IFU observations of the high-z Universe
... • IFUs provide a uniquely powerful way to study the haloes around high redshift proto-galaxies • Volumetric data are an efficient way to search for Ly-alpha galaxies – An alternative method to constrain feedback ...
... • IFUs provide a uniquely powerful way to study the haloes around high redshift proto-galaxies • Volumetric data are an efficient way to search for Ly-alpha galaxies – An alternative method to constrain feedback ...
Unit 11: Dark Energy
... Mercury, the path of light near the limb of the Sun, and the effect of gravity on light from dense stars— tests that general relativity eventually passed summa cum laude. Einstein's ideas about gravity were deeply original. He imagined that mass (and energy) would warp the fabric of space and time. ...
... Mercury, the path of light near the limb of the Sun, and the effect of gravity on light from dense stars— tests that general relativity eventually passed summa cum laude. Einstein's ideas about gravity were deeply original. He imagined that mass (and energy) would warp the fabric of space and time. ...
The solar system rotates around the sun due to the sun`s
... Scientist have studied nine different stars (A-I) and nine different galaxies (1-9). T hey documented what percent of shift each star and galaxies had. T he data is shown below. Which statement below best supports the data? A ...
... Scientist have studied nine different stars (A-I) and nine different galaxies (1-9). T hey documented what percent of shift each star and galaxies had. T he data is shown below. Which statement below best supports the data? A ...
Assignment 10
... a. antimatter and matter colliding at the center of a galaxy b. chain reactions of supernova explosions c. matter falling toward a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy d. the leftover (and stored) energy of the big bang explosion e. you can't fool me; astronomers have no compelling exp ...
... a. antimatter and matter colliding at the center of a galaxy b. chain reactions of supernova explosions c. matter falling toward a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy d. the leftover (and stored) energy of the big bang explosion e. you can't fool me; astronomers have no compelling exp ...
What is the Shape of the Universe?
... Big Bang some 14 billion years ago The Universe has been expanding ever since Thus, no two galaxies can be farther apart than 14 billion light years (1 light year 6 trillion miles) ...
... Big Bang some 14 billion years ago The Universe has been expanding ever since Thus, no two galaxies can be farther apart than 14 billion light years (1 light year 6 trillion miles) ...
On the Electrodynamics of the Big Bang Universe - SLAC
... collected into galaxies”. One model, SMF, explains all this evidence as well another puzzle, the origin of magnetic fields in our Universe. The belief that tiny fluctuations produced at Inflation Time (10−35 seconds) remain unchanged, after basic phase transitions, like separating the weak force fro ...
... collected into galaxies”. One model, SMF, explains all this evidence as well another puzzle, the origin of magnetic fields in our Universe. The belief that tiny fluctuations produced at Inflation Time (10−35 seconds) remain unchanged, after basic phase transitions, like separating the weak force fro ...
Mapping the Universe - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... is to determine how the initial power spectrum evolved into the spectrum observed today. Only in the past several years have observations, such as those of galaxy distribution and of the cosmic microwave background radiation, acquired enough data to put theories to the test. So-called cold dark matt ...
... is to determine how the initial power spectrum evolved into the spectrum observed today. Only in the past several years have observations, such as those of galaxy distribution and of the cosmic microwave background radiation, acquired enough data to put theories to the test. So-called cold dark matt ...
Static, Infinite, Etern and Auto sustentable Universe
... universe, the Big Bang Theory (BBT), as it were named by Fred Hoyle, acquired credibility when Hubble detected a redshift in the light of distant galaxies [3], and they considered that this effect was caused by separation with high speed of the galaxies. According with us, the BBT proposes an irrat ...
... universe, the Big Bang Theory (BBT), as it were named by Fred Hoyle, acquired credibility when Hubble detected a redshift in the light of distant galaxies [3], and they considered that this effect was caused by separation with high speed of the galaxies. According with us, the BBT proposes an irrat ...
Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect
... Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness with a period of the order of days and are named after the first one to be discovered, -Cephei, the fourth brightest star in the constellation Cepheus. Their significance is that the period depends ...
... Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness with a period of the order of days and are named after the first one to be discovered, -Cephei, the fourth brightest star in the constellation Cepheus. Their significance is that the period depends ...
Misconceptions in Cosmology and how to correct them
... energy concept is totally invalidated – simple! However, this does not mean Tryon was correct because he based his theory on Newton’s mechanics that assumes no mass change occurs. In fact the concept of gravitational potential energy has to abandoned and replaced by the aforementioned model when an ...
... energy concept is totally invalidated – simple! However, this does not mean Tryon was correct because he based his theory on Newton’s mechanics that assumes no mass change occurs. In fact the concept of gravitational potential energy has to abandoned and replaced by the aforementioned model when an ...
BThayerTalk3
... visible in southern hemisphere. In modern astronomy, such gravitational lensing images are used to detect a ‘dark matter’ body as the central object ...
... visible in southern hemisphere. In modern astronomy, such gravitational lensing images are used to detect a ‘dark matter’ body as the central object ...
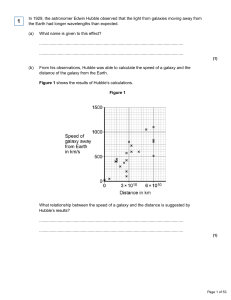
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from
... In the 1950s there were two main theories to explain how the Universe began. ...
... In the 1950s there were two main theories to explain how the Universe began. ...
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe
... • How big is the universe? – The observable universe is 14 billion light-years in radius (no it is considerably bigger and depends upon the expansion rate and the history of the expansion rate which has changed) and contains over 100 billion galaxies with a total number of stars comparable to the nu ...
... • How big is the universe? – The observable universe is 14 billion light-years in radius (no it is considerably bigger and depends upon the expansion rate and the history of the expansion rate which has changed) and contains over 100 billion galaxies with a total number of stars comparable to the nu ...
May 2015 - Hermanus Astronomy
... Our Sun came late to the Milky Way's star birth party 10 April: In one of the most comprehensive multi-observatory galaxy surveys yet, astronomers find that galaxies like our Milky Way underwent a stellar ‘baby boom’, churning out stars at a prodigious rate, about 30 times faster than today. Our Su ...
... Our Sun came late to the Milky Way's star birth party 10 April: In one of the most comprehensive multi-observatory galaxy surveys yet, astronomers find that galaxies like our Milky Way underwent a stellar ‘baby boom’, churning out stars at a prodigious rate, about 30 times faster than today. Our Su ...
Review (PPT) - Uplift Summit Intl
... A black body is a theoretical object that absorbs 100% of the radiation that is incident upon it. Because there is no reflection or transmission it appears perfectly black. Such bodies would also behave as perfect emitters of radiation, emitting the maximum amount of radiation possible at their tem ...
... A black body is a theoretical object that absorbs 100% of the radiation that is incident upon it. Because there is no reflection or transmission it appears perfectly black. Such bodies would also behave as perfect emitters of radiation, emitting the maximum amount of radiation possible at their tem ...
The Superhero's Universe: Observing the Cosmos with X-ray Vision and Beyond
... decade indicate that gas near the center is moving about half of the speed of light ★ supermassive black hole at the center ...
... decade indicate that gas near the center is moving about half of the speed of light ★ supermassive black hole at the center ...
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Stars and Gas in Galaxies
... MACHOs predicted to magnify dozens of LMC stars each year. Only a 1 or 2 are seen. ...
... MACHOs predicted to magnify dozens of LMC stars each year. Only a 1 or 2 are seen. ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... the gas cloud began to collapse and ignite to form clusters of stars—the first galaxies. ...
... the gas cloud began to collapse and ignite to form clusters of stars—the first galaxies. ...
6. Star Colors and the Hertzsprung
... discriminate not only the age of the universe but what kind of universe we live in. What is actually measured is the redshift. The redshift is related to the age of the universe when the light was emitted, but it is actually a measure of the relative size of the universe. ...
... discriminate not only the age of the universe but what kind of universe we live in. What is actually measured is the redshift. The redshift is related to the age of the universe when the light was emitted, but it is actually a measure of the relative size of the universe. ...
Physics 130 Name
... 43._____The Sun appears red at sunset because the blue light has been scattered away by the Earth’s atmosphere. 44._____Young stars in our Galaxy tend to be found in the galactic halo. 45._____Globular clusters are Population II objects. 46._____All known galaxies have sizes and masses near the valu ...
... 43._____The Sun appears red at sunset because the blue light has been scattered away by the Earth’s atmosphere. 44._____Young stars in our Galaxy tend to be found in the galactic halo. 45._____Globular clusters are Population II objects. 46._____All known galaxies have sizes and masses near the valu ...
Non-standard cosmology

A non-standard cosmology is any physical cosmological model of the universe that has been, or still is, proposed as an alternative to the Big Bang model of standard physical cosmology. In the history of cosmology, various scientists and researchers have disputed parts or all of the Big Bang due to a rejection or addition of fundamental assumptions needed to develop a theoretical model of the universe. From the 1940s to the 1960s, the astrophysical community was equally divided between supporters of the Big Bang theory and supporters of a rival steady state universe. It was not until advances in observational cosmology in the late 1960s that the Big Bang would eventually become the dominant theory, and today there are few active researchers who dispute it.The term non-standard is applied to any cosmological theory that does not conform to the scientific consensus, but is not used in describing alternative models where no consensus has been reached, and is also used to describe theories that accept a ""big bang"" occurred but differ as to the detailed physics of the origin and evolution of the universe. Because the term depends on the prevailing consensus, the meaning of the term changes over time. For example, hot dark matter would not have been considered non-standard in 1990, but would be in 2010. Conversely, a non-zero cosmological constant resulting in an accelerating universe would have been considered non-standard in 1990, but is part of the standard cosmology in 2010.