MATHEMATICAL THEORY OF PHYSICAL VACUUM
... e.g. infinite energy or mass of point charge. Naturally, any theory with a claim of being fundamental has to answer all of the questions stated above. Besides, in our opinion such kind of theory should be consistent and follow the common sense. This research goal is a brief formulation of basics of ...
... e.g. infinite energy or mass of point charge. Naturally, any theory with a claim of being fundamental has to answer all of the questions stated above. Besides, in our opinion such kind of theory should be consistent and follow the common sense. This research goal is a brief formulation of basics of ...
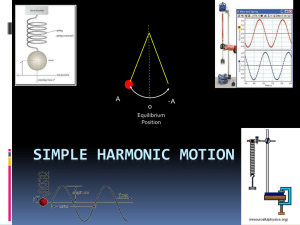
Newton`s Laws: Determining the Motion
... the equation of motion for a variety of different physical systems. The equation of motion a = a(x, v, t) = F/m can be obtained directly from an analytical expression for F. As you will learn in Chapter 4, the equation of motion can be obtained without explicitly using Newton’s second law. However, ...
... the equation of motion for a variety of different physical systems. The equation of motion a = a(x, v, t) = F/m can be obtained directly from an analytical expression for F. As you will learn in Chapter 4, the equation of motion can be obtained without explicitly using Newton’s second law. However, ...
Algebra I Study Guide for EOCE
... Therefore, your equation is y = 2x + -6. This is the general equation that fits all points on the line. Using y- y1 = m (x – x1), substitute 1 in for x1, -4 in for y1, and 2 in for m. Then distribute and get y by itself. You will get the same answer as above. Example 3: Write the equation of the lin ...
... Therefore, your equation is y = 2x + -6. This is the general equation that fits all points on the line. Using y- y1 = m (x – x1), substitute 1 in for x1, -4 in for y1, and 2 in for m. Then distribute and get y by itself. You will get the same answer as above. Example 3: Write the equation of the lin ...
637_diffusion
... • behavior of representative fluid particles • consider a single particle located at location x’ at time t’ in a turbulent fluid • trajectory of the subsequent motion: X[x’,t’;t] at any later time t • probability density function ...
... • behavior of representative fluid particles • consider a single particle located at location x’ at time t’ in a turbulent fluid • trajectory of the subsequent motion: X[x’,t’;t] at any later time t • probability density function ...