Models of the Atom
... – Only specific frequencies are allowed – And, hence, only certain energy levels ...
... – Only specific frequencies are allowed – And, hence, only certain energy levels ...
The Quantum Eraser - Brian John Piccolo
... best possible archetypal pre-existing patterns, sometimes they are a new and creative. Once the choice is made, we experience it in linear time as a chain of historical events. According to Quantum theory, the whole pattern was chosen all at once and collapsed in a tangled hierarchal relationship. T ...
... best possible archetypal pre-existing patterns, sometimes they are a new and creative. Once the choice is made, we experience it in linear time as a chain of historical events. According to Quantum theory, the whole pattern was chosen all at once and collapsed in a tangled hierarchal relationship. T ...
Name - WordPress.com
... one period of the wave is used. Intensity can be applied to other circumstances where energy is transferred. For example, one could calculate the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a garden sprinkler. The word "intensity" as used here is not synonymous with "strength", "a ...
... one period of the wave is used. Intensity can be applied to other circumstances where energy is transferred. For example, one could calculate the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a garden sprinkler. The word "intensity" as used here is not synonymous with "strength", "a ...
PHY2115 - College of DuPage
... Calculus-based study of fluids, thermodynamics, special relativity, introductory quantum mechanics, nuclear physics, and particle physics Prerequisite: PHY2112 with a C or better and completion of or concurrent enrollment in MATH2270 A. ...
... Calculus-based study of fluids, thermodynamics, special relativity, introductory quantum mechanics, nuclear physics, and particle physics Prerequisite: PHY2112 with a C or better and completion of or concurrent enrollment in MATH2270 A. ...
PPT
... Particle in a Box The waves have exactly the same form as standing waves on a string, sound waves in a pipe, etc. The wavelength is determined by the condition that it fits in the box. On a string the wave is a displacement y(x) and the square is the intensity, etc. The discrete set of allowed wave ...
... Particle in a Box The waves have exactly the same form as standing waves on a string, sound waves in a pipe, etc. The wavelength is determined by the condition that it fits in the box. On a string the wave is a displacement y(x) and the square is the intensity, etc. The discrete set of allowed wave ...
TOPPER SAMPLE PAPER 4 XI – PHYSICS
... 26. What is a conservative force? Prove that gravitational force is conservative and frictional force is non-conservative ...
... 26. What is a conservative force? Prove that gravitational force is conservative and frictional force is non-conservative ...
ENE 429 Antenna and Transmission Lines
... UPW is characterized by its propagation direction and frequency. ...
... UPW is characterized by its propagation direction and frequency. ...
How does a Bohm particle localize?
... employ the de Broglie-Bohm theory in the Anderson localization context and study the Bohm particle trajectories for wave packets in the localized, critical and diffusive phases (see picture). It will be quite instructive to see how spatial localization and multifractality arises without internal con ...
... employ the de Broglie-Bohm theory in the Anderson localization context and study the Bohm particle trajectories for wave packets in the localized, critical and diffusive phases (see picture). It will be quite instructive to see how spatial localization and multifractality arises without internal con ...
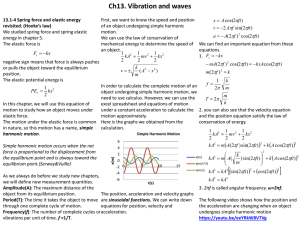
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wave if it has a frequency of 8.00 Hz. displace ...
... A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wave if it has a frequency of 8.00 Hz. displace ...
Jeopardy - Forces - Western Reserve Public Media
... rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force” is which law? A. Newton’s First Law B. Newton’s Second Law C. Newton’s Third Law ...
... rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an outside force” is which law? A. Newton’s First Law B. Newton’s Second Law C. Newton’s Third Law ...
Document
... 1925 Heisenberg states uncertainty principle 1926 Schrodinger develops wave equation 1924-6 Boson and Fermion distributions developed ...
... 1925 Heisenberg states uncertainty principle 1926 Schrodinger develops wave equation 1924-6 Boson and Fermion distributions developed ...
Landau levels
... To simplify the setup, let us consider the electron to move only on xy plane under a magnetic field pointing along the z direction. You can always bring back the motion along the z direction, which is just a translational motion with a constant momentum or velocity. Our interst here is the dynamics ...
... To simplify the setup, let us consider the electron to move only on xy plane under a magnetic field pointing along the z direction. You can always bring back the motion along the z direction, which is just a translational motion with a constant momentum or velocity. Our interst here is the dynamics ...
Section_23_Special_W..
... 23. WAVES IN A UNIFORM MEDIUM: SPECIAL CASES We consider the special case of an infinite, uniform medium with B0 B0 êz and J 0 0 . In that case we can expand an arbitrary displacement in plane wave solutions as ...
... 23. WAVES IN A UNIFORM MEDIUM: SPECIAL CASES We consider the special case of an infinite, uniform medium with B0 B0 êz and J 0 0 . In that case we can expand an arbitrary displacement in plane wave solutions as ...
4.4 Wave Characteristics
... travels onward with characteristic wave velocity v. All types of traveling waves transport energy. Study of a single wave pulse shows that it is begun with a vibration and transmitted through internal forces in the medium. Continuous waves start with vibrations too. If the vibration is SHM, th ...
... travels onward with characteristic wave velocity v. All types of traveling waves transport energy. Study of a single wave pulse shows that it is begun with a vibration and transmitted through internal forces in the medium. Continuous waves start with vibrations too. If the vibration is SHM, th ...
Wave packet
.gif?width=300)
In physics, a wave packet (or wave train) is a short ""burst"" or ""envelope"" of localized wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion, see figure) or it may change (dispersion) while propagating.Quantum mechanics ascribes a special significance to the wave packet; it is interpreted as a probability amplitude, its norm squared describing the probability density that a particle or particles in a particular state will be measured to have a given position or momentum. The wave equation is in this case the Schrödinger equation. It is possible to deduce the time evolution of a quantum mechanical system, similar to the process of the Hamiltonian formalism in classical mechanics. The dispersive character of solutions of the Schrödinger equation has played an important role in rejecting Schrödinger's original interpretation, and accepting the Born rule.In the coordinate representation of the wave (such as the Cartesian coordinate system), the position of the physical object's localized probability is specified by the position of the packet solution. Moreover, the narrower the spatial wave packet, and therefore the better localized the position of the wave packet, the larger the spread in the momentum of the wave. This trade-off between spread in position and spread in momentum is a characteristic feature of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle,and will be illustrated below.