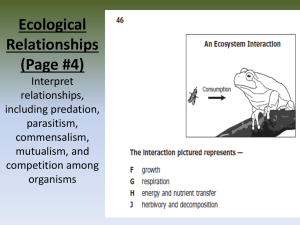
Biology EOC #14: Relationships Interpret relationships
... • Physical aspects (water, air, rocks, heat, light, altitude etc). ...
... • Physical aspects (water, air, rocks, heat, light, altitude etc). ...
Local Extinctions of Terrestrial Insectivorous Birds in a Fragmented
... sensitive to fragmentation. Abundance, measured by mist-net captures, declined with decreasing fragment size and over the 9 years of study (Stouffer & Bierregaard 1995a). Other studies of fragmentation and habitat alteration in the Neotropics also suggest negative effects on terrestrial insectivores ...
... sensitive to fragmentation. Abundance, measured by mist-net captures, declined with decreasing fragment size and over the 9 years of study (Stouffer & Bierregaard 1995a). Other studies of fragmentation and habitat alteration in the Neotropics also suggest negative effects on terrestrial insectivores ...
Ecology - TeacherWeb
... 3. What are heterotrophs? Why do we call them consumers? 4. List the different types of heterotrophs? On what basis to we classify them? 5. Compare and contrast a food chain with a food web. 6. Explain the term “trophic level” 7. What is the 10% rule as it relates to energy transfer in a food chain? ...
... 3. What are heterotrophs? Why do we call them consumers? 4. List the different types of heterotrophs? On what basis to we classify them? 5. Compare and contrast a food chain with a food web. 6. Explain the term “trophic level” 7. What is the 10% rule as it relates to energy transfer in a food chain? ...
Pine Flatwoods Study Guide for Juniors
... there are adapted to and depend upon fire to burn through the land every so often to ensure their continued health and growth. Fragmented - Broken up into smaller pieces. Fragmented land is land that has been divided up by roads, parks, farms, and houses so that an animal often cannot travel from on ...
... there are adapted to and depend upon fire to burn through the land every so often to ensure their continued health and growth. Fragmented - Broken up into smaller pieces. Fragmented land is land that has been divided up by roads, parks, farms, and houses so that an animal often cannot travel from on ...
species diversity
... • Endangered species are those considered in imminent danger of extinction • Threatened species are likely to become endangered, at least locally within the forseeable future. • Vulnerable species are naturally rare or have been locally depleted by human activities to a level that puts them at risk. ...
... • Endangered species are those considered in imminent danger of extinction • Threatened species are likely to become endangered, at least locally within the forseeable future. • Vulnerable species are naturally rare or have been locally depleted by human activities to a level that puts them at risk. ...
Chapter 4
... same place/same time Predation: one organisms feeds on another Symbiosis: two species in a relationship together ...
... same place/same time Predation: one organisms feeds on another Symbiosis: two species in a relationship together ...
Ecology - Pitt County Schools
... _______________ factors (_________________ factors) All _______________ organisms _________________ factors have effects on ______________ things and often determine which ___________ survive in a particular ______________ . For ex., lack of _____________ can cause drought in a _____________, so the ...
... _______________ factors (_________________ factors) All _______________ organisms _________________ factors have effects on ______________ things and often determine which ___________ survive in a particular ______________ . For ex., lack of _____________ can cause drought in a _____________, so the ...
Tundra Tundra is a treeless biome occurring in areas with cold
... surprisingly, the productivity of desert ecosystems is strongly influenced by the availability of water. The driest deserts support almost no plant productivity, while less-dry situations may support communities of herbaceous, succulent, and annual plants, and somewhat moister places will allow a sh ...
... surprisingly, the productivity of desert ecosystems is strongly influenced by the availability of water. The driest deserts support almost no plant productivity, while less-dry situations may support communities of herbaceous, succulent, and annual plants, and somewhat moister places will allow a sh ...
Darwinian speciation in Amazon butterflies James Mallet Predictions
... refuge theory," are not fulfilled in heliconiine and ithomiine butterflies of the Amazon. Instead, some lineages diversify rapidly, others slowly. This suggests a lineage's ability to colonize new ecological niches is more important in diversification than climatic forcing of the whole biota. I show ...
... refuge theory," are not fulfilled in heliconiine and ithomiine butterflies of the Amazon. Instead, some lineages diversify rapidly, others slowly. This suggests a lineage's ability to colonize new ecological niches is more important in diversification than climatic forcing of the whole biota. I show ...
20-sec.-2-Eco-Succession
... existing community. The disruption may stem from a natural disaster, such as a forest fire or a strong storm, or from human activities, such as farming, logging, or mining. Any new habitat is an invitation to many species that are adapted to be good pioneers. The species that predominate early in su ...
... existing community. The disruption may stem from a natural disaster, such as a forest fire or a strong storm, or from human activities, such as farming, logging, or mining. Any new habitat is an invitation to many species that are adapted to be good pioneers. The species that predominate early in su ...
GLOSSARY
... species threatened with localized extirpation or decline. Endangered species are rare species in danger of permanent extinction. Sustainable development: Use of natural resources that minimises impacts on the forest structures and processes, and that does not compromise the forest’s long-term produc ...
... species threatened with localized extirpation or decline. Endangered species are rare species in danger of permanent extinction. Sustainable development: Use of natural resources that minimises impacts on the forest structures and processes, and that does not compromise the forest’s long-term produc ...
LAB MAKE-UP: BIOLOGY 11B
... Sandy Beach. Choose a section of shoreline for each habitat type, both intertidal and nearshore, walk it carefully, and make note of the following: a. Compare the abiotic factors including: wave shock, substrate type, exposure to wind and waves, habitat types. Be specific to the habitats listed b. C ...
... Sandy Beach. Choose a section of shoreline for each habitat type, both intertidal and nearshore, walk it carefully, and make note of the following: a. Compare the abiotic factors including: wave shock, substrate type, exposure to wind and waves, habitat types. Be specific to the habitats listed b. C ...
Biomes of North America
... Belize, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama. Rainfall 200-400 cm. Species diversity is very high (# species/area). Temperatures range 25-32°C and humidity seldom below 80%. No seasons based on temperature. Broadleaf evergreen trees dominate with canopy contiguous. Soils not very fertile, all ...
... Belize, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama. Rainfall 200-400 cm. Species diversity is very high (# species/area). Temperatures range 25-32°C and humidity seldom below 80%. No seasons based on temperature. Broadleaf evergreen trees dominate with canopy contiguous. Soils not very fertile, all ...
Document
... species in same area (biotic factors) COMMUNITY – several populations in same area (biotic factors) ECOSYSTEM – community plus abiotic factors BIOSPHERE – all ecosystems on earth ...
... species in same area (biotic factors) COMMUNITY – several populations in same area (biotic factors) ECOSYSTEM – community plus abiotic factors BIOSPHERE – all ecosystems on earth ...
Biodiversity - McEachern High School
... live in rainforest, deep oceans, even cities. Which group of organisms make up the majority of the 1.7 million known species? ...
... live in rainforest, deep oceans, even cities. Which group of organisms make up the majority of the 1.7 million known species? ...
Tigris-Euphrates Equitable Water Allocation
... Marshes and Tigris Euphrates watershed. It is imperative to synthesize scientific information and to collaborate on scientific research between stakeholders and scientists throughout the basin. Building a strong international community network will help with the development of viable solutions to re ...
... Marshes and Tigris Euphrates watershed. It is imperative to synthesize scientific information and to collaborate on scientific research between stakeholders and scientists throughout the basin. Building a strong international community network will help with the development of viable solutions to re ...
Temperate deciduous forest
... • Not to be confused with species richness, which is the number of different species within a community ...
... • Not to be confused with species richness, which is the number of different species within a community ...
Upland Forests - Minnesota DNR
... Historically, the distribution and size of patches of contiguous upland forest were determined by soils, landforms, and natural disturbances (such as windstorms but especially fire). Fire, which was particularly important in drier upland forests, has been essentially replaced with timber harvest, re ...
... Historically, the distribution and size of patches of contiguous upland forest were determined by soils, landforms, and natural disturbances (such as windstorms but especially fire). Fire, which was particularly important in drier upland forests, has been essentially replaced with timber harvest, re ...
Ecological succession - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... b) Why are lichens able to grow on barren rock? ...
... b) Why are lichens able to grow on barren rock? ...
Species Concept
... habitat loss. • Organisms with highly specialized habitat needs may avoid competition, but risk extinction if their habitat is threatened. ...
... habitat loss. • Organisms with highly specialized habitat needs may avoid competition, but risk extinction if their habitat is threatened. ...
Ecological Succession
... and erosion break down rocks into smaller pieces • When lichens die, they decompose, adding small amounts of organic matter to the rock to make soil • Over time, the soil layer thickens, and grasses, wildflowers, and other plants begin to take over ...
... and erosion break down rocks into smaller pieces • When lichens die, they decompose, adding small amounts of organic matter to the rock to make soil • Over time, the soil layer thickens, and grasses, wildflowers, and other plants begin to take over ...
Species interaction
... disturbance, but later returns to its original state A disturbed community may never return to its original ...
... disturbance, but later returns to its original state A disturbed community may never return to its original ...
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project

The Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project, originally called the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project is a large-scale ecological experiment looking at the effects of habitat fragmentation on tropical rainforest; it is one of the most expensive biology experiments ever run. The experiment, which was established in 1979 is located near Manaus, in the Brazilian Amazon. The project is jointly managed by the Smithsonian Institution and INPA, the Brazilian Institute for Research in the Amazon.The project was initiated in 1979 by Thomas Lovejoy to investigate the SLOSS debate. Initially named the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project, the project created forest fragments of sizes 1 hectare (2 acres), 10 hectares (25 acres), and 100 hectares (247 acres). Data were collected prior to the creation of the fragments and studies of the effects of fragmentation now exceed 25 years.As of October 2010 562 publications and 143 graduate dissertations and theses had emerged from the project.























