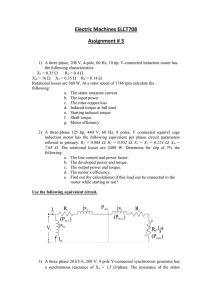
Synchronous Motor
... – Stator identical to that of a three-phase induction motor – now called the “armature” – Energize from a three-phase supply and develop the rotating magnetic field – Rotor has a DC voltage applied (excitation) ...
... – Stator identical to that of a three-phase induction motor – now called the “armature” – Energize from a three-phase supply and develop the rotating magnetic field – Rotor has a DC voltage applied (excitation) ...
Sensor less Control of BLDC Motor Drive for an
... system for an automotive fuel pump. The sensor less techniques that are based on a hysteresis comparator and a potential start up method with a high starting torque are suggested. The hysteresis comparator is used to compensate for the phase delay of the back EMFs due to a low pass filter (LPF) and ...
... system for an automotive fuel pump. The sensor less techniques that are based on a hysteresis comparator and a potential start up method with a high starting torque are suggested. The hysteresis comparator is used to compensate for the phase delay of the back EMFs due to a low pass filter (LPF) and ...
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE)
... BLDC motor is conventionally defined as a permanent magnet synchronous motor with a trapezoidal Back EMF waveform shape. Permanent magnet synchronous machines with trapezoidal Back-EMF and (120 electrical degrees wide) rectangular stator currents are widely used as they offer the following advantage ...
... BLDC motor is conventionally defined as a permanent magnet synchronous motor with a trapezoidal Back EMF waveform shape. Permanent magnet synchronous machines with trapezoidal Back-EMF and (120 electrical degrees wide) rectangular stator currents are widely used as they offer the following advantage ...
Introduction to Basic Robotics Parts/Systems
... Use combinations of gearboxes, motors, and wheels to design a drive system. ...
... Use combinations of gearboxes, motors, and wheels to design a drive system. ...
Series DC Motors
... Series Motors: Variable speed motor which changes speed drastically from one load condition to another. It has a high starting torque. Applications: hoists, electric trains, conveyors, elevators, electric cars. Compound motors: Variable speed motors. It has a high starting torque and the no-load spe ...
... Series Motors: Variable speed motor which changes speed drastically from one load condition to another. It has a high starting torque. Applications: hoists, electric trains, conveyors, elevators, electric cars. Compound motors: Variable speed motors. It has a high starting torque and the no-load spe ...
selection of electric motors for aerospace applications
... SELECTION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS FOR AEROSPACE APPLICATIONS The BLDC motor uses electronic commutation to control the current through the windings. The BLDC motors use permanent magnets on the rotor. The BLDC motor contains rotor position sensor electronics so that the power input wave form to the windi ...
... SELECTION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS FOR AEROSPACE APPLICATIONS The BLDC motor uses electronic commutation to control the current through the windings. The BLDC motors use permanent magnets on the rotor. The BLDC motor contains rotor position sensor electronics so that the power input wave form to the windi ...
TVC-S-30(ELW) 3A Dual electronic speed controller for RC tanks in
... This equipment described above has been tested and inspected for quality and function. It is intended for installation and use only as described above. This equipment does not contain any user serviceable parts. The supplier accepts no responsibility, financial or otherwise, for damages caused by u ...
... This equipment described above has been tested and inspected for quality and function. It is intended for installation and use only as described above. This equipment does not contain any user serviceable parts. The supplier accepts no responsibility, financial or otherwise, for damages caused by u ...
Stepper Motors - WordPress.com
... Motor speed determined by: supplied voltage Motor direction determined by: polarity of supplied voltage ...
... Motor speed determined by: supplied voltage Motor direction determined by: polarity of supplied voltage ...
KBBC – Microprocessor Controlled DC-DC Battery
... amps continuous output. The KBBC-44M (Part No. 9501) can operate up to 48 VDC motors, also to 40 amps continuous output. Both models are normally available from stock. Complete details of the new KBBC Micro version are shown on data sheet D-905. For high volume accounts, custom units are available ( ...
... amps continuous output. The KBBC-44M (Part No. 9501) can operate up to 48 VDC motors, also to 40 amps continuous output. Both models are normally available from stock. Complete details of the new KBBC Micro version are shown on data sheet D-905. For high volume accounts, custom units are available ( ...
Section 17.3 - CPO Science
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
Unit B
... Photo-reactive materials Chemically reactive materials Thermally reactive materials Piezoelectric materials – Crystals create a charge when pushed or pressed. ...
... Photo-reactive materials Chemically reactive materials Thermally reactive materials Piezoelectric materials – Crystals create a charge when pushed or pressed. ...
because it rotates. 17.3 Electric motors In a working electric motor
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
How Motors Operate Presented by John Freeland
... Parallel wound universal motor (field coils and armature connected in parallel): • Operates at lower rpm • Has good speed regulation with varying load ...
... Parallel wound universal motor (field coils and armature connected in parallel): • Operates at lower rpm • Has good speed regulation with varying load ...
DC Motors and Generators
... • a. Direction of current flow determines the magnetic poles of the armature • b. Changes in the direction of current flow can occur while the armature rotates – 3. Commutator reverses direction of current flow • B. Timing in a motor is controlled by the angle of commutation. ...
... • a. Direction of current flow determines the magnetic poles of the armature • b. Changes in the direction of current flow can occur while the armature rotates – 3. Commutator reverses direction of current flow • B. Timing in a motor is controlled by the angle of commutation. ...
Section 22.3 - CPO Science
... An electric motor that runs from batteries has the same three parts. The permanent magnets are on the outside, and the electromagnets turn in the rotor. ...
... An electric motor that runs from batteries has the same three parts. The permanent magnets are on the outside, and the electromagnets turn in the rotor. ...
Series 30xx - Lehner
... Our rpm / power data have been determined by using 15° timing. 6. All efficiency figures (ŋ) contain losses of motor and controller. Total efficiency of 94% contains a controller loss of ca. 1 - 2% which corresponds to a pure motor efficiency of ca. 95 - 96%. 7. Series 30xx motors are optimized for ...
... Our rpm / power data have been determined by using 15° timing. 6. All efficiency figures (ŋ) contain losses of motor and controller. Total efficiency of 94% contains a controller loss of ca. 1 - 2% which corresponds to a pure motor efficiency of ca. 95 - 96%. 7. Series 30xx motors are optimized for ...
Slide 1
... Due to the absence of rotor windings, SRM is very simple to construct, has a low inertia and allows an extremely high-speed operation. SRM operates in constant torque from zero speed up to the rated speed. Above rated speed up to a certain speed, the operation is in constant power. The range of this ...
... Due to the absence of rotor windings, SRM is very simple to construct, has a low inertia and allows an extremely high-speed operation. SRM operates in constant torque from zero speed up to the rated speed. Above rated speed up to a certain speed, the operation is in constant power. The range of this ...
Synchronous Motors
... • Constant-speed machine • Propulsion for SS “Queen Elizabeth II” – 44 MW – 10 kV – 60 Hz – 50 pole – 144 r/min ...
... • Constant-speed machine • Propulsion for SS “Queen Elizabeth II” – 44 MW – 10 kV – 60 Hz – 50 pole – 144 r/min ...
Brushless DC electric motor

Brushless DC electric motor (BLDC motors, BL motors) also known as electronically commutated motors (ECMs, EC motors) are synchronous motors that are powered by a DC electric source via an integrated inverter/switching power supply, which produces an AC electric signal to drive the motor. In this context, AC, alternating current, does not imply a sinusoidal waveform, but rather a bi-directional current with no restriction on waveform. Additional sensors and electronics control the inverter output amplitude and waveform (and therefore percent of DC bus usage/efficiency) and frequency (i.e. rotor speed).The rotor part of a brushless motor is often a permanent magnet synchronous motor, but can also be a switched reluctance motor, or induction motor.Brushless motors may be described as stepper motors; however, the term stepper motor tends to be used for motors that are designed specifically to be operated in a mode where they are frequently stopped with the rotor in a defined angular position. This page describes more general brushless motor principles, though there is overlap.Two key performance parameters of brushless DC motors are the motor constants Kv and Km.