Exploring
... Since this case has two free parameters, you can again set the connect direction and left or right region parameters – just like in the general scattering case. These parameters will have the same effect as they did before. As long as you use sine-cosine type wave functions, you will get standing wa ...
... Since this case has two free parameters, you can again set the connect direction and left or right region parameters – just like in the general scattering case. These parameters will have the same effect as they did before. As long as you use sine-cosine type wave functions, you will get standing wa ...
E Problems for Unit II
... Clock Work. Go out to the academic quad and stand at the end opposite the library, as far from the library as you can safely get while still being able to observe the clock. a) Look at the clock on the library tower. Specifically, look at the Roman numeral 8 (VIII), which is actually made up of 5 se ...
... Clock Work. Go out to the academic quad and stand at the end opposite the library, as far from the library as you can safely get while still being able to observe the clock. a) Look at the clock on the library tower. Specifically, look at the Roman numeral 8 (VIII), which is actually made up of 5 se ...
particularized wave equations and their parameters
... (3/2)h.ν. But this lowest total energy state is excluded by the Pauli exclusion principle, for this is one of the two energy states of the electron, corresponding to quantum numbers nx = ny = 1, which are nearest to the electron′s lowest (ground) state. It is not too surprising that we have been abl ...
... (3/2)h.ν. But this lowest total energy state is excluded by the Pauli exclusion principle, for this is one of the two energy states of the electron, corresponding to quantum numbers nx = ny = 1, which are nearest to the electron′s lowest (ground) state. It is not too surprising that we have been abl ...
Mid-Term Exam in MAE351 Mechanical Vibrations F(t)
... Two solutions for the above equation are shown in Fig. 3, where one is a solution of the nonlinear differential equation and the other is a solution of the linearized ...
... Two solutions for the above equation are shown in Fig. 3, where one is a solution of the nonlinear differential equation and the other is a solution of the linearized ...
HW 7 6340
... 6) This problem explores the pros and cons of using circular polarization vs. linear polarization in a transmitted wave, when the receive antenna is linearly polarized. This problem uses the concept of effective height of a wire antenna, as explained in Prob. 4. a) A vertically-polarized plane wave ...
... 6) This problem explores the pros and cons of using circular polarization vs. linear polarization in a transmitted wave, when the receive antenna is linearly polarized. This problem uses the concept of effective height of a wire antenna, as explained in Prob. 4. a) A vertically-polarized plane wave ...
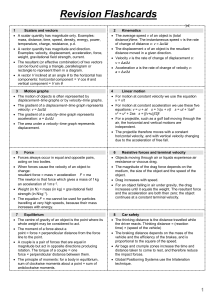
AS Revision Flash Cards File
... Kirchhoff’s first law: at any circuit junction, total current in = total current out. This is a consequence of the conservation of charge. It follows that the current is constant round any series circuit. Kirchhoff’s second law: round any circuit loop, the sum of the e.m.f.s is equal to the sum ...
... Kirchhoff’s first law: at any circuit junction, total current in = total current out. This is a consequence of the conservation of charge. It follows that the current is constant round any series circuit. Kirchhoff’s second law: round any circuit loop, the sum of the e.m.f.s is equal to the sum ...
Copenhagen Interpretation
... 2. The description of nature is probabilistic. The probability of an event is the mag squared of the wave function related to it. (Max Born) 3. Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle says it’s impossible to know the values of all of the properties of the system at the same time; properties not known wit ...
... 2. The description of nature is probabilistic. The probability of an event is the mag squared of the wave function related to it. (Max Born) 3. Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle says it’s impossible to know the values of all of the properties of the system at the same time; properties not known wit ...
2009-YJC-PH-H2-P1-Prelim-soln
... Using right hand grip rule, B field on Y due to current in X is out of the plane. Using Fleming’s left hand rule, with B acting out of plane and current flowing left, an upward force is created. Using N3L, force on X is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. ...
... Using right hand grip rule, B field on Y due to current in X is out of the plane. Using Fleming’s left hand rule, with B acting out of plane and current flowing left, an upward force is created. Using N3L, force on X is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. ...
Sample Exam 3
... The speed of a sound wave in air depends on a. its frequency b. its wavelength c. air temperature ...
... The speed of a sound wave in air depends on a. its frequency b. its wavelength c. air temperature ...
Wave packet
.gif?width=300)
In physics, a wave packet (or wave train) is a short ""burst"" or ""envelope"" of localized wave action that travels as a unit. A wave packet can be analyzed into, or can be synthesized from, an infinite set of component sinusoidal waves of different wavenumbers, with phases and amplitudes such that they interfere constructively only over a small region of space, and destructively elsewhere. Each component wave function, and hence the wave packet, are solutions of a wave equation. Depending on the wave equation, the wave packet's profile may remain constant (no dispersion, see figure) or it may change (dispersion) while propagating.Quantum mechanics ascribes a special significance to the wave packet; it is interpreted as a probability amplitude, its norm squared describing the probability density that a particle or particles in a particular state will be measured to have a given position or momentum. The wave equation is in this case the Schrödinger equation. It is possible to deduce the time evolution of a quantum mechanical system, similar to the process of the Hamiltonian formalism in classical mechanics. The dispersive character of solutions of the Schrödinger equation has played an important role in rejecting Schrödinger's original interpretation, and accepting the Born rule.In the coordinate representation of the wave (such as the Cartesian coordinate system), the position of the physical object's localized probability is specified by the position of the packet solution. Moreover, the narrower the spatial wave packet, and therefore the better localized the position of the wave packet, the larger the spread in the momentum of the wave. This trade-off between spread in position and spread in momentum is a characteristic feature of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle,and will be illustrated below.