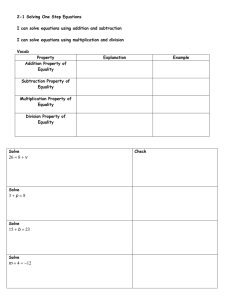
Essential Questions for this Unit: 1. What methods are used to simplif
... student’s age in terms of x pg. T79. Riverdeep Activity Rewriting Equations in terms of a specified variable pg. T79-T80. Students write their own word problems, include solution. Riverdeep Activity ...
... student’s age in terms of x pg. T79. Riverdeep Activity Rewriting Equations in terms of a specified variable pg. T79-T80. Students write their own word problems, include solution. Riverdeep Activity ...
tianhu.pdf
... Great attention has been devoted to the study of electromagneto-thermoelastic coupled problems based on the generalized thermoelastic theories. In the context of Lord–Shulman theory, Sherief and Ezzat (1998) investigated a problem of an infinitely long electrically and thermally conducting annular c ...
... Great attention has been devoted to the study of electromagneto-thermoelastic coupled problems based on the generalized thermoelastic theories. In the context of Lord–Shulman theory, Sherief and Ezzat (1998) investigated a problem of an infinitely long electrically and thermally conducting annular c ...
Chapter 5 Practice Test
... where P is the principal, r is the annual interest rate, and t is the time in years. Calculate to the nearest hundredth of a year how long it takes for an amount of money to double if interest is compounded continuously at 6.2%. Round to the nearest tenth. 9. Solve ...
... where P is the principal, r is the annual interest rate, and t is the time in years. Calculate to the nearest hundredth of a year how long it takes for an amount of money to double if interest is compounded continuously at 6.2%. Round to the nearest tenth. 9. Solve ...
Intro to the Coordinate Plane and Graphing
... Now that we have discussed equations with one variable, we can look at equations in two variables, x and y. These lines will be diagonal. In this unit, we will learn to graph these lines using a table and by using the xand y- intercepts. The graph of an equation involving two variables, x and y, is ...
... Now that we have discussed equations with one variable, we can look at equations in two variables, x and y. These lines will be diagonal. In this unit, we will learn to graph these lines using a table and by using the xand y- intercepts. The graph of an equation involving two variables, x and y, is ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.