www.astro.utu.fi
... away goes like their mass million solar mass black holes (like now at the Galactic center) take 1083 years to dissapear 1012 solar mass black holes (equivalent to expected mass of Milky Way) and would take 10101 year to dissapear ...
... away goes like their mass million solar mass black holes (like now at the Galactic center) take 1083 years to dissapear 1012 solar mass black holes (equivalent to expected mass of Milky Way) and would take 10101 year to dissapear ...
astronomy webquest…… explore the universe
... http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/stars/lifecycle/ http://btc.montana.edu/ceres/html/LifeCycle/starsbackground.htm http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Nebula.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Strange.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link= ...
... http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/astronomy/stars/lifecycle/ http://btc.montana.edu/ceres/html/LifeCycle/starsbackground.htm http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Nebula.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/the_universe/Strange.html http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link= ...
Natural Explanation for the Anthropic Coincidences
... A non-zero cosmological constant is equivalent to an energy density in a vacuum otherwise empty of matter or (what is the same thing) energy. Quantum fluctuations will also result in a non-zero vacuum energy density, and so the total energy density of the vacuum is the sum of two contributions. Wein ...
... A non-zero cosmological constant is equivalent to an energy density in a vacuum otherwise empty of matter or (what is the same thing) energy. Quantum fluctuations will also result in a non-zero vacuum energy density, and so the total energy density of the vacuum is the sum of two contributions. Wein ...
Great Discoveries in Astronomy and Astrophysics 171.112
... This course will focus on key discoveries in astronomy and astrophysics from the speed of light to the speed of the expanding and now accelerating Universe, from the discovery of Neptune to the modern detection of extrasolar planets, spanning hundreds of years and many orders of magnitude of astrono ...
... This course will focus on key discoveries in astronomy and astrophysics from the speed of light to the speed of the expanding and now accelerating Universe, from the discovery of Neptune to the modern detection of extrasolar planets, spanning hundreds of years and many orders of magnitude of astrono ...
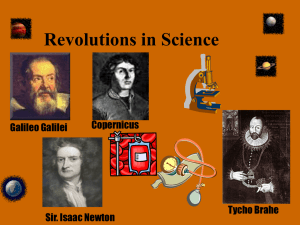
Science In The Renaissance!
... Most experts reject this idea as it completely contradicts Aristotle as well as Ptolemy and the Church. In the late 1500’s Tyco Brahe provides evidence that Copernicus was correct. Brahe observed the sky on a nightly basis to record the movements of heavenly bodies. ...
... Most experts reject this idea as it completely contradicts Aristotle as well as Ptolemy and the Church. In the late 1500’s Tyco Brahe provides evidence that Copernicus was correct. Brahe observed the sky on a nightly basis to record the movements of heavenly bodies. ...
Galaxies - schoolphysics
... side of the galaxy started out on its journey over eighty thousand years ago! If we could shrink the whole solar system out to the orbit of Pluto to the size of a grain of sand 1mm across then on the same scale our galaxy would be a disc with a diameter of some 80 m and the nearest galaxy would be a ...
... side of the galaxy started out on its journey over eighty thousand years ago! If we could shrink the whole solar system out to the orbit of Pluto to the size of a grain of sand 1mm across then on the same scale our galaxy would be a disc with a diameter of some 80 m and the nearest galaxy would be a ...
Ch. 25 - UTK Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 25.3 Galaxy Formation and Evolution These starburst galaxies show evidence of massive, recent activity. Image (a) is clearly galaxies in collision. Image (b) appears to have a supermassive black hole at its center. Image (c) is also the result of a collision. ...
... 25.3 Galaxy Formation and Evolution These starburst galaxies show evidence of massive, recent activity. Image (a) is clearly galaxies in collision. Image (b) appears to have a supermassive black hole at its center. Image (c) is also the result of a collision. ...
Matter is everything around you.
... system is explained why some planets seemed to move backwards for periods of time in their orbit around earth. He theorized that each planet also revolved in a smaller circle as well as a larger one. This was called the "epicycle." This theory would survive for 1400 years, until it was finally accep ...
... system is explained why some planets seemed to move backwards for periods of time in their orbit around earth. He theorized that each planet also revolved in a smaller circle as well as a larger one. This was called the "epicycle." This theory would survive for 1400 years, until it was finally accep ...
39 Questionable Assumptions in Modern Physics
... •Paul D. Tinari, "Use of Catastrophe Theory to Obtain a Fundamental Understanding of Elementary Particle Stability", International Journal of Theoretical Physics, V25, N7, pp. 711-715 (1986). E. P. Battey-Pratt & T. J. Racey, "Geometric Model for Fundamental Particles," International Journal of Theo ...
... •Paul D. Tinari, "Use of Catastrophe Theory to Obtain a Fundamental Understanding of Elementary Particle Stability", International Journal of Theoretical Physics, V25, N7, pp. 711-715 (1986). E. P. Battey-Pratt & T. J. Racey, "Geometric Model for Fundamental Particles," International Journal of Theo ...
WORLD YEAR OF PHYSICS 2005: EINSTEIN S IN THE 21ST
... model” of gravity, and gravitational physics has become a truly experimental science (Ref. [3]). Einstein spent most of his later years trying to come up with a way of unifying gravitational and electromagnetic interactions. He didn’t quite do it, but we have made some progress since then. If our th ...
... model” of gravity, and gravitational physics has become a truly experimental science (Ref. [3]). Einstein spent most of his later years trying to come up with a way of unifying gravitational and electromagnetic interactions. He didn’t quite do it, but we have made some progress since then. If our th ...
In Search of the Dark Matter in the Universe
... ago in an unthinkably small volume with an unthinkably high energy density, the so-called Big Bang, and is expanding ever since. However, this expansion is counteracted by the gravitational pull of the matter in the universe. Depending on how much matter there is, the expansion will continue forever ...
... ago in an unthinkably small volume with an unthinkably high energy density, the so-called Big Bang, and is expanding ever since. However, this expansion is counteracted by the gravitational pull of the matter in the universe. Depending on how much matter there is, the expansion will continue forever ...
Size and Scale of the Universe
... • There could be (and likely is) much more beyond that, but we cannot see it from this point in spacetime • Note: The matter that we can see glowing shortly after the Big Bang (detected by the light it emitted 13.7 billion years ago) is now about 46 billion light-years away due to the ongoing expans ...
... • There could be (and likely is) much more beyond that, but we cannot see it from this point in spacetime • Note: The matter that we can see glowing shortly after the Big Bang (detected by the light it emitted 13.7 billion years ago) is now about 46 billion light-years away due to the ongoing expans ...
Size and Scale of the Universe
... • There could be (and likely is) much more beyond that, but we cannot see it from this point in spacetime • Note: The matter that we can see glowing shortly after the Big Bang (detected by the light it emitted 13.7 billion years ago) is now about 46 billion light-years away due to the ongoing expans ...
... • There could be (and likely is) much more beyond that, but we cannot see it from this point in spacetime • Note: The matter that we can see glowing shortly after the Big Bang (detected by the light it emitted 13.7 billion years ago) is now about 46 billion light-years away due to the ongoing expans ...
Lecture 1 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Solar Mass = mass of the sun = 2 x 1033 grams Jupiter Mass = 0.001 solar masses = 2 x 1030 grams Earth Mass = 0.003 Jupiter masses = 6 x 1027 Astronomical Unit = distance from the Earth to the Sun Light Year = distance light travels in 1 yr = 9.4 x 1017 cm Parsec = 3.26 light years = 3.08 x 101 ...
... Solar Mass = mass of the sun = 2 x 1033 grams Jupiter Mass = 0.001 solar masses = 2 x 1030 grams Earth Mass = 0.003 Jupiter masses = 6 x 1027 Astronomical Unit = distance from the Earth to the Sun Light Year = distance light travels in 1 yr = 9.4 x 1017 cm Parsec = 3.26 light years = 3.08 x 101 ...
Cosmology and Science - Gurdjieff and the Fourth Way: A Critical
... are clear up to a point and then tend to become unclear. In this activity, there is evidently no reason to suppose that there is or will be a final form of insight (corresponding to absolute truth) or even a steady series of approximations to this. Rather, one may expect the unending development of ...
... are clear up to a point and then tend to become unclear. In this activity, there is evidently no reason to suppose that there is or will be a final form of insight (corresponding to absolute truth) or even a steady series of approximations to this. Rather, one may expect the unending development of ...
Dark Matter - UW - Laramie, Wyoming | University of Wyoming
... Can dark matter be composed of normal matter? If so, then its mass would mostly come from protons and neutrons = baryons The density of baryons right after the big bang leaves a unique imprint in the abundances of deuterium and lithium. ...
... Can dark matter be composed of normal matter? If so, then its mass would mostly come from protons and neutrons = baryons The density of baryons right after the big bang leaves a unique imprint in the abundances of deuterium and lithium. ...
Word
... Now that you have used Hubble’s constant on your own, describe the significance of Hubble’s constant in your own words. Consider these questions in your explanation. 1. Does the Universe have edges or a center? 2. What does this mean in terms of expansion? 3. Is expansion technically relative to the ...
... Now that you have used Hubble’s constant on your own, describe the significance of Hubble’s constant in your own words. Consider these questions in your explanation. 1. Does the Universe have edges or a center? 2. What does this mean in terms of expansion? 3. Is expansion technically relative to the ...
Talk - Otterbein University
... and its luminosity • The more mass a galaxy has the brighter it is the faster it rotates the wider the spectral lines are • Measuring rotation speed allows us to estimate luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
... and its luminosity • The more mass a galaxy has the brighter it is the faster it rotates the wider the spectral lines are • Measuring rotation speed allows us to estimate luminosity; comparing to observed (apparent) brightness then tells us the distance ...
File
... There are two ways that astronomers determine the distance of stars from an observer: a) Doppler Effect -The Absorption Spectrum produced by a star or planet changes depending on whether the star is moving towards or away from the observer. ...
... There are two ways that astronomers determine the distance of stars from an observer: a) Doppler Effect -The Absorption Spectrum produced by a star or planet changes depending on whether the star is moving towards or away from the observer. ...
Cosmology 2 - schoolphysics
... 21. If Hubble’s constant at present is taken to be 70 kms-1 Mpc-1 what is its value in SI units? 22. (a) A galaxy is found to be receding from the Earth at 2000 kms-1. What its distance from the Earth in light years? (b) What will be the recession velocity of a galaxy at a distance of 10 000 000 lig ...
... 21. If Hubble’s constant at present is taken to be 70 kms-1 Mpc-1 what is its value in SI units? 22. (a) A galaxy is found to be receding from the Earth at 2000 kms-1. What its distance from the Earth in light years? (b) What will be the recession velocity of a galaxy at a distance of 10 000 000 lig ...
Lesson 13 - Oregon State University
... After about 30 m, nucleosynthesis ceased. The temperature was ~ 3 x 108K and the density was ~ 30 kg/m3. Nuclear matter was 76% by mass protons, 24% alpha particles with traces of deuterium, 3He and 7Li. The /n/p ratio is 109/13/87. The relative ratio of p/4He/d/3He/7Li is a sensitive function of t ...
... After about 30 m, nucleosynthesis ceased. The temperature was ~ 3 x 108K and the density was ~ 30 kg/m3. Nuclear matter was 76% by mass protons, 24% alpha particles with traces of deuterium, 3He and 7Li. The /n/p ratio is 109/13/87. The relative ratio of p/4He/d/3He/7Li is a sensitive function of t ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... with v=Hd v=velocity, d=distance, and H=Hubble constant. Milky Way has inner nucleus, spiral arms (active star formation, halo of old stars (early shape) Cosmology. Hubble law Universe is expanding, gives universe’s age, depends on Hubble “constant” changes with time. Closed universe has gravity s ...
... with v=Hd v=velocity, d=distance, and H=Hubble constant. Milky Way has inner nucleus, spiral arms (active star formation, halo of old stars (early shape) Cosmology. Hubble law Universe is expanding, gives universe’s age, depends on Hubble “constant” changes with time. Closed universe has gravity s ...
Summation Packet KEY
... 18. The Andromeda galaxy has a blue shift. How will the Andromeda galaxy affect the Milky Way in the near future? It will move closer. If it continues to move closer, it will eventually collide with the milky way galaxy ...
... 18. The Andromeda galaxy has a blue shift. How will the Andromeda galaxy affect the Milky Way in the near future? It will move closer. If it continues to move closer, it will eventually collide with the milky way galaxy ...
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the Universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its origin, structure, evolution, and ultimate fate. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion. Cosmology as a science originated with the Copernican principle, which implies that celestial bodies obey identical physical laws to those on Earth, and Newtonian mechanics, which first allowed us to understand those physical laws.Physical cosmology, as it is now understood, began with the development in 1915 of Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, followed by major observational discoveries in the 1920s: first, Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe contains a huge number of external galaxies beyond our own Milky Way; then, work by Vesto Slipher and others showed that the universe is expanding. These advances made it possible to speculate about the origin of the universe, and allowed the establishment of the Big Bang Theory, by Georges Lemaitre, as the leading cosmological model. A few researchers still advocate a handful of alternative cosmologies; however, most cosmologists agree that the Big Bang theory explains the observations better.Dramatic advances in observational cosmology since the 1990s, including the cosmic microwave background, distant supernovae and galaxy redshift surveys, have led to the development of a standard model of cosmology. This model requires the universe to contain large amounts of dark matter and dark energy whose nature is currently not well understood, but the model gives detailed predictions that are in excellent agreement with many diverse observations.Cosmology draws heavily on the work of many disparate areas of research in theoretical and applied physics. Areas relevant to cosmology include particle physics experiments and theory, theoretical and observational astrophysics, general relativity, quantum mechanics, and plasma physics.