Chapter 22-2 and 22-3
... between average CO2 levels & average global temperatures Cause-and-effect relationship: A change in one variable causes a change in another variable ...
... between average CO2 levels & average global temperatures Cause-and-effect relationship: A change in one variable causes a change in another variable ...
How am I connected
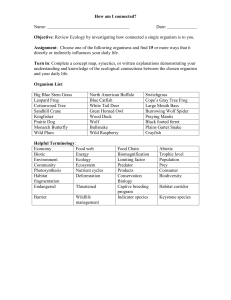
... Objective: Review Ecology by investigating how connected a single organism is to you. Assignment: Choose one of the following organisms and find 15 or more ways that it directly or indirectly influences your daily life. Turn in: Complete a concept map, synectics, or written explanations demonstratin ...
... Objective: Review Ecology by investigating how connected a single organism is to you. Assignment: Choose one of the following organisms and find 15 or more ways that it directly or indirectly influences your daily life. Turn in: Complete a concept map, synectics, or written explanations demonstratin ...
Biodiversity Web Quest
... What Is the Big Idea? (don’t forget to use the “next” button in this section) 1. What is biodiversity and how many types are there? ...
... What Is the Big Idea? (don’t forget to use the “next” button in this section) 1. What is biodiversity and how many types are there? ...
Document
... Protecting habitats and ecosystems is the main thrust of global efforts. Biologists are particularly concerned about ecological hot spots, which are places where significant numbers of habitats and species are in immediate danger of extinction. Considering local interests is part of developing plans ...
... Protecting habitats and ecosystems is the main thrust of global efforts. Biologists are particularly concerned about ecological hot spots, which are places where significant numbers of habitats and species are in immediate danger of extinction. Considering local interests is part of developing plans ...
Chapter 55 - Canyon ISD
... • 7% of the world’s land is in reserves • Biodiversity hot spot: relatively small area with exceptional concentration of endemic species and a large number of threatened or endangered animals ...
... • 7% of the world’s land is in reserves • Biodiversity hot spot: relatively small area with exceptional concentration of endemic species and a large number of threatened or endangered animals ...
SAES CH9
... Ethnobotany The study of how different cultures use the plants in their local environment ...
... Ethnobotany The study of how different cultures use the plants in their local environment ...
“brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains
... a factor in the environment that causes the population to decrease or go down. i.e. food and water, living space, weather ...
... a factor in the environment that causes the population to decrease or go down. i.e. food and water, living space, weather ...
Alien species threaten Indian ecosystems
... NEW DELHI: Invasive alien species like Lantana and Cuscutta pose a threat to the ecosystems and lead to loss of biodiversity of the country, the government today said. Invasive alien species are plants, animals, pathogens and other organisms that are non-native to an ecosystem and which may cause ec ...
... NEW DELHI: Invasive alien species like Lantana and Cuscutta pose a threat to the ecosystems and lead to loss of biodiversity of the country, the government today said. Invasive alien species are plants, animals, pathogens and other organisms that are non-native to an ecosystem and which may cause ec ...
in the ACCESS Habitable Planet story 2. What are Food webs? 5
... • Biodiversity has intrinsic value (something that has value in and of itself) and utilitarian value (goods, services, information) = FREE ecosystem services! ...
... • Biodiversity has intrinsic value (something that has value in and of itself) and utilitarian value (goods, services, information) = FREE ecosystem services! ...
Study guide 3
... Unit 3: Evolution, Biodiversity and Ecology (Chapters 13-20) Below are a list of the major topics that we focused on. Other topics from the text and videos we saw could appear on the exam, but the majority of questions will focus on these topics: Micro-Evolution: -Darwin’s ideas of descent with modi ...
... Unit 3: Evolution, Biodiversity and Ecology (Chapters 13-20) Below are a list of the major topics that we focused on. Other topics from the text and videos we saw could appear on the exam, but the majority of questions will focus on these topics: Micro-Evolution: -Darwin’s ideas of descent with modi ...
Biodiversity Webquest
... What Is the Big Idea? (don’t forget to use the “next” button in this section) 1. What is biodiversity and how many types are there? ...
... What Is the Big Idea? (don’t forget to use the “next” button in this section) 1. What is biodiversity and how many types are there? ...
1.2 Ecosystems – Student Notes
... in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include: • _____________ - produced by green plants & micro-organisms • _____________- necessary for all life • _____________ - for growth • _____________ - required for photosynthesis • _____________ - contains water & nutrients Biotic Interactions in Ecosystems • _ ...
... in an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include: • _____________ - produced by green plants & micro-organisms • _____________- necessary for all life • _____________ - for growth • _____________ - required for photosynthesis • _____________ - contains water & nutrients Biotic Interactions in Ecosystems • _ ...
Global Climate Change
... • I will be able to discuss how human activity is changing the Earth. • I will be able to discuss the value of biodiversity. ...
... • I will be able to discuss how human activity is changing the Earth. • I will be able to discuss the value of biodiversity. ...
Disruption to Ecosystems
... • The reason behind the introduction of cane toads to Australia was well intended but the results were unimagined. This is a good example of the fallibility of scientists and what can happen when an exotic species invades an ecosystem. ...
... • The reason behind the introduction of cane toads to Australia was well intended but the results were unimagined. This is a good example of the fallibility of scientists and what can happen when an exotic species invades an ecosystem. ...
Unit Curriculum Map for Environmental Science
... a. Describe factors affecting population growth of all organisms, including humans. Relate these to factors affecting growth rates and carrying capacity of the environment. c. Explain how human activities affect global and local sustainability. d. Describe the actual and potential effects of habitat ...
... a. Describe factors affecting population growth of all organisms, including humans. Relate these to factors affecting growth rates and carrying capacity of the environment. c. Explain how human activities affect global and local sustainability. d. Describe the actual and potential effects of habitat ...
Human Activities Can Alter Ecosystems
... Over the past few centuries, many ecosystems have been affected by the rapidly growing human population's need for resources. The effects of human activities are sometimes felt in only a small area. Sometimes, though, the ecological impact is more widespread or even global. ...
... Over the past few centuries, many ecosystems have been affected by the rapidly growing human population's need for resources. The effects of human activities are sometimes felt in only a small area. Sometimes, though, the ecological impact is more widespread or even global. ...
Bot3404_11_week4.2
... Ideas about how to incorporate new technology into botanical collections and studies. A bit of plant ecology but will also allow you to practice identifying trees that you will see on a daily basis. ...
... Ideas about how to incorporate new technology into botanical collections and studies. A bit of plant ecology but will also allow you to practice identifying trees that you will see on a daily basis. ...
Biodiversity is the variety or richness of life at all structural levels
... Biodiversity is the variety or richness of life at all structural levels (molecular/genetic, species, ecosystem). It is an essential renewable resource. It is exploited and depleted as a result of the “Tragedy of the Commons” phenomenon. The current rate of biodiversity loss is comparable to previou ...
... Biodiversity is the variety or richness of life at all structural levels (molecular/genetic, species, ecosystem). It is an essential renewable resource. It is exploited and depleted as a result of the “Tragedy of the Commons” phenomenon. The current rate of biodiversity loss is comparable to previou ...
Section 1 Summary Notes
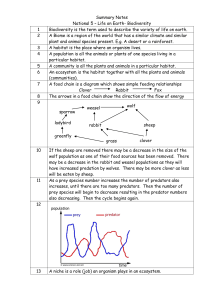
... A habitat is the place where an organism lives. A population is all the animals or plants of one species living in a particular habitat. A community is all the plants and animals in a particular habitat. An ecosystem is the habitat together with all the plants and animals (communities). A food chain ...
... A habitat is the place where an organism lives. A population is all the animals or plants of one species living in a particular habitat. A community is all the plants and animals in a particular habitat. An ecosystem is the habitat together with all the plants and animals (communities). A food chain ...
Humans in the Biosphere
... Biodiversity is one of Earth’s greatest natural resources. • Species of many kinds have provided us with foods, industrial products and medicines- including painkillers, antibiotics, heart drugs, antidepressants, and anticancer drugs. – Rosy Perwinkle plant helps treat cancers. ...
... Biodiversity is one of Earth’s greatest natural resources. • Species of many kinds have provided us with foods, industrial products and medicines- including painkillers, antibiotics, heart drugs, antidepressants, and anticancer drugs. – Rosy Perwinkle plant helps treat cancers. ...
1.2 Ecosystems - Sardis Secondary
... Abiotic Interactions in Ecosystems • It is the abiotic components that allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. – Abiotic factors include : • Oxygen - produced by green plants & microorganisms. • Water - necessary for all life. • Nutrients - for growth. • Light - required for photosy ...
... Abiotic Interactions in Ecosystems • It is the abiotic components that allow the biotic components to survive in an ecosystem. – Abiotic factors include : • Oxygen - produced by green plants & microorganisms. • Water - necessary for all life. • Nutrients - for growth. • Light - required for photosy ...
Reconciliation ecology

Reconciliation ecology is the branch of ecology which studies ways to encourage biodiversity in human-dominated ecosystems. Michael Rosenzweig first articulated the concept in his book Win-Win Ecology, based on the theory that there is not enough area for all of earth’s biodiversity to be saved within designated nature preserves. Therefore, humans should increase biodiversity in human-dominated landscapes. By managing for biodiversity in ways that do not decrease human utility of the system, it is a ""win-win"" situation for both human use and native biodiversity. The science is based in the ecological foundation of human land-use trends and species-area relationships. It has many benefits beyond protection of biodiversity, and there are numerous examples of it around the globe. Aspects of reconciliation ecology can already be found in management legislation, but there are challenges in both public acceptance and ecological success of reconciliation attempts.