1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... This question is about some of the properties of Barnard’s star. Barnard’s star, in the constellation Ophiuchus, has a parallax angle of 0.549 arc-second as measured from Earth. (a) ...
... This question is about some of the properties of Barnard’s star. Barnard’s star, in the constellation Ophiuchus, has a parallax angle of 0.549 arc-second as measured from Earth. (a) ...
Course 107: The Big Bang and the Anthropic Principle
... has only 2% of the angular momentum. ▪ This pattern is directly __ to the pattern predicted for the nebular hypothesis. ○ It will spin in the same direction as that of the spinning object from which it broke. ▪ Therefore, all the planets and moons in our solar system should be spinning the _________ ...
... has only 2% of the angular momentum. ▪ This pattern is directly __ to the pattern predicted for the nebular hypothesis. ○ It will spin in the same direction as that of the spinning object from which it broke. ▪ Therefore, all the planets and moons in our solar system should be spinning the _________ ...
Chapter 15: The Milky Way Galaxy
... the Milky Way Galaxy—billions of stars along with gas and dust bound together by mutual gravitational attraction the properties of our Milky Way Galaxy Earth’s location in the Milky Way how interstellar gas and dust enable star formation to continue in our Galaxy that observations reveal the presenc ...
... the Milky Way Galaxy—billions of stars along with gas and dust bound together by mutual gravitational attraction the properties of our Milky Way Galaxy Earth’s location in the Milky Way how interstellar gas and dust enable star formation to continue in our Galaxy that observations reveal the presenc ...
Every large galaxy seems to have a supermassive black hole at its
... The distant galaxy J1148+5251, seen as it was less than 1 billion years after the Big Bang, has a central black hole proportionally larger than those in the nearby universe. Radio observations of this and other distant galaxies suggest that galaxies formed after their black holes. ...
... The distant galaxy J1148+5251, seen as it was less than 1 billion years after the Big Bang, has a central black hole proportionally larger than those in the nearby universe. Radio observations of this and other distant galaxies suggest that galaxies formed after their black holes. ...
Document
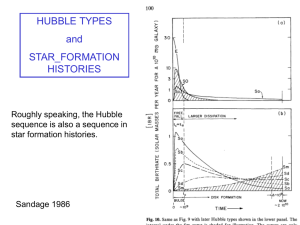
... passive evolution of stellar populations formed at z>2-3. Slope is primarily driven by mass-metallicity relation. Morphologically (HST)-selected Es and S0s (Bower et al. 1992, Aragon-Salamanca et al. 1993, Rakos et al. 1995, Stanford et al. 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, Schade et al. 1996, 1997, Ellis et ...
... passive evolution of stellar populations formed at z>2-3. Slope is primarily driven by mass-metallicity relation. Morphologically (HST)-selected Es and S0s (Bower et al. 1992, Aragon-Salamanca et al. 1993, Rakos et al. 1995, Stanford et al. 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, Schade et al. 1996, 1997, Ellis et ...
arXiv:1505.07406v1 [hep-ph] 27 May 2015
... ones, the former being responsible for the bounce replacing the initial singularity. The magnitude of the corrections is determined by a regulator. In LQC the regulator is treated as a free function of phase-space variables, usually fixed by the demand that the bounce occurs at Planckian energy dens ...
... ones, the former being responsible for the bounce replacing the initial singularity. The magnitude of the corrections is determined by a regulator. In LQC the regulator is treated as a free function of phase-space variables, usually fixed by the demand that the bounce occurs at Planckian energy dens ...
Hoag`s Object
... because more advanced telescopes revealed the knotty structure of the ring, something that would not be visible if the ring were the product of gravitational lensing.[] Many of the details of the galaxy remain a mystery, foremost of which is how it formed. So-called "classic" ring galaxies are gener ...
... because more advanced telescopes revealed the knotty structure of the ring, something that would not be visible if the ring were the product of gravitational lensing.[] Many of the details of the galaxy remain a mystery, foremost of which is how it formed. So-called "classic" ring galaxies are gener ...
Part1
... coupled to the size of the stellar disk. So this is is also (roughly) a way to guess the distribution of H2. o Exceptions: LIRG/ULIRGs and ellipticals tend to have ...
... coupled to the size of the stellar disk. So this is is also (roughly) a way to guess the distribution of H2. o Exceptions: LIRG/ULIRGs and ellipticals tend to have ...
The ANTARES telescope turns its gaze to the sky
... reveals objects such as supernova remnants, pulsars, micro-quasars in the Galaxy, extragalactic y ray bursts and active galactic nuclei, all emitters of very high energy photons (see Fig. 1). Tremendous progress has been made during the last century in understanding these new objects, helped in that ...
... reveals objects such as supernova remnants, pulsars, micro-quasars in the Galaxy, extragalactic y ray bursts and active galactic nuclei, all emitters of very high energy photons (see Fig. 1). Tremendous progress has been made during the last century in understanding these new objects, helped in that ...
Institute for Astrophysical Research Seminar Series
... Factory Trawling the X-ray Sky: The Chandra Multiwavelength Project ...
... Factory Trawling the X-ray Sky: The Chandra Multiwavelength Project ...
The Fundamental Plane, Stellar Popula6ons
... with velocity dispersion / Mstar / Mdyn (σ may be best predictor?) Early‐type galaxies (and bulges) form a Fundamental Plane in size/velocity dispersion/surface brightness (logR – logσ – logI ) space, with relaBvely small (15‐20%) intrinsic sca7er in R Stellar populaBons properBes and meas ...
... with velocity dispersion / Mstar / Mdyn (σ may be best predictor?) Early‐type galaxies (and bulges) form a Fundamental Plane in size/velocity dispersion/surface brightness (logR – logσ – logI ) space, with relaBvely small (15‐20%) intrinsic sca7er in R Stellar populaBons properBes and meas ...
The Milky Way - The Independent School
... violently active, and that will give you more clues to the evolution of galaxies. ...
... violently active, and that will give you more clues to the evolution of galaxies. ...
Order of Magnitude Icebreaker
... Order of Magnitude Group Projects ★ Nine projects proposed, with variety of ...
... Order of Magnitude Group Projects ★ Nine projects proposed, with variety of ...
The Great Debate - The Story Behind The Science
... The significance of this rotational period requires understanding Shapley's size of the Milky Way. Shapley had been a supporter of the island universe idea until he determined the Milky Way to be 300,000 light-years in diameter (10x larger than the consensus estimate). He concluded this by measuring ...
... The significance of this rotational period requires understanding Shapley's size of the Milky Way. Shapley had been a supporter of the island universe idea until he determined the Milky Way to be 300,000 light-years in diameter (10x larger than the consensus estimate). He concluded this by measuring ...
Hubble - 15 Years of Discovery
... star d-Cephei in the constellation of Cepheus. You can see the variation for yourself (if you have a little patience). If you look at the constellation Cepheus over several days, you will see that one of the bright stars changes in brightness every day – that star is d-Cephei. When we look at the ni ...
... star d-Cephei in the constellation of Cepheus. You can see the variation for yourself (if you have a little patience). If you look at the constellation Cepheus over several days, you will see that one of the bright stars changes in brightness every day – that star is d-Cephei. When we look at the ni ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... is such that the orbital speed of most stars in the galaxy does not depend strongly on its distance from the center. Away from the central bulge or outer rim, the typical stellar velocity is between 210 and 240 km/s. Hence the orbital period of the typical star is directly proportional only to the l ...
... is such that the orbital speed of most stars in the galaxy does not depend strongly on its distance from the center. Away from the central bulge or outer rim, the typical stellar velocity is between 210 and 240 km/s. Hence the orbital period of the typical star is directly proportional only to the l ...
Supplementary Information
... The optical photometry was obtained with the Suprime Camera at the SUBARU telescope in the B, R, I, and z bands, and the near-infrared J and Ks band photometry was collected with SOFI at the ESO New Technology Telescope (7). The data are complemented with optical U and V band photometry obtained as ...
... The optical photometry was obtained with the Suprime Camera at the SUBARU telescope in the B, R, I, and z bands, and the near-infrared J and Ks band photometry was collected with SOFI at the ESO New Technology Telescope (7). The data are complemented with optical U and V band photometry obtained as ...
The mass function of star clusters formed in turbulent molecular clouds
... N-body simulations of merging 8 clusters ...
... N-body simulations of merging 8 clusters ...
Supermassive Black Holes in Inactive Galaxies Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics eaa.iop.org
... holes (BHs) that accrete gas and stars and so transform gravitational potential energy into radiation. Expected BH masses are M• ~ 106–109.5M⊙. A wide array of phenomena can be understood within this picture. However, the subject has had an outstanding problem: there was no dynamical evidence that B ...
... holes (BHs) that accrete gas and stars and so transform gravitational potential energy into radiation. Expected BH masses are M• ~ 106–109.5M⊙. A wide array of phenomena can be understood within this picture. However, the subject has had an outstanding problem: there was no dynamical evidence that B ...
Local group
... g-ray emission correlates with massive star forming regions and not with the gas distribution (simulated images if the g-ray emission was distributed like the source) • Compactness of emission regions suggests little CR diffusion • 30 Doradus star forming region is a bright source of gamma rays and ...
... g-ray emission correlates with massive star forming regions and not with the gas distribution (simulated images if the g-ray emission was distributed like the source) • Compactness of emission regions suggests little CR diffusion • 30 Doradus star forming region is a bright source of gamma rays and ...
HON 392 - Chapman University
... The Contemporary Universe (Einstein/Hubble): We live on rotating planet, spinning at about 1000 mph, revolving in its one year long elliptical path around a medium size star--the Sun--at roughly 19 miles per second (67,000 miles per hour). Our Sun and Solar system as a whole--located about 2/3’s fro ...
... The Contemporary Universe (Einstein/Hubble): We live on rotating planet, spinning at about 1000 mph, revolving in its one year long elliptical path around a medium size star--the Sun--at roughly 19 miles per second (67,000 miles per hour). Our Sun and Solar system as a whole--located about 2/3’s fro ...
The Dynamics of the Galaxies in the Local Group
... • The Milky Way will merge with the Andromeda galaxy to become an elliptical galaxy – Their collision does not need to be as direct a hit as shown in the movie – They do always approach each other close enough to make a merger inevitable ...
... • The Milky Way will merge with the Andromeda galaxy to become an elliptical galaxy – Their collision does not need to be as direct a hit as shown in the movie – They do always approach each other close enough to make a merger inevitable ...
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision
... • The Milky will merge with the Andromeda galaxy to become an elliptical galaxy – Their collision does not need to be as direct a hit as shown in the movie – They do always approach each other close enough to make a merger inevitable ...
... • The Milky will merge with the Andromeda galaxy to become an elliptical galaxy – Their collision does not need to be as direct a hit as shown in the movie – They do always approach each other close enough to make a merger inevitable ...
The cosmic distance scale
... Use the relation you found in one of the preparatory exercises and the min/max magnitudes of each Cepheid to calculate the observed mean magnitudes. These have to be corrected for interstellar extinction. The light traveling to us from M100 is not just passing through the vacuum of space, some of it ...
... Use the relation you found in one of the preparatory exercises and the min/max magnitudes of each Cepheid to calculate the observed mean magnitudes. These have to be corrected for interstellar extinction. The light traveling to us from M100 is not just passing through the vacuum of space, some of it ...



![arXiv:1505.07406v1 [hep-ph] 27 May 2015](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007750137_1-1343a5635a0dda57ac4b2d01226e2ce5-300x300.png)