hair_loss_without_inflammation_of_the_skin_in_dogs
... Non-inflammatory alopecia is a group of uncommon skin disorders, characterized by hair loss that is associated with an abnormal hair growth/shed cycle Hormonal and non-hormonal diseases can be associated with non-inflammatory hair loss (alopecia) Alopecia X is a non-inflammatory alopecia relat ...
... Non-inflammatory alopecia is a group of uncommon skin disorders, characterized by hair loss that is associated with an abnormal hair growth/shed cycle Hormonal and non-hormonal diseases can be associated with non-inflammatory hair loss (alopecia) Alopecia X is a non-inflammatory alopecia relat ...
File
... • they play a role in the development of the brain and nervous system • they control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. ...
... • they play a role in the development of the brain and nervous system • they control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. ...
chapter 14-the endocrine system
... b. Aldosterone-major mineralocorticoid, this hormone regulates sodium levels in the blood. 2. Glucocorticoids-regulate the energy metabolism of most body cells and they help us resist stressors. a. Cortisol-regulates fat breakdown in the body. b. These hormones also play a role in regulating sugar l ...
... b. Aldosterone-major mineralocorticoid, this hormone regulates sodium levels in the blood. 2. Glucocorticoids-regulate the energy metabolism of most body cells and they help us resist stressors. a. Cortisol-regulates fat breakdown in the body. b. These hormones also play a role in regulating sugar l ...
Endocrine System
... » You will soon learn that a follicle consists of follicle cells and the developing egg – In males, FSH stimulates sperm development within the ...
... » You will soon learn that a follicle consists of follicle cells and the developing egg – In males, FSH stimulates sperm development within the ...
Endocrine System Hormones - VCC Library
... Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the endocrine system to communicate with cells and organs and maintain homeostasis. Hormones are released into the circulatory system and affect target cells containing specific receptors that can bind to the hormone. Once the hormone binds to the receptor ...
... Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the endocrine system to communicate with cells and organs and maintain homeostasis. Hormones are released into the circulatory system and affect target cells containing specific receptors that can bind to the hormone. Once the hormone binds to the receptor ...
March 4, 2013 Article for the Palladium Times Today`s Health for the
... increased trend to not keep scheduled office visits. This results in patients unnecessarily presenting to emergency rooms and labor and delivery units “just to be checked out” and “reassured”. This is an abuse of the system that makes it difficult for true emergencies to be seen in a timely manner. ...
... increased trend to not keep scheduled office visits. This results in patients unnecessarily presenting to emergency rooms and labor and delivery units “just to be checked out” and “reassured”. This is an abuse of the system that makes it difficult for true emergencies to be seen in a timely manner. ...
Anterior pituitary hormones
... In females, prolactin hormone stimulates milk production and is required for establishing a functional corpus luteum in some species. Hyperprolactinemia. There are many causes of Hyperprolactinemia including pregnancy, lactation, pituitary tumors, renal failure and the use of drugs that have dop ...
... In females, prolactin hormone stimulates milk production and is required for establishing a functional corpus luteum in some species. Hyperprolactinemia. There are many causes of Hyperprolactinemia including pregnancy, lactation, pituitary tumors, renal failure and the use of drugs that have dop ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Signals Maintain Homeostasis
... regulators - they are released by cells in one part of the body and affect cells in other parts of the body to speed up or slow down processes. Endocrine Hormones – are produced in endocrine glands and secreted directly in the blood and distributed by the circulatory system. ...
... regulators - they are released by cells in one part of the body and affect cells in other parts of the body to speed up or slow down processes. Endocrine Hormones – are produced in endocrine glands and secreted directly in the blood and distributed by the circulatory system. ...
BIOL242pituitaryOCT2012
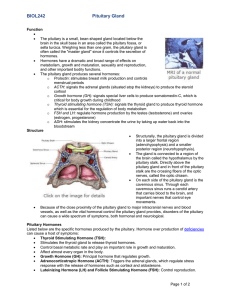
... vessels, as well as the vital hormonal control the pituitary gland provides, disorders of the pituitary can cause a wide spectrum of symptoms, both hormonal and neurological. Pituitary Hormones Listed below are the specific hormones produced by the pituitary. Hormone over production of deficiencies ...
... vessels, as well as the vital hormonal control the pituitary gland provides, disorders of the pituitary can cause a wide spectrum of symptoms, both hormonal and neurological. Pituitary Hormones Listed below are the specific hormones produced by the pituitary. Hormone over production of deficiencies ...
Vaginal Bleeding and Abdominal Pain in the Nonpregnant Patient
... Anovulatory uterine bleeding is usually due to developing hypothalamic – pituitary axis in adolescence Further work up is necessary when ...
... Anovulatory uterine bleeding is usually due to developing hypothalamic – pituitary axis in adolescence Further work up is necessary when ...
Hormone Replacement Therapy for Transgenders Do`s and Don`t`s
... Risks of Feminizing Hormones — Some General Principles ...
... Risks of Feminizing Hormones — Some General Principles ...
Polycystic Ovary syndrome (PCOs)
... weight by exercise and eating a healthy, low-calorie diet. Weight loss lowers your risk for diabetes and heart disease. Losing weight also improves menstrual function and may help some women ovulate naturally. • Metformin. This medicine helps lower blood sugar levels It is a suitable treatment for ...
... weight by exercise and eating a healthy, low-calorie diet. Weight loss lowers your risk for diabetes and heart disease. Losing weight also improves menstrual function and may help some women ovulate naturally. • Metformin. This medicine helps lower blood sugar levels It is a suitable treatment for ...
Hormone Replacement Therapy for Transgenders Do’s and Don'ts Steven M. Brown, MD
... Risks of Feminizing Hormones — Some General Principles ...
... Risks of Feminizing Hormones — Some General Principles ...
Adrenal glands
... list of terms. pLace an appropriate word or phrase on the lines within each diagram. cyclic AMP, hormone receptor, hormone receptor complex, protein synthesis ...
... list of terms. pLace an appropriate word or phrase on the lines within each diagram. cyclic AMP, hormone receptor, hormone receptor complex, protein synthesis ...
Hormone Replacement Therapy
... In the 1990s and early 2000s, the Women’s Health Initiative conducted its first largescale clinical trial to examine the effects of hormone replacement therapy. When the study was prematurely halted due to safety concerns, many practitioners panicked and stopped prescribing hormone therapy altogethe ...
... In the 1990s and early 2000s, the Women’s Health Initiative conducted its first largescale clinical trial to examine the effects of hormone replacement therapy. When the study was prematurely halted due to safety concerns, many practitioners panicked and stopped prescribing hormone therapy altogethe ...
Hormones - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Hormones and target cells Hormones are chemical signals produced by endocrine cells that can be grouped in endocrine glands. Hormones circulate in the blood stream and affect the activity of target cells that exhibit specific receptors. There are peptide, steroid and amino acid derived hormones. Th ...
... Hormones and target cells Hormones are chemical signals produced by endocrine cells that can be grouped in endocrine glands. Hormones circulate in the blood stream and affect the activity of target cells that exhibit specific receptors. There are peptide, steroid and amino acid derived hormones. Th ...
Hypopituitarism Presentation
... tandem with LH, FSH helps stimulate sperm production in men, and egg development and ovulation in women. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This hormone stimulates your adrenal glands to produce cortisol and other hormones. Cortisol helps your body deal with stress and influences many body functi ...
... tandem with LH, FSH helps stimulate sperm production in men, and egg development and ovulation in women. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This hormone stimulates your adrenal glands to produce cortisol and other hormones. Cortisol helps your body deal with stress and influences many body functi ...
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) How is PCOS diagnosed?
... Obesity commonly is associated with PCOS. Fatty tissues produce excess estrogen, which in turn contributes to insufficient FSH secretion by the pituitary gland. Insufficient FSH prevents ovulation and may worsen PCOS. In addition, obesity is associated with the development or worsening of insulin re ...
... Obesity commonly is associated with PCOS. Fatty tissues produce excess estrogen, which in turn contributes to insufficient FSH secretion by the pituitary gland. Insufficient FSH prevents ovulation and may worsen PCOS. In addition, obesity is associated with the development or worsening of insulin re ...
hormone
... glucose into the cells. (lowers blood sugar level) * These 2 hormones are important in maintaining the normal sugar or glucose level in the blood. ...
... glucose into the cells. (lowers blood sugar level) * These 2 hormones are important in maintaining the normal sugar or glucose level in the blood. ...
Hormones (secretion, regulation, function complete)
... inhibited by GHIH like hormones Stimulated by LH Stimulated by FSH ...
... inhibited by GHIH like hormones Stimulated by LH Stimulated by FSH ...
Both controlled by the posterior pituitary gland, vasopressin ______
... The adrenal medulla produces cortisol and corticosterone hormones. ...
... The adrenal medulla produces cortisol and corticosterone hormones. ...
Podcast summary chapter 15
... Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the glands of the endocrine system to communicate with other parts of the body. The cells that hormones act upon are called target cells. One hormone may have a series of different target cells, causing different but related effects in each target cell. Th ...
... Hormones are chemical messengers that allow the glands of the endocrine system to communicate with other parts of the body. The cells that hormones act upon are called target cells. One hormone may have a series of different target cells, causing different but related effects in each target cell. Th ...
ACTH
... • Autocrine communication: cells secrete chemical messengers that in some situations bind to receptors on the original cells. ...
... • Autocrine communication: cells secrete chemical messengers that in some situations bind to receptors on the original cells. ...
The Endocrine System – Chapter 9 Notes Second messenger
... _________________________ hormone (TSH or TH) Influences growth and activity of the thyroid Gonadotrophic hormones: Regulate hormonal activity of gonads _________________________ hormone (FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes _________ ...
... _________________________ hormone (TSH or TH) Influences growth and activity of the thyroid Gonadotrophic hormones: Regulate hormonal activity of gonads _________________________ hormone (FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes _________ ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.