Elements and Atomic Theory
... the year 430 b.c., a Greek philosopher named _____________________________ proposed the idea ...
... the year 430 b.c., a Greek philosopher named _____________________________ proposed the idea ...
Review Packet
... After much observation and questioning, Democritus concluded that matter could not be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. Eventually the smallest possible piece would be obtained. All elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible particles. Atoms of the sam ...
... After much observation and questioning, Democritus concluded that matter could not be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. Eventually the smallest possible piece would be obtained. All elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible particles. Atoms of the sam ...
Chapter 2: Matter is Made up of Atoms
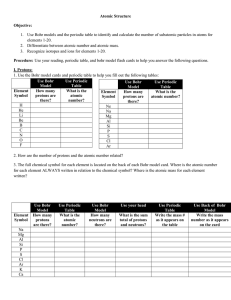
... Atomic number (Z) of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element. ...
... Atomic number (Z) of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of that element. ...
Atomic Structure and Periodicity
... Na > Li for solid metals only - in aqueous solution the reducing strength is Li > K > Na Why change in position for lithium in aqueous solution?- Lithium's small size gives it a high charge density which makes it more able to bond to water (hydration energy - energy released when a substance bonds t ...
... Na > Li for solid metals only - in aqueous solution the reducing strength is Li > K > Na Why change in position for lithium in aqueous solution?- Lithium's small size gives it a high charge density which makes it more able to bond to water (hydration energy - energy released when a substance bonds t ...
Atoms Notes Matter: anything that has mass and takes up space 3
... Nucleus-center of the atom, contains protons and neutrons Electron cloud-surrounds the nucleus Atomic number: number of protons Atomic mass: protons and neutrons ...
... Nucleus-center of the atom, contains protons and neutrons Electron cloud-surrounds the nucleus Atomic number: number of protons Atomic mass: protons and neutrons ...
Atomic Structure_Bohr Flashcards
... 12. If protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged particles. What is the overall charge for each element listed above? 13. Suppose you do not have access to the Bohr models for the above elements. Describe how you can determine the number of electrons for a neutral element j ...
... 12. If protons are positively charged and electrons are negatively charged particles. What is the overall charge for each element listed above? 13. Suppose you do not have access to the Bohr models for the above elements. Describe how you can determine the number of electrons for a neutral element j ...
Atoms
... particular orbital an electron has the same energy, regardless how far from the nucleus it happens to be. Things to remember about orbitals: Orbitals have defined shape and size Electron in an particular orbital has the same energy regardless where within the orbital it is “found” Orbitals of ...
... particular orbital an electron has the same energy, regardless how far from the nucleus it happens to be. Things to remember about orbitals: Orbitals have defined shape and size Electron in an particular orbital has the same energy regardless where within the orbital it is “found” Orbitals of ...
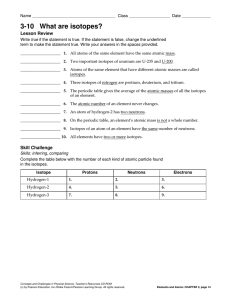
3-10 What are isotopes?
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
... reason for this? ____________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. According to the table, how are isotopes named? ______________________________________________ 6. What is true a ...
CHEMISTRY IM 06 SYLLABUS 1
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
... will contain between eight and ten compulsory questions of the fill-in type requiring short answers; Section B will consist of between four and sixcompulsory structured questions; Section C will require candidates to choose two out of four long questions. Each of section A and B will carry 30 marks ...
Atomic Structure Worksheet
... mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is a positively charged nuclear particle with a mass of about 1 AMU. 8. The nucleus is the small, positively charged center of the atom. 9. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nuc ...
... mass number. 6. A neutral nuclear particle having a mass of about 1 AMU is called the neutron. 7. The proton is a positively charged nuclear particle with a mass of about 1 AMU. 8. The nucleus is the small, positively charged center of the atom. 9. In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nuc ...
honors_chapter_4
... All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Chemical ...
... All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. Atoms of different elements can combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Chemical ...
File
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
... Daltons atomic theory was based on the following hypotheses : 1. Elements are composed of extremely small particles called atoms. 2. All atoms of a given element are identical, having the same size, mass and chemical properties. The atoms of one element are different from the atoms of all other ele ...
Chemistry Scavenger Hunt
... 2. There are three main phases of matter: _____________, ____________, and _____________. There is also a fourth phase, ______________, but it exists at very high temperatures. Science Is Fun Go to the “ChemTime Clock” and answer the questions below. http://www.scifun.org/ChemTime/ChemTime.html 1. A ...
... 2. There are three main phases of matter: _____________, ____________, and _____________. There is also a fourth phase, ______________, but it exists at very high temperatures. Science Is Fun Go to the “ChemTime Clock” and answer the questions below. http://www.scifun.org/ChemTime/ChemTime.html 1. A ...
Atom - U of L Class Index
... 4. Atoms are indestructible & retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the combination of atoms of unlike elements in small whole-number ratios. ...
... 4. Atoms are indestructible & retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the combination of atoms of unlike elements in small whole-number ratios. ...
Sample Exam 1 Key
... following could be the atom? a) phosphorus b) xenon c) aluminum d) boron 5. These two elements follow a “duet” rather than an octet rule. What are they? a) helium and neon b) hydrogen and helium c) sodium and chloride d) this is a trick question: all elements follow an octet rule. 6. Which of the fo ...
... following could be the atom? a) phosphorus b) xenon c) aluminum d) boron 5. These two elements follow a “duet” rather than an octet rule. What are they? a) helium and neon b) hydrogen and helium c) sodium and chloride d) this is a trick question: all elements follow an octet rule. 6. Which of the fo ...
Nature of Atoms Atomic Structure
... between the partially negative O atoms and the partially positive H atoms of two water ...
... between the partially negative O atoms and the partially positive H atoms of two water ...
Atomic Structure (history of atom)
... Atoms of the same ELEMENT are identical ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are joined, separated or rearranged Atoms of one element ...
... Atoms of the same ELEMENT are identical ATOMS of any one ELEMENT are different from those of any other element Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are joined, separated or rearranged Atoms of one element ...
Atomic Structure
... Find the numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following elements. Then name the most common isotope of each. ...
... Find the numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the following elements. Then name the most common isotope of each. ...
Ch 6.7 - Explaining the Atom
... Evidence of Learning: Students can … - describe and relate atomic number, atomic mass, and mass number. - find the number of neutrons in an atom from its atomic number and atomic ...
... Evidence of Learning: Students can … - describe and relate atomic number, atomic mass, and mass number. - find the number of neutrons in an atom from its atomic number and atomic ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.