Galaxy Zoo: Pre and post‐workshop information
... distance of distant galaxies i.e. more distant galaxies are receding faster. The gradient of this graph is called H0 (Hubble’s constant), this gives the time since the Big Bang i.e. the age of the universe. The most accurate value for the Hubble constant has been determined using a different techniqu ...
... distance of distant galaxies i.e. more distant galaxies are receding faster. The gradient of this graph is called H0 (Hubble’s constant), this gives the time since the Big Bang i.e. the age of the universe. The most accurate value for the Hubble constant has been determined using a different techniqu ...
Historical overview
... “Their analogy with the stellar system in which we find ourselves, their shape, which is just what it ought to be according to our theory, the feebleness of their light which demands a presupposed infinite distance: all this is in perfect harmony with the view that these elliptical figures are just ...
... “Their analogy with the stellar system in which we find ourselves, their shape, which is just what it ought to be according to our theory, the feebleness of their light which demands a presupposed infinite distance: all this is in perfect harmony with the view that these elliptical figures are just ...
gravity - in a secure place with other
... Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND): empirically fits the data as well as the Dark Matter Theory But MOND violates the Equivalence Principle therefore if its correct, Einstein’s theory has a major ...
... Modified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND): empirically fits the data as well as the Dark Matter Theory But MOND violates the Equivalence Principle therefore if its correct, Einstein’s theory has a major ...
WEDNESDAY JULY 1
... within 100 ly of Earth could be catastrophic for us. How would you go about determining if you were in any danger from it? ...
... within 100 ly of Earth could be catastrophic for us. How would you go about determining if you were in any danger from it? ...
stars - Legacy High School
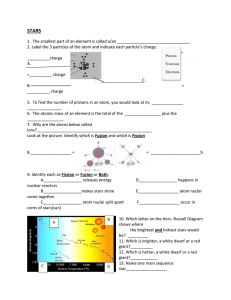
... 16. The less massive stars end their lifecycle as a _____________ ___________________. 17. The most massive stars will end up as a ___________________ _______________. 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving aw ...
... 16. The less massive stars end their lifecycle as a _____________ ___________________. 17. The most massive stars will end up as a ___________________ _______________. 18. When nuclear fusion is occurring in a star, the element_____________ fuses to form______________. 19. When objects are moving aw ...
大爆炸---宇宙的起源 - 中正大學化學系
... point, a "primeval atom" where and when the fabric of time and space came into existence. Lemaître's Big Bang theory was advocated and developed by George Gamow, who introduced big bang nucleosynthesis (BBN) and whose associates, Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman, predicted the cosmic microwave backgro ...
... point, a "primeval atom" where and when the fabric of time and space came into existence. Lemaître's Big Bang theory was advocated and developed by George Gamow, who introduced big bang nucleosynthesis (BBN) and whose associates, Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman, predicted the cosmic microwave backgro ...
大爆炸---宇宙的起源
... point, a "primeval atom" where and when the fabric of time and space came into existence. Lemaître's Big Bang theory was advocated and developed by George Gamow, who introduced big bang nucleosynthesis (BBN) and whose associates, Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman, predicted the cosmic microwave backgro ...
... point, a "primeval atom" where and when the fabric of time and space came into existence. Lemaître's Big Bang theory was advocated and developed by George Gamow, who introduced big bang nucleosynthesis (BBN) and whose associates, Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman, predicted the cosmic microwave backgro ...
cosmological horizon
... How do galaxies form, and how do they change over time? Why do we see so many different kinds of galaxies? Are their differences a result of ‘nature’ or ‘nurture’? How do the properties of galaxies depend on their environment? ...
... How do galaxies form, and how do they change over time? Why do we see so many different kinds of galaxies? Are their differences a result of ‘nature’ or ‘nurture’? How do the properties of galaxies depend on their environment? ...
P1 - Foundation
... • all the galaxies are moving away from us (red shift) • the further away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away. (red shift) • Scientists have also detected a cosmic microwave background radiation or CMBR. This is received from all parts of the Universe and is thought to be the heat left over fr ...
... • all the galaxies are moving away from us (red shift) • the further away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away. (red shift) • Scientists have also detected a cosmic microwave background radiation or CMBR. This is received from all parts of the Universe and is thought to be the heat left over fr ...
8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae
... 8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification ...
... 8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification ...
123mt13a
... A basic assumption in any Cosmological model is that the Universe Contains matter (not necessary) Is expanding Is infinite in extent Is governed by only a small number of fundamental forces (e.g. 4) Is homogeneous on some size scale ...
... A basic assumption in any Cosmological model is that the Universe Contains matter (not necessary) Is expanding Is infinite in extent Is governed by only a small number of fundamental forces (e.g. 4) Is homogeneous on some size scale ...
The Merger of Two Disk Galaxies
... This is the oldest radiation and the farthest we can possibly see ...
... This is the oldest radiation and the farthest we can possibly see ...
How the universe began
... The universe was once smaller • So small – all matter and energy squashed in one tiny place • Cosmic egg • The big bang theory • Hugh explosion 14 billion years ago • Scientists can detect cosmic backgound radiation coming from all directions – this is called the ‘echo of the big bang’ ...
... The universe was once smaller • So small – all matter and energy squashed in one tiny place • Cosmic egg • The big bang theory • Hugh explosion 14 billion years ago • Scientists can detect cosmic backgound radiation coming from all directions – this is called the ‘echo of the big bang’ ...
Grade 11 Cosmology PPT File
... slope of the Hubble Law Graph. Slope = Velocity/Distance (Hubble Constant) The inverse of the Hubble Constant then has the dimension of time, and can be taken as an estimate of the age of the Universe! The Hubble Constant has been found to be between 50 and 100 km/s per kiloparsec. The Universe has ...
... slope of the Hubble Law Graph. Slope = Velocity/Distance (Hubble Constant) The inverse of the Hubble Constant then has the dimension of time, and can be taken as an estimate of the age of the Universe! The Hubble Constant has been found to be between 50 and 100 km/s per kiloparsec. The Universe has ...
Unit 3 Review Sheet
... What are the 2 major pieces of evidence for the expansion of the Universe and why is each one important? ...
... What are the 2 major pieces of evidence for the expansion of the Universe and why is each one important? ...
Class 28, 27 July
... – A little later, the protons and neutrons make Helium (most Helium in the universe was formed in the first 3 minutes after the Big Bang) – Nuclei, electrons, and photons in big “soup” • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • This leads to OSCILLATIONS! • Size of oscillatio ...
... – A little later, the protons and neutrons make Helium (most Helium in the universe was formed in the first 3 minutes after the Big Bang) – Nuclei, electrons, and photons in big “soup” • Nuclei try to collapse (gravity), photons push back (pressure) • This leads to OSCILLATIONS! • Size of oscillatio ...
Non-standard cosmology

A non-standard cosmology is any physical cosmological model of the universe that has been, or still is, proposed as an alternative to the Big Bang model of standard physical cosmology. In the history of cosmology, various scientists and researchers have disputed parts or all of the Big Bang due to a rejection or addition of fundamental assumptions needed to develop a theoretical model of the universe. From the 1940s to the 1960s, the astrophysical community was equally divided between supporters of the Big Bang theory and supporters of a rival steady state universe. It was not until advances in observational cosmology in the late 1960s that the Big Bang would eventually become the dominant theory, and today there are few active researchers who dispute it.The term non-standard is applied to any cosmological theory that does not conform to the scientific consensus, but is not used in describing alternative models where no consensus has been reached, and is also used to describe theories that accept a ""big bang"" occurred but differ as to the detailed physics of the origin and evolution of the universe. Because the term depends on the prevailing consensus, the meaning of the term changes over time. For example, hot dark matter would not have been considered non-standard in 1990, but would be in 2010. Conversely, a non-zero cosmological constant resulting in an accelerating universe would have been considered non-standard in 1990, but is part of the standard cosmology in 2010.