Wandering in the Redshift Desert
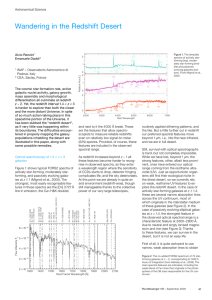
... COSMOS pBzKs (and along with them a much larger number of star-forming galaxies in the desert) would take about a quarter of the time we have estimated above for FORS2, i.e., some 350 VLT nights. This still looks like a lot of time, yet is somewhat more affordable than a mere FORS2 brute force effor ...
... COSMOS pBzKs (and along with them a much larger number of star-forming galaxies in the desert) would take about a quarter of the time we have estimated above for FORS2, i.e., some 350 VLT nights. This still looks like a lot of time, yet is somewhat more affordable than a mere FORS2 brute force effor ...
Astronomy and Astrophysics (ASTRO)
... stars, to understand the past and future of our Sun, the Milky Way galaxy and the other galaxies in the universe. Basic concepts of cosmology, dark matter and dark energy. Use of computer models to calculate the structure and evolution of stars and protostars, and to analyze actual ...
... stars, to understand the past and future of our Sun, the Milky Way galaxy and the other galaxies in the universe. Basic concepts of cosmology, dark matter and dark energy. Use of computer models to calculate the structure and evolution of stars and protostars, and to analyze actual ...
1Cmoles.pdf
... It will make possible the study of many different astronomical problems in a selfcontained way. By design, the ALHAMBRA-Survey will provide precise (∆z < 0.015(1 + z)) photometric redshifts and SED classification for ≥ 300, 000 galaxies and AGNs. Thanks to the unbiased nature of this survey (i.e. ne ...
... It will make possible the study of many different astronomical problems in a selfcontained way. By design, the ALHAMBRA-Survey will provide precise (∆z < 0.015(1 + z)) photometric redshifts and SED classification for ≥ 300, 000 galaxies and AGNs. Thanks to the unbiased nature of this survey (i.e. ne ...
The Magellan 20 Telescope Science Goals
... of our overall view of the cosmos. The basic framework on which an understanding of galaxy and structure formation can be built is well in hand. Gravitational instabilities amplify tiny primordial density fluctuations and drive the hierarchical growth of structure. The amplitude Figure 2. The WMAP i ...
... of our overall view of the cosmos. The basic framework on which an understanding of galaxy and structure formation can be built is well in hand. Gravitational instabilities amplify tiny primordial density fluctuations and drive the hierarchical growth of structure. The amplitude Figure 2. The WMAP i ...
A Zoo of Galaxies - Portsmouth Research Portal
... example of this idea is the map shown in Figure 2, published by William Herschel in 1785 (Herschel 1785), and based on star counts made by himself and his sister Caroline. This diagram demonstrates an understanding of the Galaxy as a collection of stars, and while there is a a lot wrong with it (for ...
... example of this idea is the map shown in Figure 2, published by William Herschel in 1785 (Herschel 1785), and based on star counts made by himself and his sister Caroline. This diagram demonstrates an understanding of the Galaxy as a collection of stars, and while there is a a lot wrong with it (for ...
A Zoo of Galaxies
... example of this idea is the map shown in Figure 2, published by William Herschel in 1785 (Herschel 1785), and based on star counts made by himself and his sister Caroline. This diagram demonstrates an understanding of the Galaxy as a collection of stars, and while there is a a lot wrong with it (for ...
... example of this idea is the map shown in Figure 2, published by William Herschel in 1785 (Herschel 1785), and based on star counts made by himself and his sister Caroline. This diagram demonstrates an understanding of the Galaxy as a collection of stars, and while there is a a lot wrong with it (for ...
Evolution of galaxy morphology - Lecture 1 - NCRA-TIFR
... Where e refers to effective values and n is the Sérsic index. For n=4 it becomes the de Vaucouleurs function; for n=1 an exponential, and when n=0.5, a Gaussian! For values in the range 1-4, approximately, it describes bulges in late-type spiral galaxies (or pseudo-bulges) to bulges in early-type sp ...
... Where e refers to effective values and n is the Sérsic index. For n=4 it becomes the de Vaucouleurs function; for n=1 an exponential, and when n=0.5, a Gaussian! For values in the range 1-4, approximately, it describes bulges in late-type spiral galaxies (or pseudo-bulges) to bulges in early-type sp ...
What problems of physics and astrophysics seem
... morally antiquated. It is difficult to formulate this point clearly, but this is the fate of all papers and books of this kind. Incidentally, when I was young, a great role for me was played by O D Khvol'son's book The Physics of Our Days (New Concepts of Contemporary Physics in a Generally Accessib ...
... morally antiquated. It is difficult to formulate this point clearly, but this is the fate of all papers and books of this kind. Incidentally, when I was young, a great role for me was played by O D Khvol'son's book The Physics of Our Days (New Concepts of Contemporary Physics in a Generally Accessib ...
Galaxies and their properties
... that κ0 = (37±3) km s−1 kpc−1 and κ0 /Ω0 = 1.35±0.05. Thus, the sun oscillates about 1.35 times in the radial direction, by the time it completes an orbit around the galactic center. ...
... that κ0 = (37±3) km s−1 kpc−1 and κ0 /Ω0 = 1.35±0.05. Thus, the sun oscillates about 1.35 times in the radial direction, by the time it completes an orbit around the galactic center. ...
Part 9: Story of the Universe
... the orbit of an object experiencing the gravitational attraction of another body will undergo motion best explained by conic curves (ellipse, parabola or hyperbola) defined by initial conditions. • Also, the centre of mass of the two objects going around each other will be the stable point around wh ...
... the orbit of an object experiencing the gravitational attraction of another body will undergo motion best explained by conic curves (ellipse, parabola or hyperbola) defined by initial conditions. • Also, the centre of mass of the two objects going around each other will be the stable point around wh ...
THE MORPHOLOGICAL DEMOGRAPHICS OF GALAXIES IN THE
... The archeological nature of galaxy evolution studies prevents us from following individual galaxies over time. In consequence we are only left with snapshots at different lookback times from where we attempt, as excavators, to piece together their evolutionary histories from the motion of different ...
... The archeological nature of galaxy evolution studies prevents us from following individual galaxies over time. In consequence we are only left with snapshots at different lookback times from where we attempt, as excavators, to piece together their evolutionary histories from the motion of different ...
PHY 375 - DePaul University
... We will use the full relativistic Doppler effect formula to avoid faster than light recession velocity (but see posted lecture notes about why this step angers theoreticians, especially because faster than light motions are not a problem in general relativity; in fact, the preference is to keep dist ...
... We will use the full relativistic Doppler effect formula to avoid faster than light recession velocity (but see posted lecture notes about why this step angers theoreticians, especially because faster than light motions are not a problem in general relativity; in fact, the preference is to keep dist ...
Chapter 15 THE MILKY WAY IN RELATION TO OTHER GALAXIES
... M33 definitely is a small Sc spiral with essentially no bulge component. Its luminosity distribution is closely exponential, although the photometry by Kent (1987b) shows a central increase in surface brightness over the exponential. This is not a bulge component, because the light is there still do ...
... M33 definitely is a small Sc spiral with essentially no bulge component. Its luminosity distribution is closely exponential, although the photometry by Kent (1987b) shows a central increase in surface brightness over the exponential. This is not a bulge component, because the light is there still do ...
Lecture Topics 1023
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
... ASTR 1023 Lecture Topics These are the headings of the paragraphs into which ASTR 1023 lectures are divided. Use them to check your notes for completeness, and to see how the course is organized. It is also a good idea to cross-check these topics with your reading assignments, because some topics ar ...
21_Testbank
... B) about ten C) about a hundred D) about a thousand E) about the same, but it does so for much longer Answer: C 15) Why do we believe that starburst galaxies represent a temporary stage in galaxy evolution? A) We observe starbursts to last only a few years at a time. B) Such galaxies produce so much ...
... B) about ten C) about a hundred D) about a thousand E) about the same, but it does so for much longer Answer: C 15) Why do we believe that starburst galaxies represent a temporary stage in galaxy evolution? A) We observe starbursts to last only a few years at a time. B) Such galaxies produce so much ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS (ASTRO)
... ASTRO 150: Stars, Galaxies, and Cosmology (3-0) Cr. 3. F.S. For the nonscientist. A survey of astronomy with a focus on the universe beyond our solar system. Basic observational astronomy and the history of astronomy. Stellar astronomy: motions, distances, sizes, spectra; types of stars; variability ...
... ASTRO 150: Stars, Galaxies, and Cosmology (3-0) Cr. 3. F.S. For the nonscientist. A survey of astronomy with a focus on the universe beyond our solar system. Basic observational astronomy and the history of astronomy. Stellar astronomy: motions, distances, sizes, spectra; types of stars; variability ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of the galaxy takes about 200 million years. Answer: B 25) Which of the following correctl ...
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of the galaxy takes about 200 million years. Answer: B 25) Which of the following correctl ...
ppt
... and Paul Butler detected evidence that a planet, about the same mass as Jupiter, was circling the star. In 1999 they discovered two other ...
... and Paul Butler detected evidence that a planet, about the same mass as Jupiter, was circling the star. In 1999 they discovered two other ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of the galaxy takes about 200 million years. Answer: B 25) Which of the following correctl ...
... A) It contains between 100 billion and 1 trillion stars. B) Our solar system is located very close to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. C) The galaxy is about 100,000 light-years in diameter. D) One rotation of the galaxy takes about 200 million years. Answer: B 25) Which of the following correctl ...
Microsoft Word 97
... 7) In the directions in which we see the Milky Way in the sky, we are looking through the relatively thin, pancake-like disk of matter that forms a major part of our Milky Way Galaxy. a) This disk is about 90,000 light years across, an enormous, gravitationally bound system of stars. b) The Milky Wa ...
... 7) In the directions in which we see the Milky Way in the sky, we are looking through the relatively thin, pancake-like disk of matter that forms a major part of our Milky Way Galaxy. a) This disk is about 90,000 light years across, an enormous, gravitationally bound system of stars. b) The Milky Wa ...
Introduction to Observational Cosmology
... The basic pillars of our cosmological picture (i.e. we are starting with the answer first) 1. Averaged over sufficiently large scales, the universe is nearly homogeneous and isotropic (=cosmological principle) 2. The universe, i.e. space itself, is expanding so that the distance D between any pairs ...
... The basic pillars of our cosmological picture (i.e. we are starting with the answer first) 1. Averaged over sufficiently large scales, the universe is nearly homogeneous and isotropic (=cosmological principle) 2. The universe, i.e. space itself, is expanding so that the distance D between any pairs ...
lecture outlines
... 5. The Copernican System: an explanation- the 3 motions of the heavens 6. The Copernican System: an evaluation- stellar parallax, planetary predictions, eccentrics and epicycles 7. De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium and the Osiander preface (1543) 8. Digges and the concept of an infinite universe 9 ...
... 5. The Copernican System: an explanation- the 3 motions of the heavens 6. The Copernican System: an evaluation- stellar parallax, planetary predictions, eccentrics and epicycles 7. De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium and the Osiander preface (1543) 8. Digges and the concept of an infinite universe 9 ...
P7 Further Physics : Observing the Universe
... Parallax and parsec quantitatively. The distinction between intrinsic brightness (related to star colour and size) and apparent brightness, seen from Earth. ...
... Parallax and parsec quantitatively. The distinction between intrinsic brightness (related to star colour and size) and apparent brightness, seen from Earth. ...
Six thousand versus 14 Billion: How large and how old is the
... of a human hair! You would not be able to notice this shift with your bare eye (let alone hit a bullseye that small). Such a measurement is very difficult to do and no wonder it took until the 19th century to actually detect a parallax shift reliably. In fact, it still is hard today, but appare ...
... of a human hair! You would not be able to notice this shift with your bare eye (let alone hit a bullseye that small). Such a measurement is very difficult to do and no wonder it took until the 19th century to actually detect a parallax shift reliably. In fact, it still is hard today, but appare ...























