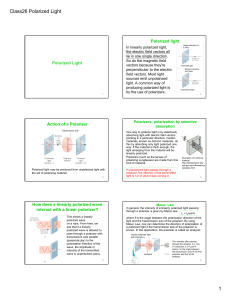
Periodic Structures - Photonics Research Group
... diffraction gratings for optical filters, monochromators and spectrum analyzes are only a few. Especially because of the introduction of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) in optical fiber communication, gratings are becoming indispensable for various filter functions. We will start by analyzing ...
... diffraction gratings for optical filters, monochromators and spectrum analyzes are only a few. Especially because of the introduction of wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) in optical fiber communication, gratings are becoming indispensable for various filter functions. We will start by analyzing ...
ELEC 401 – Microwave Electronics Plane Electromagnetic Waves
... Example (from “Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics” by F. T. Ulaby): An xpolarized electric field of a 1 GHz plane wave travels in the +z-direction in free-space, and has its maximum at (t=0, z=5 cm) with the value of 1.2p (mV/cm). Using these information, find the expressions of Electric and ...
... Example (from “Fundamentals of Applied Electromagnetics” by F. T. Ulaby): An xpolarized electric field of a 1 GHz plane wave travels in the +z-direction in free-space, and has its maximum at (t=0, z=5 cm) with the value of 1.2p (mV/cm). Using these information, find the expressions of Electric and ...
Physics Toolkit - Effingham County Schools
... displacement of the wave peak, ∆d, then dividing this by the time interval, ∆t, to find the speed, given by v = ∆d /∆t ...
... displacement of the wave peak, ∆d, then dividing this by the time interval, ∆t, to find the speed, given by v = ∆d /∆t ...
Ion dynamics in electron beam–plasma interaction: particle-in
... has been proposed long ago as basic mechanism for the interpretation of type III solar radio bursts (Cairns and Melrose, 1985). In this resonant three-wave interaction the frequency of the ion acoustic mode is very small against the plasma frequency which makes it very difficult to resolve separated ...
... has been proposed long ago as basic mechanism for the interpretation of type III solar radio bursts (Cairns and Melrose, 1985). In this resonant three-wave interaction the frequency of the ion acoustic mode is very small against the plasma frequency which makes it very difficult to resolve separated ...
4 OSCILLATIONS AND WAVES
... second when we are resting and maybe two or three times this rate as we exert ourselves. Stroboscopes can be used to freeze the motion in engines and motors where periodic motion is essential, but too strong vibrations can be potentially very destructive. The practical techniques that have been deve ...
... second when we are resting and maybe two or three times this rate as we exert ourselves. Stroboscopes can be used to freeze the motion in engines and motors where periodic motion is essential, but too strong vibrations can be potentially very destructive. The practical techniques that have been deve ...
Pearson Physics Level 20 Unit IV Oscillatory Motion and Mechanical
... string is increased as the string is shortened. 22. If you strike a tuning fork with different forces you will alter the amplitude of the vibrations of its arms. This results in an increase in the volume of the sound produced by the tuning fork. 23. (a) The central maximum of an interference pattern ...
... string is increased as the string is shortened. 22. If you strike a tuning fork with different forces you will alter the amplitude of the vibrations of its arms. This results in an increase in the volume of the sound produced by the tuning fork. 23. (a) The central maximum of an interference pattern ...
OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY Layout
... First, I would like to thank my supervisor Professor António Miguel Morgado for all his support and guidance over the past year. His motivation and help were essential in overcoming every obstacle and small detail of this work. I would also like to thank Professor José Paulo Domingues for his guidan ...
... First, I would like to thank my supervisor Professor António Miguel Morgado for all his support and guidance over the past year. His motivation and help were essential in overcoming every obstacle and small detail of this work. I would also like to thank Professor José Paulo Domingues for his guidan ...
A relativistic beam-plasma system with electromagnetic waves
... Condition 共14兲 is necessary for neglecting the nonlinear response of the background plasma on the short plasma oscillation time scale. There are additional restrictions that apply when slower time scale effects are considered. For example, since we consider only long laser pulses, the ponderomotive ...
... Condition 共14兲 is necessary for neglecting the nonlinear response of the background plasma on the short plasma oscillation time scale. There are additional restrictions that apply when slower time scale effects are considered. For example, since we consider only long laser pulses, the ponderomotive ...
1 (PREVIEW Dan Winter`s new book: www.fractalfield.com/fractalspac
... scientists-‐ although friendly to spiritual ideas-‐ the actual concept of what a chakra is-‐ has not yet reached the level of what is called science. This is not so much – to say that chakra’s ...
... scientists-‐ although friendly to spiritual ideas-‐ the actual concept of what a chakra is-‐ has not yet reached the level of what is called science. This is not so much – to say that chakra’s ...
Read PDF - Physics (APS)
... that there are resolvable tidal forces across the spatial extent of the interferometer, then the wave function of an interfering particle can no longer be approximated as traveling along a single populated geodesic. Instead, the two arms follow separate trajectories that accelerate with respect to o ...
... that there are resolvable tidal forces across the spatial extent of the interferometer, then the wave function of an interfering particle can no longer be approximated as traveling along a single populated geodesic. Instead, the two arms follow separate trajectories that accelerate with respect to o ...
Chapter 3. EM-wave Propagation Above the Terrain
... [2] Chew, W. C., Waves and Fields in Inhomogeneous Media, New York: IEEE Press, ...
... [2] Chew, W. C., Waves and Fields in Inhomogeneous Media, New York: IEEE Press, ...
attosecond light sources
... the electric fields from sources at 1, 3 and 5 times a fundamental frequency. The sum of the fields is seen to be localized into shorter and shorter times. This approach was seen to be impractical and was never seriously pursued. However, in an example of serendipitous discovery that is so important ...
... the electric fields from sources at 1, 3 and 5 times a fundamental frequency. The sum of the fields is seen to be localized into shorter and shorter times. This approach was seen to be impractical and was never seriously pursued. However, in an example of serendipitous discovery that is so important ...
Swept Source OCT for retinal imaging on small animals
... all the precious help provided during this last year. Last, but not least, I would like to thank my parents, my sister, my grandparents and my girlfriend for all the support and encouragement given throughout these years. All that I am, I owe it to all of you. Thank you all so much. ...
... all the precious help provided during this last year. Last, but not least, I would like to thank my parents, my sister, my grandparents and my girlfriend for all the support and encouragement given throughout these years. All that I am, I owe it to all of you. Thank you all so much. ...