Chapter 4 Summary
... within which species can survive. The number of organisms in a population can be affected by a single limiting factor, as described in the limiting factor principle. Important limiting factors include dissolved oxygen (DO) content, temperature, sunlight, nutrient availability, and salinity. Most pro ...
... within which species can survive. The number of organisms in a population can be affected by a single limiting factor, as described in the limiting factor principle. Important limiting factors include dissolved oxygen (DO) content, temperature, sunlight, nutrient availability, and salinity. Most pro ...
Principles of Ecology
... causing further changes in community These predictable changes that occurs in community over time= ecological succession ...
... causing further changes in community These predictable changes that occurs in community over time= ecological succession ...
Biosphere Review
... 5. Different Environments = Different Organisms • Not all organisms have the same needs. Different environments provide different things to support different organisms. ...
... 5. Different Environments = Different Organisms • Not all organisms have the same needs. Different environments provide different things to support different organisms. ...
Primary Succession
... Communities • Limiting Factor: biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the members, reproduction, or distribution of an organism Most species have a range of tolerance for these factors – this plots like a bell-shaped curve ...
... Communities • Limiting Factor: biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the members, reproduction, or distribution of an organism Most species have a range of tolerance for these factors – this plots like a bell-shaped curve ...
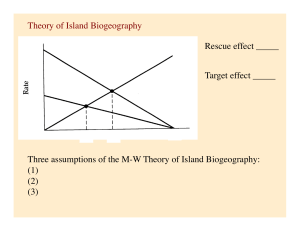
Theory of Island Biogeography Rescue effect _____ Target effect
... What would you expect for distance and size effects if the matrix can be crossed or not? ...
... What would you expect for distance and size effects if the matrix can be crossed or not? ...
6.3.2 populations and sustainability student version
... maintained/restored, strategies to ensure this include: Leave surface of bog undisturbed and wet. Ditches should surround bogs to prevent flooding of neighbouring land. Removal of seedling trees, as trees use huge amounts of water during transpiration and can dry out bogs and prevent growth of b ...
... maintained/restored, strategies to ensure this include: Leave surface of bog undisturbed and wet. Ditches should surround bogs to prevent flooding of neighbouring land. Removal of seedling trees, as trees use huge amounts of water during transpiration and can dry out bogs and prevent growth of b ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Annual precipitation ranges from 25-100 cm. Temperatures range from -45oC to 45oC. North American grasslands (prairies) grew on fertile soils supporting large herds of migratory grazing buffalo. Mediterranean climate receives most precipitation in the winter, thus grasses do not grow as tall as th ...
... Annual precipitation ranges from 25-100 cm. Temperatures range from -45oC to 45oC. North American grasslands (prairies) grew on fertile soils supporting large herds of migratory grazing buffalo. Mediterranean climate receives most precipitation in the winter, thus grasses do not grow as tall as th ...
diagnostic test - Qld Science Teachers
... A. ecology B. ecosystem C. environment 2. All the living and non-living conditions that act on an organism and affect its chances of survival is the: A. ecology B. living factor C. environment 3. Another term meaning ‘living’ is: A. biology B. biotic C. ecological 4. Another term for ‘non-living’ is ...
... A. ecology B. ecosystem C. environment 2. All the living and non-living conditions that act on an organism and affect its chances of survival is the: A. ecology B. living factor C. environment 3. Another term meaning ‘living’ is: A. biology B. biotic C. ecological 4. Another term for ‘non-living’ is ...
Patches - carmelacanzonieri.com
... Convoluted patches have a long perimeter and abundant exchanges with the matrix. A convoluted patch causes complex patterns of turbulence in water and wind flow. Most turbulence will be on the outside of a-remnant patch, and the inside of a disturbance patch ...
... Convoluted patches have a long perimeter and abundant exchanges with the matrix. A convoluted patch causes complex patterns of turbulence in water and wind flow. Most turbulence will be on the outside of a-remnant patch, and the inside of a disturbance patch ...
Environmental preservation is the strict setting aside of natural
... fishing, mining and so on. Just as often legal devices such as laws and regulations may be employed, such as the Endangered Species Act in the United States, which is not dependent on designating a specific geographic area aside for conservation. A government's environmental policy will determine wh ...
... fishing, mining and so on. Just as often legal devices such as laws and regulations may be employed, such as the Endangered Species Act in the United States, which is not dependent on designating a specific geographic area aside for conservation. A government's environmental policy will determine wh ...
Chapter 20
... warblers, bluebirds or pipits) to feed and raise one very large child that was, literally, left on their doorstep. There are also many internal and external parasites such as lice, parasitic wasps, and tapeworms. Community Stability Your friend, Susan, asks you why the rain forests are so diverse, w ...
... warblers, bluebirds or pipits) to feed and raise one very large child that was, literally, left on their doorstep. There are also many internal and external parasites such as lice, parasitic wasps, and tapeworms. Community Stability Your friend, Susan, asks you why the rain forests are so diverse, w ...
Impacts of Climate Change on Mediterranean Biodiversity and
... northern Alpine (25%), and Atlantic (31%) regions are consistently less sensitive. (Thuiller et al. 2005, PNAS 102). ...
... northern Alpine (25%), and Atlantic (31%) regions are consistently less sensitive. (Thuiller et al. 2005, PNAS 102). ...
Niche, refers to the role that a species plays within its ecosystem. In
... resources, etc. A pest is any organism that man believes is undesirable, has a negative impact on the human environment, or is in competition with human use of a resource, either natural, or cultivated. Early Pesticide Use: ...
... resources, etc. A pest is any organism that man believes is undesirable, has a negative impact on the human environment, or is in competition with human use of a resource, either natural, or cultivated. Early Pesticide Use: ...
Terrestrial Biomes - Social Circle City Schools
... – Camels have a highly developed nasal structure that prevents water loss and its hair is efficient at reflecting the sun’s heat. ...
... – Camels have a highly developed nasal structure that prevents water loss and its hair is efficient at reflecting the sun’s heat. ...
Ecology
... replacement of species after a major disruption in a community where there has been life before. ...
... replacement of species after a major disruption in a community where there has been life before. ...
Forest and Range Ecology
... • “Area managed for production of timber and other forest products, or maintained as wooded vegetation for such indirect benefits as protection of catchment areas or recreation”. (Lund 1998) ...
... • “Area managed for production of timber and other forest products, or maintained as wooded vegetation for such indirect benefits as protection of catchment areas or recreation”. (Lund 1998) ...
Types of Forests
... for over two-thirds of the leaf area of land plants, and contain about 70% of carbon present in living things. They have been held in reverence in folklore and worshipped in ancient religions. However, forests are becoming major casualties of civilization as human populations have increased over the ...
... for over two-thirds of the leaf area of land plants, and contain about 70% of carbon present in living things. They have been held in reverence in folklore and worshipped in ancient religions. However, forests are becoming major casualties of civilization as human populations have increased over the ...
ecology ppt
... ("carrying capacity“). Populations in this kind of environment show what is known as logistic growth. ...
... ("carrying capacity“). Populations in this kind of environment show what is known as logistic growth. ...
Risks to biodiversity from hydraulic fracturing for natural gas in the
... Loss of forest cover and change in the spatial pattern of cover are often confounded, but cause different responses.44 Edge effects on forest biota range from 10 m for trees to as much as 500 m for certain birds.45 Forest fragmentation, which affects dispersal, pollination, herbivory, and predation, ...
... Loss of forest cover and change in the spatial pattern of cover are often confounded, but cause different responses.44 Edge effects on forest biota range from 10 m for trees to as much as 500 m for certain birds.45 Forest fragmentation, which affects dispersal, pollination, herbivory, and predation, ...
Development of Seed Transfer Zones for Two Title text here
... In 2008 Region One initiated its Seed Transfer Zone Study to determine seed transfer guidelines for core revegetation species. 2011 represents its fourth year of this effort. Each year, two species are selected for common garden study. Red osier dogwood (Cornus sericea ssp. sericea) and shinyleaf sp ...
... In 2008 Region One initiated its Seed Transfer Zone Study to determine seed transfer guidelines for core revegetation species. 2011 represents its fourth year of this effort. Each year, two species are selected for common garden study. Red osier dogwood (Cornus sericea ssp. sericea) and shinyleaf sp ...
Habitat typing
... bank at the time of major disturbance, or what the weather is like during the time of sapling establishment. Therefore, succession can take communities to very different climax states on physically identical sites. Often disturbance is frequent enough to prevent the establishment of a climax communi ...
... bank at the time of major disturbance, or what the weather is like during the time of sapling establishment. Therefore, succession can take communities to very different climax states on physically identical sites. Often disturbance is frequent enough to prevent the establishment of a climax communi ...
Rocky_Mountain_Ecosystems_Course_Outline
... Unit 1: Intro to Ecology and Rocky Mountain Ecosystems a. What is ecology? b. Ecosystems i. Interactions, Habitat, Niche, Keystone species ii. Levels of organization iii. EcosystemCommunityPopulationSpeciesOrganism… c. Local ecosystems i. Characteristics of Local Ecosystems ii. MT Ecosystems Map ...
... Unit 1: Intro to Ecology and Rocky Mountain Ecosystems a. What is ecology? b. Ecosystems i. Interactions, Habitat, Niche, Keystone species ii. Levels of organization iii. EcosystemCommunityPopulationSpeciesOrganism… c. Local ecosystems i. Characteristics of Local Ecosystems ii. MT Ecosystems Map ...
Name - MabryOnline.org
... 2. Individuals decrease the size of a population when they emigrate from it. _________________________ ...
... 2. Individuals decrease the size of a population when they emigrate from it. _________________________ ...
factors in the environment that are not alive
... What is the zone called between 21 and 25 degrees? ...
... What is the zone called between 21 and 25 degrees? ...
Download PDF Flier PDF, 256.92 KB
... $30,406 per annum. Those with a strong track record may receive a fee waiver. » Funding is available for project costs and conference travel. ...
... $30,406 per annum. Those with a strong track record may receive a fee waiver. » Funding is available for project costs and conference travel. ...
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project

The Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project, originally called the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project is a large-scale ecological experiment looking at the effects of habitat fragmentation on tropical rainforest; it is one of the most expensive biology experiments ever run. The experiment, which was established in 1979 is located near Manaus, in the Brazilian Amazon. The project is jointly managed by the Smithsonian Institution and INPA, the Brazilian Institute for Research in the Amazon.The project was initiated in 1979 by Thomas Lovejoy to investigate the SLOSS debate. Initially named the Minimum Critical Size of Ecosystems Project, the project created forest fragments of sizes 1 hectare (2 acres), 10 hectares (25 acres), and 100 hectares (247 acres). Data were collected prior to the creation of the fragments and studies of the effects of fragmentation now exceed 25 years.As of October 2010 562 publications and 143 graduate dissertations and theses had emerged from the project.