hole • Quasar Ast 207 F2009
... 1 LY Using “adaptive optics” technique on Gemini 8m telescope. ...
... 1 LY Using “adaptive optics” technique on Gemini 8m telescope. ...
OSP2016Level 3 Map - Oregon Star Party
... experience or a 20 inch telescope to be successful – although in some cases that will help. The only way to see these cool objects for yourself is to give them a go. The minimum aperture listed for each object is a rough estimate. The idea is to show approximately what size telescope might be need ...
... experience or a 20 inch telescope to be successful – although in some cases that will help. The only way to see these cool objects for yourself is to give them a go. The minimum aperture listed for each object is a rough estimate. The idea is to show approximately what size telescope might be need ...
What is it? - Carmenes - Calar Alto Observatory
... stars with very low masses. With 1 m/s-class stability in the near infrared and simultaneous monitoring of activity indicators in the visible, exoearths can be detected in the habitable zones of several of the targeted M dwarfs, some of which may also be transiting. The instrument is well-suited for ...
... stars with very low masses. With 1 m/s-class stability in the near infrared and simultaneous monitoring of activity indicators in the visible, exoearths can be detected in the habitable zones of several of the targeted M dwarfs, some of which may also be transiting. The instrument is well-suited for ...
Dark Matter— More Than Meets The Eye
... maxi- or mini- black holes. Or massive cold gas clouds. All these phenomena are baryonic. There is some observational evidence for the existence of MACHOs. Because they can warp space enough to focus light from a distant star, MACHOs have played a critical role in a number of microlensing events in ...
... maxi- or mini- black holes. Or massive cold gas clouds. All these phenomena are baryonic. There is some observational evidence for the existence of MACHOs. Because they can warp space enough to focus light from a distant star, MACHOs have played a critical role in a number of microlensing events in ...
Powerpoint Review
... A nebula condensed into a protostar The protostar formed a main sequence star The sun is currently a main sequence star. More specifically the sun is in the middle of its main sequence stage. At some point in the future, the sun will end its main sequence stage and it will begin to swell to form a r ...
... A nebula condensed into a protostar The protostar formed a main sequence star The sun is currently a main sequence star. More specifically the sun is in the middle of its main sequence stage. At some point in the future, the sun will end its main sequence stage and it will begin to swell to form a r ...
Measuring Interstellar Extinction
... appearing in the form of dark regions, is that of Sir William Herschel who in 1784 observed a section of the sky containing no stars. The nature of such dark spots remained a mystery through many years, even as late as the publication of the famous Atlas of the Selected Regions of the Milky Way by E ...
... appearing in the form of dark regions, is that of Sir William Herschel who in 1784 observed a section of the sky containing no stars. The nature of such dark spots remained a mystery through many years, even as late as the publication of the famous Atlas of the Selected Regions of the Milky Way by E ...
There are billions of galaxies, many containing
... determine how bright the star actually is, which is called ...
... determine how bright the star actually is, which is called ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.