
Topic 4 - Introduction to Quantum Theory
... nx ( x) A sin kx A sin L Since, in this case the particle is confined by INFINITE potential barriers, we know particle must be located between x=0 and x=L →Normalisation condition reduces to : L ...
... nx ( x) A sin kx A sin L Since, in this case the particle is confined by INFINITE potential barriers, we know particle must be located between x=0 and x=L →Normalisation condition reduces to : L ...
Quantum_PPT
... • Electrons are emitted from a negatively charged metal plate with a potential difference when UV-light falls on it. ...
... • Electrons are emitted from a negatively charged metal plate with a potential difference when UV-light falls on it. ...
Chapter40_VGO
... detector after passing through an experimental apparatus. • Consequently, the probability that it will be detected at some position is 100%. • The statement that the photon or electron has to land somewhere on the x-axis is expressed mathematically as ...
... detector after passing through an experimental apparatus. • Consequently, the probability that it will be detected at some position is 100%. • The statement that the photon or electron has to land somewhere on the x-axis is expressed mathematically as ...
Discussion Question 13B
... (d) Write down an expression for the magnetic field B(x,y,z,t). Express your answer algebraically (i.e. no numbers) in terms of the symbols k, ω, and B0 (the latter being the magnetic field amplitude). Be sure to indicate the direction of the magnetic field. The E and B fields of an electromagnetic ...
... (d) Write down an expression for the magnetic field B(x,y,z,t). Express your answer algebraically (i.e. no numbers) in terms of the symbols k, ω, and B0 (the latter being the magnetic field amplitude). Be sure to indicate the direction of the magnetic field. The E and B fields of an electromagnetic ...
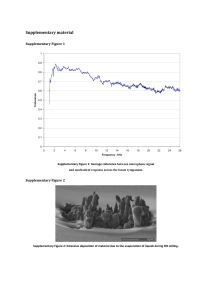
Supplementary Figure 1
... For a membrane in tension, T, in the x-y plane, the wave equation for small-amplitude transverse waves are derived by considering a square element Δx Δy of the membrane. When the membrane is displaced, there arises a force in the z direction from each of the two pairs of tensile forces T Δx and T Δy ...
... For a membrane in tension, T, in the x-y plane, the wave equation for small-amplitude transverse waves are derived by considering a square element Δx Δy of the membrane. When the membrane is displaced, there arises a force in the z direction from each of the two pairs of tensile forces T Δx and T Δy ...
Lecture 3: Electronic Band Theory: A Many
... Left: The winding of the angle θ about vortices in an electric band. Right: multiple bands with different vortex numbers. The total vortex number, called the Chern number, determines the Hall conductance. A famous result by Thouless, Kohmoto, Nightingale (D. J. Thouless, M. Kohmoto, M. P. Nightingal ...
... Left: The winding of the angle θ about vortices in an electric band. Right: multiple bands with different vortex numbers. The total vortex number, called the Chern number, determines the Hall conductance. A famous result by Thouless, Kohmoto, Nightingale (D. J. Thouless, M. Kohmoto, M. P. Nightingal ...
Session 26 - Iowa State University
... c) Suppose a manufacturing error occurred and the oven was made 6.0 cm longer than specified in part (a). In this case, what would have to be the frequency of the microwaves for there still to be five antinodal planes of the electric field along the width of the oven? ...
... c) Suppose a manufacturing error occurred and the oven was made 6.0 cm longer than specified in part (a). In this case, what would have to be the frequency of the microwaves for there still to be five antinodal planes of the electric field along the width of the oven? ...
[2011 question paper]
... (d) Promote the classical canonical variables to quantum mechanical operators and evaluate [π̂X , π̂Y ] where π̂X = P̂X − eÂX /c and π̂Y = P̂Y − eÂY /c. (e) Write the quantum mechanical Hamiltonian for a particle moving in a plane in the above magnetic field. By comparing the Hamiltonian and the c ...
... (d) Promote the classical canonical variables to quantum mechanical operators and evaluate [π̂X , π̂Y ] where π̂X = P̂X − eÂX /c and π̂Y = P̂Y − eÂY /c. (e) Write the quantum mechanical Hamiltonian for a particle moving in a plane in the above magnetic field. By comparing the Hamiltonian and the c ...
Chapter 4 Electron Configuration
... emit electrons from sodium metal while a dim beam of violet light will. http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/mod1.html#c5 If the packet of energy (photon, quantum) is not equal to or greater than the difference between two electron orbitals the energy will not be absorbed. ...
... emit electrons from sodium metal while a dim beam of violet light will. http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/mod1.html#c5 If the packet of energy (photon, quantum) is not equal to or greater than the difference between two electron orbitals the energy will not be absorbed. ...
Document
... To displace any function f(x) to the right, just change its argument from x to x-a, where a is a positive number. ...
... To displace any function f(x) to the right, just change its argument from x to x-a, where a is a positive number. ...
Problem set 4
... R = 21 mc2 α2 where α is the so-called fine-structure constant. h3i 7. Consider a wave packet moving in a medium with dispersion relation ω = ω(k) Z dk ψ(x, t) = ψ̃(k)ei(kx−ω(k)t) 2π ...
... R = 21 mc2 α2 where α is the so-called fine-structure constant. h3i 7. Consider a wave packet moving in a medium with dispersion relation ω = ω(k) Z dk ψ(x, t) = ψ̃(k)ei(kx−ω(k)t) 2π ...
LECTURE 2. THE DEVELOPMENT OF QUANTUM MECHANICS
... v = velocity amd h = Planck’s constant.. Note the inverse relationship of m and λ. Which means that a 1g mass (very heavy) at 1m/s has λ = 7 x 10-33m, but 1 proton at speed of light has λ = 1 x 10-11m. Uncertainty Principle: If photons are waves, then in the same way we can’t say what the location o ...
... v = velocity amd h = Planck’s constant.. Note the inverse relationship of m and λ. Which means that a 1g mass (very heavy) at 1m/s has λ = 7 x 10-33m, but 1 proton at speed of light has λ = 1 x 10-11m. Uncertainty Principle: If photons are waves, then in the same way we can’t say what the location o ...
Wave packet
.gif?width=300)
In physics, a wave packet (or wave train) is a short ""burst"" or ""envelope"" of localized wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion, see figure) or it may change (dispersion) while propagating.Quantum mechanics ascribes a special significance to the wave packet; it is interpreted as a probability amplitude, its norm squared describing the probability density that a particle or particles in a particular state will be measured to have a given position or momentum. The wave equation is in this case the Schrödinger equation. It is possible to deduce the time evolution of a quantum mechanical system, similar to the process of the Hamiltonian formalism in classical mechanics. The dispersive character of solutions of the Schrödinger equation has played an important role in rejecting Schrödinger's original interpretation, and accepting the Born rule.In the coordinate representation of the wave (such as the Cartesian coordinate system), the position of the physical object's localized probability is specified by the position of the packet solution. Moreover, the narrower the spatial wave packet, and therefore the better localized the position of the wave packet, the larger the spread in the momentum of the wave. This trade-off between spread in position and spread in momentum is a characteristic feature of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle,and will be illustrated below.












![[2011 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881811_1-8ef23f7493d56bc511a2c01dcc81fc96-300x300.png)









