The Evolution of Filial Piety in Ancient China and Its Influence on
... Chapter, and the other is about the “governing the country with filial concept”, developed around the topics of how to support, direct and cultivate people with filial concept. 2.2 The Classic of Filial Piety and Filial Piety Policy in the Han Dynasty The Han rulers spoke highly of The Classic of Fi ...
... Chapter, and the other is about the “governing the country with filial concept”, developed around the topics of how to support, direct and cultivate people with filial concept. 2.2 The Classic of Filial Piety and Filial Piety Policy in the Han Dynasty The Han rulers spoke highly of The Classic of Fi ...
Qin Shi Huangdi â the First Emperor Qin`s achievements: Qin`s
... Although Qin made many positive changes to China, he was not popular by all scholars at the time. In 213 BC, Qin held a celebration banquet. At the banquet, a scholar declared nothing lasted long, unless it was based on Ancient traditions. He was implying that Qin’s reign would not last very long. T ...
... Although Qin made many positive changes to China, he was not popular by all scholars at the time. In 213 BC, Qin held a celebration banquet. At the banquet, a scholar declared nothing lasted long, unless it was based on Ancient traditions. He was implying that Qin’s reign would not last very long. T ...
The Design Aesthetics of Lacquerware in the Han Dynasty
... There is wide cultural background of the beginning and development of the design of the Han Dynasty Lacquerware. The design theory of the Han Dynasty lacquerware inherited a lot and carried forward the system of the Qin Dynasty and the culture of Chu. The Han Dynasty has inherited the Qin Dynasty’s ...
... There is wide cultural background of the beginning and development of the design of the Han Dynasty Lacquerware. The design theory of the Han Dynasty lacquerware inherited a lot and carried forward the system of the Qin Dynasty and the culture of Chu. The Han Dynasty has inherited the Qin Dynasty’s ...
DRAFT Fall of the Qin Dynasty Lesson Plan Central Historical
... improve transport on roads), and Chinese script. The photo on the right is of a plaque inscribed with seal script, the official script of the dynasty. The Qin dynasty also ordered massive construction projects, such as the development of a road system and canals, the unification of various northern ...
... improve transport on roads), and Chinese script. The photo on the right is of a plaque inscribed with seal script, the official script of the dynasty. The Qin dynasty also ordered massive construction projects, such as the development of a road system and canals, the unification of various northern ...
A Resource Guide for Students and Teachers
... for our kingdom. Now we have the same kind of coins everywhere, so merchants can sell their goods and customers can buy what they want easily. You know, here in our city we attracted merchants from the west and east of us, so we used to have to deal with two different types of coins, ...
... for our kingdom. Now we have the same kind of coins everywhere, so merchants can sell their goods and customers can buy what they want easily. You know, here in our city we attracted merchants from the west and east of us, so we used to have to deal with two different types of coins, ...
Legalism in the Qin (Ch`in) Dynasty (221
... second thing he did was go to war with his neighbors, including the last Zhou king. It took him quite a while to get rid of everyone who was bothering him in ancient China. Finally, all of China was under his control. That had never happened before. The different feudal states in China had been at w ...
... second thing he did was go to war with his neighbors, including the last Zhou king. It took him quite a while to get rid of everyone who was bothering him in ancient China. Finally, all of China was under his control. That had never happened before. The different feudal states in China had been at w ...
15. The Resurgence of Empire in East Asia
... ©2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
... ©2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
The Resurgence of Empire in East Asia
... ©2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
... ©2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
wanted poster - cloudfront.net
... The Qin Dynasty lasted from 256-206 B.C. Cheng, from the state of Qin, lead his people to revolt against the Zhou in 246 B.C. and finally over threw them in 256 B.C. Qin wanted a new title. For the last 1,500 years Chinese rules had been called wang or “King.” Qin wanted to be called Shihuangdi mean ...
... The Qin Dynasty lasted from 256-206 B.C. Cheng, from the state of Qin, lead his people to revolt against the Zhou in 246 B.C. and finally over threw them in 256 B.C. Qin wanted a new title. For the last 1,500 years Chinese rules had been called wang or “King.” Qin wanted to be called Shihuangdi mean ...
ASIA 110: Introduction to Asia (China)
... Why is this period called ‘Period of Disunity’? Why is this period often omitted (or treated as part of the Han) in the official Chinese histories? In what ways was the Period of Disunity like the Warring States Period? Which 2 major rebellions led to the fall of the Han? What did these 2 rebe ...
... Why is this period called ‘Period of Disunity’? Why is this period often omitted (or treated as part of the Han) in the official Chinese histories? In what ways was the Period of Disunity like the Warring States Period? Which 2 major rebellions led to the fall of the Han? What did these 2 rebe ...
Chapter 22 Qin Dynasty
... became metal coins made of gold or bronze. • The coins had holes in the center so that people could carry several of them together on a cord. ...
... became metal coins made of gold or bronze. • The coins had holes in the center so that people could carry several of them together on a cord. ...
Document
... b.c. The construction linked together the restored ruins of older walls created in the Zhou Dynasty to create a 5000 kilometer (10,000 li) section. This is the origin of the 10,000-li wall name. First Emperor Qin Shi Huang ...
... b.c. The construction linked together the restored ruins of older walls created in the Zhou Dynasty to create a 5000 kilometer (10,000 li) section. This is the origin of the 10,000-li wall name. First Emperor Qin Shi Huang ...
ASIA 110: Introduction to Asia (China)
... How was the Period of Disunity like the Warring States Period? Why should we resist describing the struggles in this period as “Chinese” vs. “barbarians”? Which dynasty briefly unified China in the middle of this period? How did that dynasty fall? What is the importance of the 16 states and ...
... How was the Period of Disunity like the Warring States Period? Why should we resist describing the struggles in this period as “Chinese” vs. “barbarians”? Which dynasty briefly unified China in the middle of this period? How did that dynasty fall? What is the importance of the 16 states and ...
Lesson 4 Qin and The Great Wall
... Qin used peasants, captured enemies, criminals, scholars, and anyone else who irritated him, and put them all to work building the Great Wall. Laborers were not paid for their work. It was slave labor. About 3,000,000 people worked on the wall during the Qin Dynasty. Rocks fell on people. Walls cave ...
... Qin used peasants, captured enemies, criminals, scholars, and anyone else who irritated him, and put them all to work building the Great Wall. Laborers were not paid for their work. It was slave labor. About 3,000,000 people worked on the wall during the Qin Dynasty. Rocks fell on people. Walls cave ...
Wall of China Project
... United States’ southern border from Mexico. Do you think this fence should be extended the way the Great Wall of China was? Would it accomplish its purpose? Compare China’s Great Wall with the Iron Curtain that separated East Germany from West Germany. Was the purpose of the Iron Curtain to keep peo ...
... United States’ southern border from Mexico. Do you think this fence should be extended the way the Great Wall of China was? Would it accomplish its purpose? Compare China’s Great Wall with the Iron Curtain that separated East Germany from West Germany. Was the purpose of the Iron Curtain to keep peo ...
Name _________________________________________ ... Mr. Zindman’s Class ...
... The largest river in China is the Yangtze river, and it is the third largest river in the world, next only to the Nile in Africa and Amazon in South America. The Yangtze is known as the "golden waterway," because it links western and eastern areas of the country. ...
... The largest river in China is the Yangtze river, and it is the third largest river in the world, next only to the Nile in Africa and Amazon in South America. The Yangtze is known as the "golden waterway," because it links western and eastern areas of the country. ...
Records of the Historian Shiji
... [B]ut the land he won over was nothing but brackish swamp, unfit for the cultivation of the five grains. After this, the young men were called up from all over the empire and sent to guard the northern frontier along the river. The troops spent over ten years fighting in the wastes and wildernesses, ...
... [B]ut the land he won over was nothing but brackish swamp, unfit for the cultivation of the five grains. After this, the young men were called up from all over the empire and sent to guard the northern frontier along the river. The troops spent over ten years fighting in the wastes and wildernesses, ...
Qin Dynasty (221 – 207 B.C.) Qin inherited the territory and
... conquer and absorb many non-Chinese tribes and states scattered within, west and below the big loop of the Yellow River, also moving southwards and east into Hubei province. Because of its occupation of relatively remote western regions, Qin was regarded by other Chinese states as somewhat foreign a ...
... conquer and absorb many non-Chinese tribes and states scattered within, west and below the big loop of the Yellow River, also moving southwards and east into Hubei province. Because of its occupation of relatively remote western regions, Qin was regarded by other Chinese states as somewhat foreign a ...
Details about Destination Cities
... When Zhu Yuanzhang, the first Emperor of the Ming dynasty (1368-1644), captured Huizhou, a hermit named Zhu Sheng admonished him that he should "built high walls, store abundant food supplies and take time to be an Emperor," so that he could fortify the city and unify the other states. After the est ...
... When Zhu Yuanzhang, the first Emperor of the Ming dynasty (1368-1644), captured Huizhou, a hermit named Zhu Sheng admonished him that he should "built high walls, store abundant food supplies and take time to be an Emperor," so that he could fortify the city and unify the other states. After the est ...
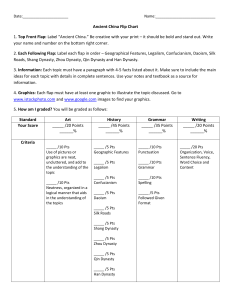
Ancient China Flip Chart 1. Top Front Flap: Label “Ancient China
... Ancient China Flip Chart 1. Top Front Flap: Label “Ancient China.” Be creative with your print – it should be bold and stand out. Write your name and number on the bottom right corner. 2. Each Following Flap: Label each flap in order – Geographical Features, Legalism, Confucianism, Daoism, Silk Road ...
... Ancient China Flip Chart 1. Top Front Flap: Label “Ancient China.” Be creative with your print – it should be bold and stand out. Write your name and number on the bottom right corner. 2. Each Following Flap: Label each flap in order – Geographical Features, Legalism, Confucianism, Daoism, Silk Road ...
Year 7 Hist - Ancient China
... Year 7 Hist - Ancient China 2 What goes tick-tick, woof-woof? A watch dog. Each line of the puzzle has one word hidden in a list of random letters. The blank space is a missing letter that belongs to that word. Decide what word is hidden in the letters and write in the space the missing letter. A wo ...
... Year 7 Hist - Ancient China 2 What goes tick-tick, woof-woof? A watch dog. Each line of the puzzle has one word hidden in a list of random letters. The blank space is a missing letter that belongs to that word. Decide what word is hidden in the letters and write in the space the missing letter. A wo ...
File - Mr. Wathen Online Portal
... A rebel general overthrew the last Tang emperor in 907. In 960, the Song dynasty was founded. • It was forged by a general named Zhao Kuangyin. ...
... A rebel general overthrew the last Tang emperor in 907. In 960, the Song dynasty was founded. • It was forged by a general named Zhao Kuangyin. ...
The Great Wall of China
... than horse riding. • Signal towers contained approximately 3 people to create a fire. • Some parts of the wall were connected and made tougher for further attacks. ...
... than horse riding. • Signal towers contained approximately 3 people to create a fire. • Some parts of the wall were connected and made tougher for further attacks. ...
The Basic Outline - Birmingham Public Schools
... historical Silk Road, located near today's Mary. Several cities have existed on this site, which is significant for the interchange of culture and politics at a site of major strategic value. It is claimed that Merv was briefly the largest city in the world in the twelfth century. The site of ancien ...
... historical Silk Road, located near today's Mary. Several cities have existed on this site, which is significant for the interchange of culture and politics at a site of major strategic value. It is claimed that Merv was briefly the largest city in the world in the twelfth century. The site of ancien ...
Chang'an

Chang'an (/ˈtʃɑːŋˈɑːn/, About this sound listen ) (simplified Chinese: 长安; traditional Chinese: 長安; pinyin: Cháng'ān; Wade–Giles: Ch'ang-an) is an ancient capital of more than ten dynasties in Chinese history, today known as Xi'an. Chang'an means ""Perpetual Peace"" in Classical Chinese. During the short-lived Xin dynasty, the city was renamed ""Constant Peace"" (Chinese: 常安; pinyin: Cháng'ān); yet after its fall in AD 23, the old name was restored. By the time of the Ming dynasty, the name was again changed to Xi'an, meaning ""Western Peace"", which has remained its name to the present day.Chang'an had been settled since the Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao Culture established in Banpo in the city's suburb. Also in the northern vicinity of the modern Xi'an, the tumulus ruler Qin Shi Huang of Qin dynasty held his imperial court, and constructed his massive mausoleum guarded by the famed Terracotta Army.From its capital at Xianyang, the Qin dynasty ruled a larger area than either of the preceding dynasties. The imperial city of Chang'an during the Han dynasty was located in northwest of today's Xi'an. During the Tang dynasty, the area to be known as Chang'an included the area inside the Ming Xi'an fortification, plus some small areas to its east and west, and a major part of its southern suburbs. The Tang Chang'an hence, was 8 times the size of the Ming Xi'an, which was reconstructed upon the premise of the former imperial quarter of the Sui and Tang city. During its heyday, Chang'an was one of the largest and most populous cities in the world. Around AD 750, Chang'an was called a ""million people's city"" in Chinese records, while modern estimates put it at around 800,000–1,000,000 within city walls. According to the census in 742 recorded in the New Book of Tang, 362,921 families with 1,960,188 persons were counted in Jingzhao Fu (京兆府), the metropolitan area including small cities in the vicinity.