The Universe - HMXEarthScience
... Which conclusion can be made by comparing the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? A) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. B) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet ...
... Which conclusion can be made by comparing the standard spectrum to the spectrum produced from this distant star? A) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet end of the spectrum and the star is moving toward Earth. B) The star’s spectral lines have shifted toward the ultraviolet ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS
... to extend from ~107 eV to ~1012 eV, again describable as a power law which continuously steepens to an index of ~3.5 and is possibly cut-off at ~1013 eV. Even to this day, nearly a century after their discovery, we still do not understand precisely how and where cosmic rays are accelerated or what t ...
... to extend from ~107 eV to ~1012 eV, again describable as a power law which continuously steepens to an index of ~3.5 and is possibly cut-off at ~1013 eV. Even to this day, nearly a century after their discovery, we still do not understand precisely how and where cosmic rays are accelerated or what t ...
File
... • A protostar’s temperature continually increases until it reaches about 10,000,000 °C. • At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins. Nuclear fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of n ...
... • A protostar’s temperature continually increases until it reaches about 10,000,000 °C. • At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins. Nuclear fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of n ...
Galaxies - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... • Galaxies and clusters of galaxies are organized on irregular sheets separated by voids containing few galaxies. • The density fluctuations seen in the cosmic microwave background are likely the seeds for the formation of the sheets, clusters, and galaxies. • How that process occurs is now being wo ...
... • Galaxies and clusters of galaxies are organized on irregular sheets separated by voids containing few galaxies. • The density fluctuations seen in the cosmic microwave background are likely the seeds for the formation of the sheets, clusters, and galaxies. • How that process occurs is now being wo ...
Multiple Choice, continued
... • A protostar’s temperature continually increases until it reaches about 10,000,000 °C. • At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins. Nuclear fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of n ...
... • A protostar’s temperature continually increases until it reaches about 10,000,000 °C. • At this temperature, nuclear fusion begins. Nuclear fusion is a process in which less-massive atomic nuclei combine to form more-massive nuclei. The process releases enormous amounts of energy. • The onset of n ...
Astronomy Chapter 17 – Galaxies A. Main Ideas 1. Discovering
... ⇒ Galaxies interact with each other on a regular basis. Two galaxies may collide and the gravitational interaction will change the shape of both galaxies. When galaxies collide very few stars in either galaxy actually collide with each other because the stars are so far apart in each galaxy. Galaxie ...
... ⇒ Galaxies interact with each other on a regular basis. Two galaxies may collide and the gravitational interaction will change the shape of both galaxies. When galaxies collide very few stars in either galaxy actually collide with each other because the stars are so far apart in each galaxy. Galaxie ...
Chapter 27 Quasars, Active Galaxies, and Gamma
... from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
... from stars, nebulae, and some galaxies. • There were also point-like, or star-like, radio sources which varied rapidly these are the `quasi-stellar’ radio sources or quasars. • In visible light quasars appear as points, like stars. ...
Atoms, Einstein, Universe
... Part 1 examines our long journey to discover the micro-world— molecules, atoms, and everything smaller—and introduces those who led the way. For 2500 years, some of the brightest minds struggled to discover what everything we see is made of. In 1905, Einstein provided the critical insights that firm ...
... Part 1 examines our long journey to discover the micro-world— molecules, atoms, and everything smaller—and introduces those who led the way. For 2500 years, some of the brightest minds struggled to discover what everything we see is made of. In 1905, Einstein provided the critical insights that firm ...
of the Sun
... INFLATION ERA – the universe explodes from smaller than an atom to the size of a grapefruit. Expansion slows when the driving force is transformed into matter and energy ...
... INFLATION ERA – the universe explodes from smaller than an atom to the size of a grapefruit. Expansion slows when the driving force is transformed into matter and energy ...
Doppler Effect
... Matter “seen” by its gravitational pull (lensing) • Motions of galaxies within clusters (Zwicky) • Rotation of galaxies (Rubin) • Bending of distant galaxy light by intervening clusters (Gravitational Lensing) • Collision of two clusters of galaxies • Planck spacecraft: about 5% common matter, 25% d ...
... Matter “seen” by its gravitational pull (lensing) • Motions of galaxies within clusters (Zwicky) • Rotation of galaxies (Rubin) • Bending of distant galaxy light by intervening clusters (Gravitational Lensing) • Collision of two clusters of galaxies • Planck spacecraft: about 5% common matter, 25% d ...
Ramin A. Skibba - Southern California Center for Galaxy Evolution
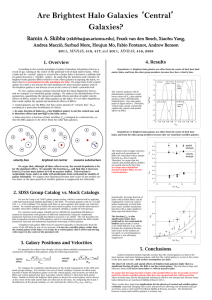
... BHGs are central galaxies but have a peculiar velocity relative to their host dark matter halos. Models in which the brightest halo galaxy is always the central galaxy and is always at the center of the dark matter halo are ruled out by the data. By comparing the R and S distributions of the group c ...
... BHGs are central galaxies but have a peculiar velocity relative to their host dark matter halos. Models in which the brightest halo galaxy is always the central galaxy and is always at the center of the dark matter halo are ruled out by the data. By comparing the R and S distributions of the group c ...
A Study of the Spiral Galaxy M101 Elizabeth City State University
... Data Set and Image Processing We used images taken at SPM in Baja, Mexico in June 1994. Narrow-band filters isolated select wavelengths of light to allow one to examine the galaxy in detail and look for regions of high and low ionization, including HII regions. Table 3 describes the observing site. ...
... Data Set and Image Processing We used images taken at SPM in Baja, Mexico in June 1994. Narrow-band filters isolated select wavelengths of light to allow one to examine the galaxy in detail and look for regions of high and low ionization, including HII regions. Table 3 describes the observing site. ...
electric charge - National Physical Laboratory
... distances less than a millimetre or greater than a few kilometres. Such distances are too tiny or too far to perceive directly times less than a second or more than a fraction of a lifetime. Such times are too small or too long for us to appreciate ...
... distances less than a millimetre or greater than a few kilometres. Such distances are too tiny or too far to perceive directly times less than a second or more than a fraction of a lifetime. Such times are too small or too long for us to appreciate ...
Formation of Globular Clusters: In and Out of Dwarf Galaxies
... Not easy. Assuming that GCs follow galactic star formation rate produces too many red/metal-rich clusters with a unimodal metallicity distribution. Globular clusters formed earlier than the majority of field stars in host galaxy. ...
... Not easy. Assuming that GCs follow galactic star formation rate produces too many red/metal-rich clusters with a unimodal metallicity distribution. Globular clusters formed earlier than the majority of field stars in host galaxy. ...
SS_L4
... approximately parallel to the galactic plane. Field strongly tied to the ionized plasma in the ISM. Small local perturbations in the field lead to local potential wells. ISM condenses in these wells, increasing their strength as it pulls the magnetic field with it Rayleigh-Taylor instability. Prov ...
... approximately parallel to the galactic plane. Field strongly tied to the ionized plasma in the ISM. Small local perturbations in the field lead to local potential wells. ISM condenses in these wells, increasing their strength as it pulls the magnetic field with it Rayleigh-Taylor instability. Prov ...
Presidential
... For the OSD model, {g_00} is necessarily Unity. We now allow it to be non-zero, this amounts to introducing small non-zero tangential pressures (with M=M_0 only). ...
... For the OSD model, {g_00} is necessarily Unity. We now allow it to be non-zero, this amounts to introducing small non-zero tangential pressures (with M=M_0 only). ...
Question 1 The star Regulus, in the constellation Leo, appears
... . 2. elliptical galaxies with bright, starlike nuclei. ...
... . 2. elliptical galaxies with bright, starlike nuclei. ...
TRANSIT
... around the World. Our calendar includes Leap Years every 4 years, which allows for a 365.25 day year, which is not quite right. So, we add other adjustments every 200 years and then every thousand years etc, as required. He then explained a large variety of other calendars used or in use throughout ...
... around the World. Our calendar includes Leap Years every 4 years, which allows for a 365.25 day year, which is not quite right. So, we add other adjustments every 200 years and then every thousand years etc, as required. He then explained a large variety of other calendars used or in use throughout ...
Dynamics of elliptical galaxies
... Orbits in elliptical galaxies Classification of stellar orbits in elliptical galaxies is much more complicated than for disk galaxies. Most important distinction is between axisymmetric galaxies (prolate or oblate) and triaxial galaxies. In an axisymmetric galaxy, there is a plane, perpendicular to ...
... Orbits in elliptical galaxies Classification of stellar orbits in elliptical galaxies is much more complicated than for disk galaxies. Most important distinction is between axisymmetric galaxies (prolate or oblate) and triaxial galaxies. In an axisymmetric galaxy, there is a plane, perpendicular to ...
Earth and Space - Kennesaw State University College of Science
... stable protons and neutrons can form – By 300,000 years, the universe had expanded and cooled (to about 4000°K) enough so that light could pass “through” empty space without bumping into matter – The universe continued to expand and cool, to its present temperature of about 4°K. The first galaxies w ...
... stable protons and neutrons can form – By 300,000 years, the universe had expanded and cooled (to about 4000°K) enough so that light could pass “through” empty space without bumping into matter – The universe continued to expand and cool, to its present temperature of about 4°K. The first galaxies w ...
Astronomy in 1936 The History of the Universe
... • HI gas flow shows discontinuity due to shocks at inner edges of spiral arms. • Bright young stars also in narrow arms. • Observed width ∆θ ~ t*(Ω - Ωp) , as predicted. ...
... • HI gas flow shows discontinuity due to shocks at inner edges of spiral arms. • Bright young stars also in narrow arms. • Observed width ∆θ ~ t*(Ω - Ωp) , as predicted. ...
Summary: Star Formation Near and Far
... How is the collapse of star-forming clumps initiated? A widely accepted view has been that self-gravitating clumps gradually separate from a magnetic field by slow ambipolar diffusion until a configuration approximating a singular isothermal sphere is formed, which then begins to collapse from the i ...
... How is the collapse of star-forming clumps initiated? A widely accepted view has been that self-gravitating clumps gradually separate from a magnetic field by slow ambipolar diffusion until a configuration approximating a singular isothermal sphere is formed, which then begins to collapse from the i ...
Nobel Prize in Physics 2002: Riccardo Giaconni
... million degrees, because of the strong gravitational field of unseen dark matter. Detail X-ray observations of this gas give astronomers clues about the distribution of dark matter in the Universe, and therefore, are important observations from the point of view of evolution of the Universe and cosm ...
... million degrees, because of the strong gravitational field of unseen dark matter. Detail X-ray observations of this gas give astronomers clues about the distribution of dark matter in the Universe, and therefore, are important observations from the point of view of evolution of the Universe and cosm ...
4. Star formation 4.1 Jeans` criterion
... • Stars form in molecular clouds. • Dimensions ~ 10pc, density ~ 5x109 m-3, temperature ~ 10 K. • Galactic magnetic field strongly tied to ionized plasma in ISM. • Field lines run parallel to galactic plane. • Local perturbations –> potential wells –> condensations. AS 3003 ...
... • Stars form in molecular clouds. • Dimensions ~ 10pc, density ~ 5x109 m-3, temperature ~ 10 K. • Galactic magnetic field strongly tied to ionized plasma in ISM. • Field lines run parallel to galactic plane. • Local perturbations –> potential wells –> condensations. AS 3003 ...